* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Brain
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
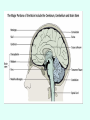
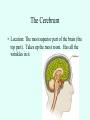
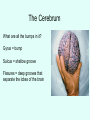
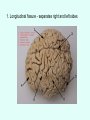
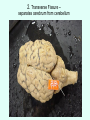
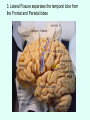
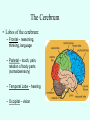
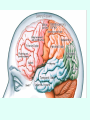
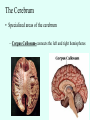
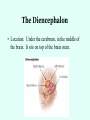
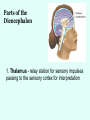
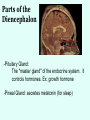
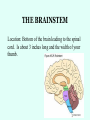
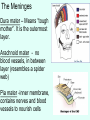
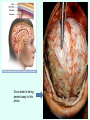
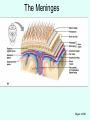
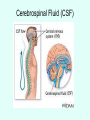
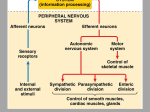
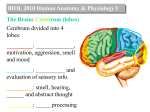
THE BRAIN Chapter 7 Major Divisions of the Brain • 1. Cerebrum • 2. Diencephalon • 3. Brain Stem • 4. Cerebellum The Cerebrum • Location: The most superior part of the brain (the top part). Takes up the most room. Has all the wrinkles in it. The Cerebrum What are all the bumps in it? Gyrus = bump Sulcus = shallow groove Fissures = deep grooves that separate the lobes of the brain 1. Longitudinal fissure - separates right and left sides 2. Transverse Fissure – separates cerebrum from cerebellum 3. Lateral Fissure separates the temporal lobe from the Frontal and Parietal lobes The Cerebrum • Functions of the Cerebral Cortex: – Controls speech, memory, logical and emotional response, consciousness, interpretation of sensation, and voluntary movement • It is split into 4 major lobes The Cerebrum • Lobes of the cerebrum: – Frontal – reasoning, thinking, language – Parietal – touch, pain, relation of body parts (somatosensory) – Temporal Lobe – hearing – Occipital – vision The Cerebrum • Specialized areas of the cerebrum – Broca’s area- responsible for speech usually located only in the left side. Damage to this area causes the inability to say words properly (you know what you want to say but you can’t vocalize the words) . The Cerebrum • Specialized areas of the cerebrum – Basal Ganglia- help regulate volunteer motor activities by stopping or starting movement. It modifies instructions sent to the skeletal muscles. – Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease are disorders of the basal ganglia. (page 253-254) The Cerebrum • Specialized areas of the cerebrum – Corpus Collosum-connects the left and right hemispheres Take the Left Brain – Right Brain Test The Diencephalon • Location: Under the cerebrum, in the middle of the brain. It sits on top of the brain stem. Parts of the Diencephalon 1. Thalamus - relay station for sensory impulses passing to the sensory cortex for interpretation Parts of the Diencephalon 2. Hypothalamus – most important regulatory center of the autonomic nervous system -controls temperature, water balance, & metabolism - also controls many drives and emotions (thirst, appetite, sex, pain, and pleasure centers) Parts of the Diencephalon -Pituitary Gland: The "master gland" of the endocrine system. It controls hormones. Ex: growth hormone -Pineal Gland: secretes melatonin (for sleep) Thalamus Pineal gland Hypothalamus Corpus callosum THE BRAINSTEM Location: Bottom of the brain leading to the spinal cord. Is about 3 inches long and the width of your thumb. THE BRAINSTEM Parts of the Brainstem: Midbrain- visual reflexes, eye movements Pons- relay sensory information Medulla Oblongata- regulates breathing, heart rate, blood pressure Medulla Oblongata Pons Midbrain CEREBELLUM Location: lower, back of brain. It is under the occipital lobe. CEREBELLUM • Function: Balance and coordination Protection of the Brain The Meninges & Cerebral Spinal Fluid The Meninges Dura mater – Means “tough mother”. It is the outermost layer. Arachnoid mater - no blood vessels, in between layer (resembles a spider web) Pia mater -inner membrane, contains nerves and blood vessels to nourish cells Dura mater is being peeled away in this photo. The Meninges Figure 13.25a Cerebrospinal Fluid • Is a watery broth similar to blood plasma, from which it forms. • It forms a watery cushion that products the fragile nervous tissue from blows and other trama. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Problems • Meningitis- inflammation to the meninges. It is a serious threat because the bacteria or virus can spread to the CNS. • Encephalitis- is inflammation of the brain • Hydrocephalus- is water on the brain because a tumor (or something) is blocking drainage of the CSF. Treated with a shunt. • A spinal tap is done to test CSF