* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit2-PedigreesWeb
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
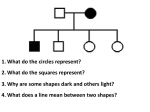
Unit 2 – Pedigrees • Autosomal recessive inheritance – – – – – All sufferers of the trait are homozygous recessive, e.g. cystic fibrosis. Men and women are affected in approximately equal numbers. The trait can skip generations. The trait is expressed relatively rarely. Parents of a sufferers may not show the trait if they are heterozygotes. Individuals which carry the defective allele but are not affected are called carriers. – Non-sufferers are homozygous dominant or heterozygote (i.e. carriers). • Autosomal dominant inheritance - Sufferers may be homozygotes dominant or heterozygotes. – Trait appears in every generation. When a branch of the family tree does not express the trait, the traits fails to reappear in future generations. – Each sufferer of the trait has at least one affected parent. – Men and women are affected in approximately equal numbers. – Example: Huntington Chorea cc cc cc cc What’s new? • http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/scienceenvironment-32932922 http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/huntingtonsdisease/pages/introduction.aspx • Autosomal incomplete dominance – Incomplete dominance is when heterozygous individuals have a partly expressed form, i.e. an intermediate phenotype of the disorder. – The fully expressed form of the disorder is found in individuals homozygous for the defective allele. – The partly expressed form occurs much more frequently than the fully expressed form. – The fully expressed form of the disorder occurs rarely. – Each sufferer of the fully expressed form has two parents who suffer the partly expressed form of the disorder. – Men and women are affected in approximately equal numbers. – Example is sickle cell anaemia • https://www.dnalc.org/resources/3d/17sickle-cell.html • Sex linked recessive single gene disorder • Men will be affected a lot more than women. • If a normal male and carrier female have a number of children then they might expect half their daughters to be normal and half to be carriers; half their sons to be normal and half their sons to be affected. • An example of sex linked recessive trait is haemophilia • http://www.nature.com/nature/outlook/hae mophilia/#video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QlkbGSF yNYo • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2pp17E4 E-O8 Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis • How is pre-implantation genetic diagnosis performed? • Cells of embryo created using IVF are removed and screened for specific inherited conditions Pre-implantation genetic diagnosis • How is pre-implantation genetic diagnosis performed? • Cells of embryo created using IVF are removed and screened for specific inherited conditions • What abnormalities can be detected using PGD? • Cystic fibrosis, Huntington chorea • http://guide.hfea.gov.uk/pgd/ • What fertility treatment is PDG often performed alongside? • IVF • Video about new type of screening for IVF • PGD and designer babies – Ethical issues