* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Patient Age Injection Site Needle Size
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
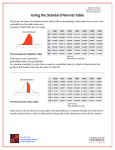
MASSACHUSETTS DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH TRAINING MODULE VACCINE AND MEDICATION PREPARATION AND ADMINISTRATION Presented by: Marie C. Regis DNP, RN Regional Immunization Nurse Metro Boston Region Massachusetts Department of Public Health November 9, 2010 4/30/2017 1 Learning Objectives Understand general guidelines of vaccine/medication preparation and administration Describe four different administration routes Describe infection control principles Describe patient preparation, comfort and safety Describe response to emergencies, adverse events, and errors List federal and state requirements for documentation and record keeping 4/30/2017 2 Correct Administration of Vaccines/Medications Keep current with best practices of vaccine/medication preparation and administration Adhere to agency policies for safety Use available resources and guidelines Complete accurate and legible documentation 4/30/2017 CDC 3 Administration/Dispensing Best Practice Use 5 Rights of Medication Administration: Right Patient: verify name and age, screen for contraindications and precautions Right Drug: check label, review package insert, verify for appropriate patient/age Right Dose: determined by age and/or weight Right Route: e.g. IM, subcutaneous, PO, intranasal Right Time: refer to dosing schedules and minimum intervals between doses 4/30/2017 4 Standing Orders Use current medication and emergency standing orders that are reviewed and signed by a physician or Medical Director (vaccine/medication specific & emergency orders) Have signed orders at clinic site Orders should include: name of vaccine/medication, dose, route/method of administration and inclusion/exclusion criteria Model vaccine standing orders available at: http://www.mass.gov/dph/imm 4/30/2017 5 Confidentiality and Privacy Assure the confidentiality of patients’ information and their rights to privacy Provide privacy at stations with screens and adequate space Ask only what you “need to know” for safe administration of vaccine or medication Comply with HIPAA and FERPA 4/30/2017 6 Vaccine Information Statement (VIS) Developed by CDC Conveys risks and benefits of vaccine Required by federal law Vaccine specific Must use current edition (unaltered) Must be given before each dose of each vaccine Provide an opportunity for questions Available in multiple languages at: www.immunize.org/vis 4/30/2017 7 Medication Information Sheet Name and formulation of medication Directions for use Dosing administration information Signs & symptoms of adverse reactions/side effects Provide an opportunity for questions 4/30/2017 8 Screening for Contraindications and Precautions Use appropriate screening tool Limit questions to “need to know” Vaccinator/dispenser responsible for final review of screening questions Protect confidentiality and privacy Sample immunization screening tools available at http://www.immunize.org Request an interpreter if needed 4/30/2017 9 Screening for Contraindications and Precautions (cont.) Know your package insert! Some important considerations are: Anaphylaxis/Allergy Age Acute illness Underlying medical conditions Pregnancy Vaccination history Current medications 4/30/2017 10 Vaccine Formulations 4/30/2017 CA DPH 11 Injectable Vaccine Preparation Always use sterile technique Check expiration date, color and consistency Follow package insert instructions 4/30/2017 12 Preparation: Reconstituting Vaccine/Medication Clean diluent vial stopper with alcohol and place vial on flat surface Instill air equal to dosage into vial Invert vial and withdraw diluent Clean vaccine/medication vial stopper with alcohol and place vial on flat surface Inject diluent into vaccine/medication vial Mix vaccine/medication and diluent per package insert instructions. When mixed, it should look as described in the package insert (e.g. color, no extraneous particulate matter, etc.) 4/30/2017 CA DPH 13 Preparation: Drawing up Injectable Vaccine/Medication Clean vial stopper