* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download physical science 9.4
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
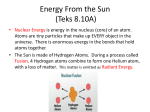
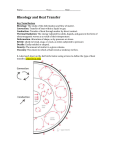
AUSTRALIAN CURRICULUM PHYSICAL SCIENCE 9.4 9.4.1 Physical Sciences: Science Understandings Energy transfer through different mediums can be explained using wave and particle models: exploring how and why the movement of energy varies according to the medium through which it is transferred. discussing the wave and particle models and how they are useful for understanding aspects of phenomena. investigating the transfer of heat in terms of convection, conduction and radiation, and identifying situations in which each occurs. understanding the processes underlying convection and conduction in terms of the particle model. exploring the properties of waves, and situations where energy is transferred in the form of waves, such as light. 9.4 Science as a Human Endeavour: Nature and development of science Scientific understanding, including models and theories, are contestable and are refined over time through a process of review by the scientific community: investigating how the theory of plate tectonics developed, based on evidence from seafloor spreading and occurrence of earthquakes and volcanic activity. advances in scientific understanding often rely on developments in technology and technological advances are often linked to scientific discoveries. considering how common properties of electromagnetic radiation relate to its uses, such as microwave cooking. OBJECTIVES PHYSICAL SCIENCE 9.4.1 1. Be able to use wave and particle models to explain energy transfer through different media. radiation: heat is radiated in the form of a wave of infrared radiation - it does not require a medium and can pass through a vacuum. convection: heat can be transferred within a fluid (gas or liquid) by convection currents. evaporation: when a liquid evaporates, heat energy is transferred to the gas particles. conduction: heat is transferred from one object or particle in contact with another. heat always passes from a hotter object to a cooler one, causing its temperature to rise. 2. Discussing the wave and particle models and how they are useful for understanding aspects of phenomena. Wave model: State that infra-red radiation, a form of light and a part of the Electromagnetic Spectrum, reaches us from the Sun through Space as a waveform. Convection and conduction are not possible in Space. Understand that this radiant heat can be reflected just like other parts of the Electromagnetic Spectrum. Relate this understanding to the use reflective foil insulation in houses and mirrored surfaces in the Thermos flask minimise heat escape from the flask. Particle model: Review your understanding of the Kinetic Theory of Matter, the Particle Theory covered in coursework 8.3 Investigating Chemistry. Refer to the Five Postulates. Use this Theory to explain the amount of energy found in different forms of matter i.e. solids, liquids and gases. Explain how energy is transferred during phase changes e.g. freezing, melting and evaporation. Be able to explain in terms of the Kinetic Theory why dew forms on grass or droplets of moisture form on a cold surface. Explain the processes of expansion and contraction in terms of the energy of the particles making up a substance. Explain how heat absorption causes a change in the energy of the particles i.e., a change in temperature. 3. Investigating the transfer of heat in terms of convection, conduction and radiation, and identifying situations in which each occurs. convection currents – Earth Processes e.g., tectonic movements, sea breeze. conduction of heat – loss of body heat to a cold surface, condensation of water onto a cold surface, cooking food in a saucepan/frypan. radiant heat from the Sun or from any hot object.