* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1933: Inauguration of Franklin Delano Roosevelt
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Empire of Japan wikipedia , lookup
Imperial Japanese Navy wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied naval bombardments of Japan during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aleutian Islands Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
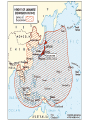
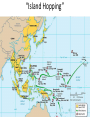
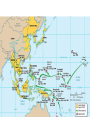
World War II While America „slept“ • 1931: Japan invades Manchuria • 1933: Germany withdraws from the League of Nations • 1935: Hitler denounces the disarmament clauses in the Treaty of Versailles • 1936: Spanish Civil War begins • 1937: Japan attacks China • 1938: The Anschluss • 1939: Germany invades Poland • 1940 – 1941: Germany conquers Denmark, Norway, Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, France Era of Extreme Propaganda Virtually overnight, the entire US industry had to be retooled, factories went from Fords to tanks • • • • • “Europe First” Policy 1942: Manhattan Project initiated June 6, 1944: D-DAY German advance stopped April 12th: FDR dies, Truman takes over • April 30th 1945: Hitler suicide • May 8th unconditional surrender of the Third Reich War in Germany “over” “Island Hopping” June 4 – 7, 1942:Midway June 4 – 7, 1942: Battle of Midway • one of the most important naval battles of World War II • Japanese hoped that another demoralizing defeat would force the U.S. to capitulate in the Pacific War, ensuring Japanese dominance in the Pacific • U.S. inflicted irreparable damage on the Japanese fleet • John Keegan: "the most stunning and decisive blow in the history of naval warfare." • It was Japan's first naval defeat since the Battle of Shimonoseki Straits in 1863 • After Midway Japan's shipbuilding and pilot training programs were unable to keep pace in replacing their losses, while the U.S. steadily increased its output in both areas and was able to establish naval parity in the Pacific Guadalcanal: Aug 7,1942 – Feb 9,1943 Guadalcanal: Aug 7,1942 – Feb 9,1943 • first major offensive by Allied forces against the Empire of Japan • Objective: deny the use of the southern Solomon Islands by the Japanese (it would threaten the supply and communication routes between the US, Australia, and New Zealand. • also intended to use Guadalcanal as base to support campaign • The Battle of Guadalcanal was one of the first prolonged campaigns in the Pacific • Strained the logistical capabilities Spring 1945: Okinawa and Iwo Jima Battle of Okinawa, 1 April – 22 June 1945 • • • • • • • largest amphibious assault in the Pacific War of World War II Plan: use Okinawa as a base for air operations on the planned invasion of Japanese mainland (coded Operation Downfall) The battle has been referred to as tetsu no ame or tetsu no bōfū in Japanese highest number of casualties in the Pacific Theater during World War II. Mainland Japan lost 77,166 soldiers, who were either killed or committed suicide Allies suffered 14,009 deaths 42,000-150,000 local civilians were killed or committed suicide Hiroshima and Nagasaki - After German capitulation, Japan refuses to surrender - Truman: „They will be met with complete and utter destruction“ - August 6th, 1945: „Little Boy“ dropped on Hiroshima (~ 85.000 casualties) - August 9th: „Fat Man“ dropped on Nagasaki (~ 70.000 casualties) - A nuke near you The Outcome of WW II • • • • • Germany divided Marshall Plan Truman Doctrine Problems with Russia Cold War Other Developments: • 1949: NATO organized: mutual defense treaty. (An attack on one country would be considered an attack on each and every one, and they would all be allied until the threat was defeated) – Clause triggered: 2001 War on Terror – Soviet answer: Warsaw Pact • 1950 – 1953: Korean War – Domino Theory – Ends in a truce (38th Parallel) The Eisenhower Era 1953 - 1961 o popular as the commander in chief of the Allied forces in Europe. o People voted for the man in 1953, not for a political platform. “I Like Ike” o greatest concern = communism and its goal of world domination. o developed the new policy of “Massive Retaliation” o Concept of massive retaliation was only meant to be implemented in the event of an actual attack o Very scary time Kennedy‘s Presidency • Cuban Missile Crisis: marked a change in United States – Soviet relations both parties realized that they would have to deescalate the arms race, or risk a nuclear winter signed the Limited Test Ban Treaty • attempts to stimulate the economy, developed programs to aid education, fight poverty worldwide, health insurance for elders, prepared a legislative agenda that would have moved aggressively on such issues as civil rights, created the Peace Corps,, secured funding for the Space Program • Program for social and educational reform: New Frontier • He went against the “prime directive”, exploring strange new worlds and saw it fit to fix or change them, when they needed it. JFK repeatedly violated “social norms” (especially in areas such as Civil Rights) when HE thought it was the right thing to do. November 22 1963