with alcohol between each needle insertion and place vial on flat surface Instill air equal to dosage into multidose vial Invert vial and withdraw dose into syringe Expel bubbles and excess liquid while needle in vial Recap needle, and label syringe if not using immediately (initials, contents, time, and date) 4/30/2017 14 Multi-Dose Vial Contains a preservative Good until expiration date unless contaminated, or manufacturer or package insert states otherwise Date, time and initial vial after opening Use open vial first and rotate stock 4/30/2017 CDC 15 Vaccinator Prefilling of Syringes In order to reduce the risk of medication administration errors and ensure vaccine viability, providers should avoid pre-filling syringes, and this practice is strongly discouraged. In situations where pre-filling syringes is unavoidable, medication administration errors may be reduced by: Storing syringes with vaccine of same type and same lot number together in separate containers Labeling each container and labeling each syringe with: Type of vaccine; lot number Date and time vaccine was drawn up Initials of the person who drew up vaccine Vaccinator Prefilling of Syringes May result in vaccine/medication administration errors and wastage Keep prefilled syringes on cold packs, and protect from light. If kept at room temperature, discard after 30 minutes Discard unused, prefilled syringes at end of the clinic day Consider using manufacturer-supplied prefilled syringes (if available) for large immunization events 4/30/2017 CDC 17 Manufacturer Prefilled Syringes Most contain no, or only trace amounts of, preservative Removing the syringe cap or attachment of a needle breaks the sterile seal Do not remove the cap or attach a needle until ready to use Once needle attached, unused syringes should be discarded at end of the clinic day 4/30/2017 CDC 18 Single Dose Vial Most contain no, or only trace amounts of, preservative Once opened, vial should be used or discarded at the end of the clinic day 4/30/2017 CDC 19 Other Preparation Issues Not necessary to change needles between drawing up or reconstituting and administration unless needle is contaminated or bent Never mix different vaccines/medication in the same syringe unless approved by the FDA 4/30/2017 CDC 20 Inactivated Vaccines Made from viruses and bacteria that have been killed (e.g. Tdap, pneumococcal vaccine) Can be given on same day as any other vaccine, live or inactivated Follow manufacturer’s recommended schedule for subsequent doses if applicable (e.g. Hepatitis B series) 4/30/2017 21 Live Vaccines Made from weakened (attenuated) virus in order to produce immune response without causing severe effects of disease (e.g. LAIV, MMR, varicella) Multiple live vaccines and inactivated vaccines can be given on same day, depending on administration route When administering live vaccines on different days, follow manufacturer’s instruction regarding necessary minimum intervals between doses (usually 28 days) 4/30/2017 CDC 22 General Dosage Guidelines With any vaccine/medication formulation Refer to package insert (e.g. age, weight guidelines) Follow current standing orders Apply 5 rights of medication administration 4/30/2017 23 Administration Routes 4/30/2017 CA DPH 24 Intramuscular (IM) Injection Sites Site selection depends on person’s age, muscle development and vaccine/medication Preferred vaccine site for children, adolescents and adults is upper arm (deltoid muscle) Vaccine site for toddlers can be either upper arm (deltoid) or anterolateral thigh (vastus lateralis) Vaccine site for infants is anterolateral thigh (vastus lateralis) Use anatomical landmarks to locate site 4/30/2017 CDC 25 Intramuscular (IM) Injection Sites Infant/Child/Adolescent/Adult Vastus Lateralis - infant site Deltoid - child and adult site 4/30/2017 (alternative site when deltoid contraindicated) CDC 26 Intramuscular (IM) Tissue 90°Angle Dermis Fatty Tissue Muscle Tissue 4/30/2017 CDC 27 Intramuscular (IM) Sites and Needle Sizes Patient Age Injection Site Needle Size Newborn (0-28 days) Anterolateral thigh muscle 5/8” (22-25 gauge) Infant (1-12 months) Anterolateral thigh muscle 1” (22-25 