* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WhatsInSolarSystem - School
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Planet Nine wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Eris (dwarf planet) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
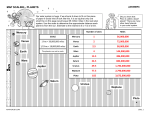
What's in the Solar System? describe the location and nature of the main constituents of our Solar System, including planets, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, centaurs and Trans-Neptunian Objects (TNOs) recall the names of planets and dwarf planets in order of their mean distance from the Sun demonstrate an understanding of the scale and size of our Solar System using scale models (for example balls of different sizes at appropriate spacing, model Solar Systems such as the Spaced Out project) The Sun Our Sun is a star, a huge ball of Hydrogen and Helium with a nuclear reaction, fusion, happening in its core. It formed from a cloud of Hydrogen billions of years ago and when it formed a number of objects were formed too or relatively shortly after. These objects make up what we call our solar system. Planets and Dwarf Planets Planets According to the International Astronomical Union a planet is an object which: 1. Is in orbit around the Sun 2. Has a mass big enough so that its gravity pulls it into a nearly round shape 3. Has "cleared the neighbourhood" around its orbit. Dwarf Planets As telescopes and techniques have improved astronomers have discovered more and more distant and smaller objects in our solar system. In the late 20th century several objects were discovered comparable in size to Pluto, e.g. Sedna and Eris. If Pluto was a planet then these objects too should be planets and future objects of similar size. This is why the third statement above was decided upon in 2006. The third statement means that there are no other objects, other than its own satellites, in the region of its orbit. Objects such as Pluto which do not meet condition 3 are referred to as dwarf planets. There are (as I write this) officially 8 planets and 5 dwarf planets in our solar system. Planet Distance (AU) Dwarf Planet Distance (AU) Mercury 0.4 Ceres 2.7 (Asteroid belt) Venus 0.7 Pluto 39 (Kuiper belt) Earth 1 Haumea 43 (Kuiper belt) Mars 1.5 Makemake 46 (Kuiper belt) Jupiter 5.2 Eris 68 (Scattered disc) Saturn 9.4 Uranus 19 Neptune 30 Ceres Makemake Eris Small Solar System Bodies (SSSB) These are objects which are neither planets nor dwarf planets. They include the following. Asteroids Asteroids are smaller than planets but larger than meteoroids, i.e. they are greater than 10m in diameter. They do not have a coma as comets do. Most are found within a region called the Asteroid Belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Comets Comets are objects which display a coma, a fuzzy atmosphere, when they are close to the Sun. They are balls of dust, rock and ice. Centaurs These objects which have crossed the orbits of one or more of the giant planets. As centaurs in mythology were half man and half horse these objects behave like a cross between a comet and an asteroid. They remain inside the solar system yet have quite eccentric orbits. Some have been seen to have a coma, as comets do. Centaurs include Hidalgo and Chiron. Asteroids The comet Hale Bop The orbit of Hidalgo Trans-Neptunian Objects These objects orbit the Sun at a greater average distance than Neptune. Over 1,000 of these objects have been discovered the largest of which is Eris. Pluto is also one. Kuiper Belt objects, Scattered Disk objects and Oort Cloud objects are all trans-neptunian. The SpacedOut project is basically a scale model of our solar system. For more info see HERE.