* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
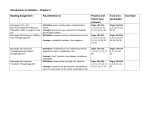
Download Your child has most likely come home using some math vocabulary
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
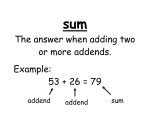
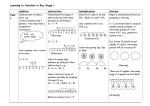
Common Core Vocabulary Your child has most likely come home using some math vocabulary that is unfamiliar to you. Use this page to find out what they are talking about! This page can also be a resource to you when there is unfamiliar vocabulary on homework assignments. Words are listed alphabetically. Addend: one of the numbers being added (Example: 3 is an addend in 3 + 9) Algorithm: number sentence (example 40,762 + 30,473 = 71,235) also referred to as "standard algorithm" Array: grouping objects into equal rows and columns (this models multiplication) Associated Ratio: the relationship in a ratio of the part to the part or the part to the total. (Example: In a ratio of 2 cups of red paint to 3 cups of blue paint, the associated ratio would be 2 cups of red paint to 5 cups of purple since the red and blue paint are used to make the purple which is the total) Base Ten Units: a.k.a place value units Commutative Property: being able to switch around the addends or factors in a number sentence without changing the value. Example: 4 X 2 and 2 X 4 (the order doesn't change the value) Convert: change (from one form or unit to another) Coordinate Plane: Count On: counting up from one addend to the total (example: 3+4... 3,4,5,6,7) Counting Path: the pattern used to count (a line drawn from object to object to count them) Decompose (decomposition): break down Example 1: 14= 10 + 4 OR 10 + 2 + 2 Example 2: (5 X 4) + (3 X 4)= 32 Difference: the answer to subtraction Digit: a numeral between 0 and 9 Distributive Property: the breaking apart or finding products of two smaller arrays to help find he product of a larger array. Expanded Form: a number expressed by each place value (Example: 100 + 30 + 5) Exponent: how many times a number is to be used in a multiplication sentence Exponential Form: writing a number using exponents Expression: a number sentence without an equal sign (Example: 2 + 5 or 3 X 7) Equation: 3 = 2 + 1 An expression that includes an equal sign. This is used interchangeably with number sentence. Equivalent: Equal to Factors: numbers that are multiplied to get a product (Example: the four in 4 X 2) Five Frame: a visual way to organize a number (this shows 3) Five Group Cards: image of up to 5 dots grouped per row to represent a number Five Group Drawing: Hand drawn groups of 5 dots. Used to model addition and subtraction problems. Can be drawn horizonally or vertically. 8-1=7 Hidden Partner: number pairs that make a given sum (Example: in the number 5, 2 and 3 are hidden partners) Make Ten Solutions: When adding, breaking an addend apart to make a ten and then adding to find the total. Midpoint: middle Multiplication/multiply: an operation showing how many times a number is added to itself. Number Path: number line used for counting Number Bond: visual way to break apart a number into part, part, whole Number Sentence: 3 = 2 + 1 This is used interchangeably with equation. Number Stairs: a visual way to count by stacking numbers Number Story: stories with add to or take from situations (a.k.a word problems) Partial Product: a strategy used for multiplying by using each place value and then adding these together. Example: 2 X 0.423 Percent: a rate per (or out of) 100. Perimeter: distance around the outside of a figure. Place Value: the numerical value that a digit has by the position of it in a number (Example: the value of 5 in the number 52 is 50) Place Value Disks: a way to represent a number (in regards to place value) using circles or dots Product: the answer to a multiplication problem Quantity: amount Quotient: the answer to a division problem Rate: how many units of one quantity there are for every 1 unit of the second quantity (for a proportional relationship between two quantities). Ratio: used to indicate that there is a relationship between two amounts (numbers must be positive and not zero) in the A:B format Rekenrek:(a.k.a an abacus) is a tool used for counting tens. Related Number Sentence: Example: 7 - 5 = 2 and 7 - 2 = 5 are related. (a.k.a's- turn arounds, go togethers and fact families) Represent: show RDW: Read, Draw, Write- a strategy used at all grade levels for solving word problems. Standard Form: a number written in the format: 135 (the typical way we see a number written) Sum: the answer to an addition problem (2 + 4 = 6) Tape Diagram: a visual bar diagram method for modeling problems Ten Counting: eleven is 1 ten 1; twelve is 1 ten 2; twenty is 2 tens, etc. Ten Frame: a visual way to organize groups of 10 into two rows or columns of 5. Unit: one segment (of a partitioned tape diagram, of a specific place value, etc.) Unit Rate: the numeric value of the rate (Example: in the rate 2.5 mph the unit rate is 2.5) Unknown: the "missing" number in a number sentence Value: how much Value of a Ratio: how much a ratio equals- (Example: 2:3 is the quotient of 2/3) Variable: unknown quantity in a equation shown with a letter (3 + n) Word Form: a number only in words (example: one hundred thirty-five)