gauge) Anterolateral thigh muscle 1-1 ¼” (22-25 gauge) Alternate site: Deltoid muscle 5/8-1” (22-25 gauge) Deltoid muscle 5/8-1” (22-25 gauge) Alternate site: Anterolateral thigh muscle 1-1 ¼” (22-25 gauge) Deltoid muscle 1-1 ½” (22-25 gauge) Alternate site: Anterolateral thigh muscle 1-1 ¼” (22-25 gauge) Toddler (1-2 years) Children (3-18 years) Adults (19 years and older) 4/30/2017 www.immunize.org 28 How to Locate Deltoid Muscle The injection site is 2-3 fingerbreadths below the shoulder tip (acromion), above level of armpit (axilla) and on the lateral midline of the arm. Draw an imaginary inverted triangle below the shoulder tip, using the above anatomical landmarks. The deltoid site for injection is the middle of the muscle (triangle). 4/30/2017 clavicle acromion axilla humerus 29 Intramuscular (IM) Injection Technique Assess patient’s muscle mass Clean injection site with alcohol; allow to air dry With your dominant hand, insert needle at a 90-degree angle to the muscle Push down on plunger and inject entire contents of syringe Remove/retract needle and briefly apply light pressure to injection site with dry cotton ball or gauze Immediately put used syringe in sharps container Cover injection site with bandage if indicated 4/30/2017 CDC 30 Intramuscular Injection (IM) Technique 4/30/2017 31 CDC Intramuscular (IM) Injection Site Infant Anterolateral Thigh (vastus lateralis muscle) 4/30/2017 CDC 32 How to Locate Vastus Lateralis The anterolateral thigh Position client in supine or sitting position The upper landmark is the greater trochanter of the femur Injection site is the middle third and anterior lateral aspect of thigh The lower landmark is the lateral femoral condyle 4/30/2017 33 X Marks the Spot! 4/30/2017 Australian Gov’t Health & Aging 34 Subcutaneous (SC) Injection Injection into the fatty tissue below the dermis and above the muscle Usual sites are thigh and upper outer triceps area of the arm 4/30/2017 CDC 35 Subcutaneous Tissue 45° Angle Dermis Fatty Tissue Muscle Tissue 4/30/2017 CDC 36 Subcutaneous (SC) Sites and Needle Sizes Patient Age Injection Site Needle length Birth to 12 months Fatty tissue over the anterolateral thigh muscle 5/8” (23-25 gauge) 12 months and older Fatty tissue over anterolateral thigh or fatty tissue over triceps 5/8” (23-25 gauge) 4/30/2017 www.immunize.org 37 Subcutaneous Injection Sites 4/30/2017 CDC 38 Subcutaneous Injection Technique Clean injection site with alcohol; allow to air dry With thumb and index finger of your non-dominant hand, bunch fatty tissue of injection site With your dominant hand, insert needle at a 45-degree angle to skin; insert entire needle Push down on plunger and inject entire contents of syringe Remove needle and briefly apply light pressure with dry cotton ball or gauze to injection site Immediately put used syringe in sharps container Cover injection site with bandage if indicated 4/30/2017 CDC 39 Subcutaneous Injection Technique 4/30/2017 40 CDC Injectable Administration Issues Aspiration not required for vaccines No reports of injury from failure to aspirate Can result in vaccine wastage When administering multiple doses at the same time, it is preferable to use separate limbs Injection sites in same limb should be separated by at least 1 inch if possible Use safety syringes/needles or needle-free devices to reduce risk of injury 4/30/2017 41 Oral (PO) Vaccine Administration 4/30/2017 MERCK 42 Oral (PO) Administration Follow instructions per package insert Assess ability to swallow Assess for allergies/contraindications and precautions Assess fluid needs and restriction Remain with client until all medication is swallowed If patient spits up, do not re-administer medication 4/30/2017 43 Intranasal Injection Technique 4/30/2017 44 CA DPH Intranasal Administration Administer as directed according to package insert If dose is divided in the sprayer, half the contents of the dose should be sprayed into each nostril at the same visit Tell the patient to breathe normally (do not sniff) Do not repeat if the person sneezes, coughs or some dribbles out after administration 4/30/2017 45 Infection Control Hand Hygiene Required between patients and before