* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Standard SSWH18
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
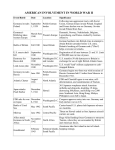
Bell Ringer On the computer. Standard SSWH18 THE STUDENT WILL DEMONSTRATE AN UNDERSTANDING OF THE GLOBAL POLITICAL, ECONOMIC, AND SOCIAL IMPACT OF WORLD WAR II. Element A Describe the major conflicts and outcomes; include Pearl Harbor, El-Alamein, Stalingrad, D-Day, Guadalcanal, the Philippines, and the end of the war in Europe and Asia. Essential Question What were the major conflicts of WWII? How would you describe the major conflicts of WWII? What were the outcomes of World War II? I. Major Battles of World War II. A. Pearl Harbor. 1. Japan attack US bases on Hawaii in 2 waves. a. 1st wave=180 planes, all were seen by US radar operators 1 hour before the attack with no alarm because they were expecting planes from California, the opposite direction. b. 2nd wave- 160 planes. 2. Outcome- Use removed from policy of neutrality. a. President Roosevelt asked Congress to declare war. b. US enters war on both the Atlantic and Pacific front. I. Major Battles of World War II. B. Battle of El-Alamein. 1. 1st battle = a stalemate with allies suffering heavy casualties. 2. 2nd battle= allies massive artillery on Germans. a. Germany were outnumbered, short on supplies and reinforcements. b. 10 days of attacks, allies broke through enemy lines and forced axis forces to retreat. 3. Outcomea. Allies secured N.Africa and the Suez Canal. b. 1st major Allied victory over the Germans. I. Major Battles of World War II. C. Battle of Stalingrad. 1. Orders and Battle. a. Germans advanced to gain oil fields and take city. b. Russians ordered “not a step backwards.” c. one of the most brutal battles involving hand to hand combat & constant Germans by day, Soviets by night. 2. Soviets counter offensive. a. Germans faced harsh winter with no food, ammunitions, or heat. b. Germans forced to surrender. 3. Outcome = a complete German Army group lost. a. 91,000 Germans taken prisoner. b. Soviets begin march to Berlin. retake of the city. I. Major Battles of World War II. D. Battle of Guadalcanal. 1. USA- Landed unopposed. 2. US Goals a. Stop Japan from cutting off sea routes between Australia & US. b. protect Australia from invasion. c. Provide a springboard for assault on the Japanese. 3. Japan’s goals a. Retreat and Consulate. b. Build an airfield. 4. US naval forces forced to retreat leaving marines on their own to keep island. 5. Outcomea. Japanese convoys attacked with major damage. b. Australia safe, sea route protected. c. Another major gain by the Allies in their Island hopping mission. I. Major Battles of World War II. E. D-Day 1. June 6, 1944. Allied invasion of Normandy. a. 160,000 Allies landed, with support from 5,000 ships, & 13,000 aircraft. 2. Outcome a. 100,000 soldiers begin the invasion of France and Germany. b. Allies gained hold of Europe to start destruction of Germany. I. Major Battles of World War II. F. Battle of the Philippines. 1. Allied major assault through Central Pacific & Japanese defenses. 2. A series of bloody battles through the islands in which Japan’s fleet was heavily damaged. 3. Outcome a. Japan had very few aircrew left. b. Victory for the Allies/American in the move to Japan. II. Victory In Europe 1. May 8, 1945. 2. After the battle of the Bulge Germany was weakened to the point of surrender. 3. Germany surrender after Allies and the Soviets meet at the city of Berlin, and Hitler commits suicide. III. Victory In Japan 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. August 6th, 1945- Atomic Bomb dropped on Hiroshima killing 80,000. August 8th- Truman threatens more devastation on Japan. - Soviet union declares war on Japan. August 9th – Atomic Bomb dropped on Nagasaki. August 11th- Japan surrenders, with conditional sovereignty of emperor. Surrendered rejected. August 13th- Hirohito orders Japanese surrender. September 2nd- Formal surrender signed aboard the USS.Missouri. WOrk Work on Essay. Closing Q&A