* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
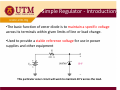
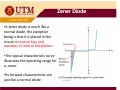
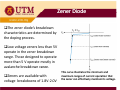
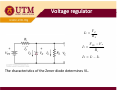
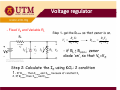
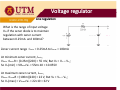
Chapter 2 DIODE part 3 ZENER DIODE MENJANA MINDA KREATIF DAN INOVATIF objectives ¾Diode zener –Introduction ¾ Diode zener ener – I-V I V characteristic characteristic, data sheet ¾Diode zener zener-applications applications Simple Regulator ‐ Introduction Simple Regulator •The basic function of zener diode is to maintain a specific voltage across its terminals within given limits of line or load change. •Used to provide a stable reference voltage for use in power supplies and other equipment supplies and other equipment This particular zener circuit will work to maintain 10 V across the load This particular zener circuit will work to maintain 10 V across the load. Zener Diode •A zener diode is much like a normal diode, the exception being is that it is placed in the circuit in reverse bias and operates in reverse breakdown operates in reverse breakdown. •This typical characteristic curve yp illustrates the operating range for a zener. •Its forward characteristics are just like a normal diode just like a normal diode Zener Diode The zener diode’s breakdown y characteristics are determined by the doping process. Low voltage zeners less than 5V l l h operate in the zener breakdown range Those designed to operate range. Those designed to operate more than 5 V operate mostly in avalanche breakdown range. Zeners are available with voltage breakdowns of 1.8V‐2.0V l b kd f 1 8V 2 0V This curve illustrates the minimum and maximum ranges of current operation that the zener can effectively maintain its voltage the zener can effectively maintain its voltage. Data sheet Data sheet As with most devices, zener diodes have given characteristics such as temperature coefficients and characteristics such as temperature coefficients and power ratings that have to be considered. The data sheet provides this information sheet provides this information. Data sheet Data sheet Application ‐ regulator Application In this simple illustration of zener regulation circuit, the zener diode will “adjust” its impedance based on varying input voltages and loads (RL) to be able to maintain its designated zener voltage. Zener current will increase or decrease directly with voltage input changes. The zener current will increase or decrease inversely with varying loads. Again, the zener has a finite range of operation. Voltage regulator Voltage regulator VZ I = RL L V PS − V Z II = Ri IZ = II − IL The characteristics of the Zener diode determines VL. Zener diode diode ‐ analysis • Three types of Zener diode circuit analysis – Fixed VS and RL – Fixed VS and variable RL – Variable VS and fixed RL Zener diode diode as a Voltage regulator as a Voltage regulator 1. Assume zener diode in open circuit 2 Determine the voltage across the zener 2. Determine the voltage across the zener diode, VL 3 If V 3. If VL>Vz, zener diode zener diode ‘ON’ ON hence V hence VL=Vz 4. If VL<Vz, diode is not a voltage regulator and VL value remain value remain Voltage regulator Voltage regulator ‐ Fixed V Fixed VS and R and RL The applied dc voltage is fixed, as the load resistor. The analysis : 1. Determine the state of the Zener diode by removing it from the network and calculating the voltage across the resulting open circuit. Voltage regulator Voltage regulator 2. Substitute the appropriate equivalent circuit and solve for the desired unknowns. - For the on state diode, the voltages across parallel elements must be the same. VL=VZ The Zener diode current is determined by KCL: IZ = IR – IL The power dissipated by the Zener diode is determined by: PZ = VZ IZ - For the off state diode, the equivalent circuit is open-circuit. Voltage regulator Voltage regulator - Fixed VS and Variable RL Rs + Vs - Step 1- get the RLmin so that zener is on. RLVs VL = RS + RL RL min RSVZ = VS − VZ - if RL ≥ RLmin, zener diode ‘on’,, so that VL=VZ Step 2: Calculate the IZ using KCL: 2 condition 1. If RLmin , then ILmax and IZmin because of constant I1 2. If RLmax, then ILmin and IZmax Voltage regulator Voltage regulator I Z min or max = I1constant − I L max or min VS − VZ = I Where 1 RS and I L max ; Izmax taken from data sheet Izmin = 0, if not given VZ = RL min or RL max VZ = I L min Voltage regulator Voltage regulator Load regulation When RL = ∞ (open cct), load current is zero.All current pass through zener diode. When RL is connected, current is divided between diode and RL.As RL increases, IL decrease and IZ increases, and vice versa. Iz can decrease until Izmin, any lower diode will not able to regulate.At Izmin IL is maximum. Therefore, RL must be minimum. Total current through R is constant. Voltage regulator Voltage regulator Example on load regulation What is ILmax and Ilmin to maintain regulation? Wh i i i What is minimum R RL? Given rated value : 1mA < IZ < 50mA Solution When IL=0, (R ( L = ∞) , I ) Z =Izmax=IT IZ max = IT = VIN − VZ 24 − 12 = = 25.5mA R 470 This value is less than 50mA, RL can be removed without disturbing regulation. ILmax occurs when IZ is minimum IL max = IT − Iz min = 25.5mA A − 1mA A = 24.5mA A Minimum value of RL is RL min = VZ I L max = 12 = 490Ω 24.5mA Voltage regulator Voltage regulator - Variable VS and fixed RL Rs + Vs - St 1Step 1 gett the th VSmin so that th t zener is i on. ( R + RS )VZ RLVs VS min = L VL = RS + RL RL if VS ≥ VSmin, zener diode d ode will w ll ‘on’, on , so that VL=VZ Step 2: Calculate the IZ using KCL: 2 condition 1. if VSmin , then I1min and IZmin because of constant IL 2. if VSmax, thenI1max and IZmax Voltage regulator Voltage regulator I Z min or max = I1min or max − I Lconstant where VL IL = RL and I1min ; Izmax= Pzmax/Vz VS min − VZ = RS or VS max = I1max RS + VZ Voltage regulator Voltage regulator Line regulation What is the range of input voltage VIN if the zener diode is to maintain regulation with zener current regulation with zener current between 0.25mA and 100mA? Zener current range : Izmin = 0.25mA to Izmax = 100mA At minimum zener current, I At minimum zener current Izmin, VRmin =IzminR = (0.25m)(220) = 55 mV, But VR = Vin – Vz,; So Vin(min) = VRmin+Vz = 55m+10 = 10.055V At maximum zener current, Izmax , VRmax =IzmaxR = (100m)(220) = 22 V, But VR = Vin – Vz,; S Vin(max) = V So V ( ) VRmax+V Vz = 22+10 = 32 V 22 10 32 V Percent regulation Percent regulation Defination: Line regulation Load regulation g VNL – Output voltage at minimum load current (RL = ∞, I.e. IL = 0) VFL – Output voltage at maximum load current Zener limiting Zener diodes can used for limiting just as normal diodes. Recall p p in previous chapter studies about limiters. The difference to consider for a zener limiter is its zener breakdown characteristics.