vaccine/medication administration Alcohol-based hand sanitizer can be used when soap and water unavailable Gloves not required unless: 4/30/2017 potential for exposure to blood or body fluids open lesions on hands agency policy If you do wear gloves, change between each patient 46 Infection Control (cont.) Follow blood-borne pathogen policy (including needle stick policy) Use PPE (personal protective equipment) as required Immediately dispose of used or contaminated syringes, vials, nasal sprayers, and oral vaccine ampules, as medical waste in sharps/biohazard container Never detach, recap or cut a used needle 4/30/2017 47 Patient Preparation Display confidence and establish a sense of security and trust with the patient Prepare patients for administration; consider their age and stage of development Encourage parents/patients to take active role before, during and after administration Use age-appropriate techniques that provide distraction and minimize the stress and discomfort of vaccination 4/30/2017 48 Patient Comfort & Safety Have patients seated for vaccination Strongly recommend patients are observed for 15-20 minutes after they are vaccinated If syncope develops, patients should be observed until symptoms resolve Counsel patient about the use of pain relievers to decrease discomfort and possible fever post vaccination 4/30/2017 49 Expect the Unexpected While anaphylactic/allergic reactions following vaccinations are rare, you need to be ready to respond with personnel, facilities and equipment/supplies. Emergency Standing Orders need to be current and signed by physician or Medical Director prior to clinic Have emergency supplies available and know how to use them Model Emergency Standing Orders can be found at: http://www.mass.gov/dph/imm 4/30/2017 50 Positioning 4/30/2017 CA DPH 51 Positioning 4/30/2017 CA DPH 52 Suggested Vaccination/Medication Dispensing Station Supplies Vaccine/medication Cold packs w/plastic containers Needles (different sizes) Safety syringes Sharps/biohazard containers Latex free gloves Hand sanitizer Water/cups Pill crusher 4/30/2017 Medicine cups Teaspoons/bowls Alcohol wipes Gauze/bandages Adhesive tape Tissues/paper towels Table covering Trash container/bag Required forms/pens 53 Required Documentation for Administration of Vaccine Patient’s name and age Vaccine name, manufacturer, lot number, expiration date and dose number Publication date on VIS, date VIS was given Anatomical site, route and dose amount Date vaccine administered Vaccinator’s name, initials, address, signatures, and credentials Clinic name, address and contact person Signed consent is not required except when a parent/guardian is not present 4/30/2017 54 Emergency Supplies BP and stethoscope (child & adult, extralarge cuffs) Cell phone or access to an on-site phone 3x3 gauze pads Alcohol wipes Bandages Hand sanitizer 4/30/2017 Latex free vinyl gloves (small, medium, large & extra large) Flashlight & batteries Thermometer & probe covers Instant cold packs Cots, Blankets, Pillows Wrist watch with second hand 55 Emergency Supplies (cont.) Acetaminophen 325 mg tablets Ibuprofen 200mg tablets Diphenhydramine 25 mg tablets Diphenhydramine 50 mg injectable-(carpujet) Epipen & Epipen Jr. & Aqueous Epinephrine 1:1000 injectable 1mg/ml Diphenhydramine elixir 12.5 mg/5ml suspension 25 mg/5ml 4/30/2017 Syringes-3mL-1” 23g, 5/8” 25g, 1mL Ammonia inhalant Airways (large & small) Pocket masks with one way valve (adult & pediatric) Tongue depressors AED 56 Vaccine/Medication Errors Report error immediately to direct supervisor Monitor client for adverse reaction (if appropriate) Frequently seen errors: Wrong vaccine, medication Wrong dose for age Wrong site, route or needle length Expired/recalled vaccine, medication or diluent Wrong time, errors in spacing of doses Report vaccine/medication administration errors to the Institute for Safe Medication Practices www.ismp.org 4/30/2017 57 ISMP Institute of Safe Medication Practices Report medication/vaccine administration errors to ISMP online at: www.ismp.org Institute for Safe Medication Practices 200 Lakeside Drive; Suite 200 Horsham, PA 19044-2321 Phone: 215-947-7797 