* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 22.3: Space Probes
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
Observations and explorations of Venus wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Colonization of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
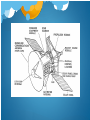
Objectives Describe 5 discoveries made by space probes Explain how space-probe missions help us better understand the Earth Describe how NASA’s new strategy of “faster, cheaper, and better” relates to space probes Space Probe Un-crewed vehicle that carries scientific instruments to planets or other bodies in space Complete missions that would be dangerous or expensive for humans to undertake Closer To Home: Inner Solar System Much closer than other planets in the solar system Missions to: Moon Venus Mars Luna & Clementine Soviet Union United States Luna 1: Fist space probe that flew past the moon launched in 1959 Clementine (1994): Crater of the moon may contain water Luna 9: First landing on the moon’s surface launched in 1966 Lunar Prospector (1998): Frozen water exists on the moon Luna & Clementine Venus Venera 9: Soviet Union launch in 1975 Parachuted into Venus’s atmosphere and sent images and data back to Earth Surface Temperature ~464 degrees Celsius Atmospheric pressure much higher than on Earth Chemistry showed similar rocks to Earth Severe Greenhouse effect Our atmosphere? Venera 9 Venus Magellan: United States launched in 1989 Used radar to map 98% of the surface of Venus Used to generate 3-D images Geology of Venus is similar to Earth: Plate Tectonics Active Volcanoes Magellan Image From Venus: Volcanic Pancake Domes Mars Viking Missions: Pair of probes launched by U.S. in 1975 Look for signs of life by gathering soil and analyzing Found that Mars was once warmer and wetter Only led to more questions about Mars Viking 2 Obiter Right: Dust Storm On Mars Taken by Viking 2 Orbiter Mars Mars Pathfinder: Launched by the U.S. in 1996 Could explore Mars at a lower cost than Viking Images showed dry water channels Mars once had water Sojourner: Collected data and images for 3 months as moved around the planet’s surface Mars Pathfinder Mars Science Laboratory (Curiosity) Eight Science Objectives: 1. Nature & Inventory of Carbon 2. Look for building blocks of life 3. Effects of biological processes 4. Investigate composition of surface 5. Process of Earth & soil development 6. Atmospheric evolution process 7. Cycling of water and carbon dioxide 8. Determine surface radiation Far Out: The Outer Solar System These probes take longer to reach their destination Outer Solar System: Jupiter Saturn Uranus/Neptune/Pluto Pioneer Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 Launch by the U.S. in 1972 First to study the outer solar system Sampled solar wind: the flow of particles coming from the sun Pioneer 10 (1983) because the first to travel past Pluto Voyager First to detect Jupiter’s faint rings Flew by all four gas giants (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune) Some are still sending back data from past the edge of the solar system Jupiter Galileo Missions: Launched in 1989 and arrived at Jupiter in 1995 Sent a smaller probe into Jupiter’s atmosphere to measure composition, density, temperature, and cloud structure Studied Geology of major moons Two moons had magnetic field Europa has an ocean of liquid water under its icy surface Saturn Cassini Mission Launch in 1997, seven year journey to Saturn where it toured Saturn’s moons Huygens probe descended into Saturn’s moon Titan Interested in Titan because of its atmosphere Discovery Planetary Science Investigations Smaller missions using fewer resources and shorter development times Enhance our understanding of the solar system Improve performance through the use of new technology and broaden participation in NASA missions