Fax: 215-914-1492 VAERS Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System Report all clinically significant postvaccination events via online, mail, phone or fax www.vaers.hhs.gov VAERS P.O. Box 1100, Rockville, MD 20849-1100 1-800-338-2382 (phone) 1-877-721-0366 (fax) Vaccinator/Dispenser Responsibilities Be informed about storage, handling, preparation, administration and contraindications of vaccine/medication to be administered/dispensed Relay information on the risks and benefits of accepting or refusing vaccine/medication Screen for contraindications and precautions prior to administration Be mindful of security and safety of vaccine/medication, sharps and biohazards 4/30/2017 60 Vaccinator/Dispenser Responsibilities (cont.) Understand documentation used for administration/dispensing Complete required documentation accurately and legibly Be able to access and use emergency equipment Hold current licensure and/or certification (e.g. CPR) Report adverse events (ISMP & VAERS) Report vaccine/medication errors 4/30/2017 61 Medication Storage and Handling Follow package insert and manufacturer’s instruction Be mindful of security and safety of medication at your station 4/30/2017 62 Vaccine Storage and Handling The cold chain begins with the manufacturer and ends with administration of the vaccine to the patient Proper storage temperatures must be maintained per manufacturer recommendations Injectable vaccine syringes/vials maximum 30 minutes at room temperature IN sprayers kept at 2 - 8° C (35 - 46°F) Protect vaccine from exposure to light Keep vaccine on cold packs at stations 4/30/2017 CDC 63 MDPH Contact Numbers MDPH Epidemiology/Immunization Program 617-983-6800 (24x7) 888-658-2850 MDPH Vaccine Unit 617-983-6828 4/30/2017 64 Please join us for the other training modules! Planning a Clinic/EDS/POD: November 12th, 3:00-4:30 All-Staff Briefing & Just-In-Time Training: November 15th, 3:00-4:30 Vaccine Management, Storage and Handling: November 16th, 3:00-4:00 4/30/2017 65 Vaccine Key Resources MDPH Guidelines for Compliance with Federal and State Vaccine Administration Requirements http:/www.mass.gov/Eeohhs2/docs/dph/cdc/immunization/guidelines_v accine_compliance.pdf MDPH General Protocols for Vaccine Storage, Administration, Standing Orders, and Mass Immunization Clinics, Sept 2009 http://www.mass.gov/Eeohhs2/docs/dph/cdc/immunization/mso_protoc ols_general.pdf MMWR: General Recommendations on Immunization, Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), December 2006 http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/rr/rr5515.pdf Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (The Pink Book) from the CDC http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/default.htm#download 4/30/2017 66 Online Resources Massachusetts Department of Public Health, Immunization Program www.mass.gov/dph/imm CDC: Vaccines and Immunizations http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines World Health Organization: Department of Immunization, Vaccines and Biologicals http://www.who.int/immunization/en National Vaccine Program Office (NVPO) @ HHS http://www.hhs.gov/nvpo Red Book: 2009 Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases of the American Academy of Pediatrics http://aapredbook.aappublications.org/ 4/30/2017 67 Online Resources Massachusetts Department of Public Health, School Health Division http://mass.gov/dph/fch/schoolhealth California Department of Public Health, Immunization Branch http://www.eziz.org Immunization Action Coalition http://www.immunize.org 4/30/2017 68 Online Resources MDPH: Recommendations for Drawing-Up Vaccine and Other Documentations Requirements for Clinical Sessions or Large Clinics (Nov 2009) http://www.mass.gov/Eeohhs2/docs/dph/cdc/immunization/mso_r ecommendation_drawing_up_vaccine.pdf CDC’s Guide to Vaccine Contraindications and Precautions http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/recs/vacadmin/downloads/contraindications-guide-508.pdf Institute for Safe Medication Practices http://www.ismp.org Vaccine Adverse Events Reporting System (VAERS) http://www.vaers.hhs.gov 4/30/2017 69 QUESTIONS?? Thank You ! 4/30/2017 70