* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Autonomic nervous system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
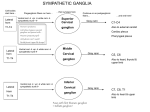
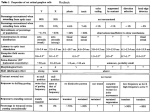
Autonomic nervous system (visceral nervous system): Is the large part of PNC, which innervated the smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, the glands and viscera. This system divided into two parts: 1-Sympathetic nervous system (Adrenergic nervous system) (thoraco-lumber). 2-Parasympathetic nervous system (cholinergic) (craniosacral in location) These two parts of the autonomic nervous system regulates the action of the viscera by their general opposite actions. Autonomic ganglion –are the centers of aggregation can be classified into: 1. Vertebral ganglion or paravertebral: these series of ganglion located along the ventrolateral side of the bodies of the vertebral. These ganglions with longitudinal interganglionic nerve fibers, constitutes the paired sympathetic trunks. 2. Collateral or prevertebral ganglion: it is located in proximity to the thoracic, abdominal and pelvic viscera or within their wall and found along the sympathetic trunk. 3. Terminal or peripheral ganglion- these ganglions of the cranial sacral cephalic region in relation to certain of the cranial nerves. Each portion of autonomic nervous system consists of the two nervous chains: 1-Preganglionic neuron: characteristic by aHas its cell body in the visceral efferent column of the brain and f the spinal cord. bIts fine mylinated axons. cPass to some autonomic ganglion where synapses occur. 2-Postganglionic neurons: a-the cell body located in ganglion or ganglia outside the brain and spinal cord. b-its unmylinated axons. c-extend from the ganglia to the visceral efferent. The autonomic system frequently divided on a pharmacological or functional basis to the (adrenergic fiber and cholinergic fiber) Adrenergic fibers: referred to the sympathetic system this is: 1-serves to protect the body in a crisis. 2- it serves the flight or fight response .(it stimulation causes the dilation of the pupil , increase heart rate, raises the blood pressure and increase the blood flow to the somatic muscles. Respiration increased and at the same time, peristalsis is inhibition.) 3-the general effect of sympathetic stimulation is the same as an injection of epinephrine in the blood stream. An epinephrine like substance, noradrenalin, is released at most post ganglion sympathetic terminals. *most of sympathetic fibers to the smooth muscles and sweat gland of the skin, however are cholinergic Cholinergic fibers: referred to the parasympathetic system 1. Stimulation of parasympathetic system usually acts to conserve the body (it is slows the heart, constrict the pupil, increase peristalsis, and empties the bladder and the rectum. 2. Acetylcholine is liberated at the terminals of most of the parasympathetic effectors neurons and act as transmitter at postganglionic parasympathetic terminals. The other different between the two portions of the autonomic nervous system: 1. The parasympathetic activity is more specific, discrete and local where as the sympathetic effect are wider and spread. 2. The preganglionic fibers in sympathetic is shorter than the postganglionic fibers. 3. The preganglionic fibers in parasympathetic are larger than the postganglionic fibers. Sympathetic system : 1. this system innervation is typically describe as thoracolumber in origin. 2. The thoracic division extend to the deep , central area , thoracic limb and part of the abdominal area. 3. The lumber division extend to the caudal abdominal and pelvic viscera and the pelvic limb and tail . 4. the nerve cells of the sympathetic system found in the gray intermediate lateral column of the spinal cord, in the thoracolumber region. 5. the axon of this cells leave spinal cord with the ventral root of the spinal nerve and continue in course with mixed nerve after that separated from the ventral root to form the one or more communicating rami( white ) which attached to vertebral autonomic ganglion which found along sympathetic trunk, this fibers called preganglionic fibers. 6. than that the fibers conduct with other cells which the axon leave it and conduct with spinal nerve again to form gray communicating rami ( postganglionic fibers which distributed with spinal; nerves branches . 7. therefore the sympathetic system consists of chain autonomic ganglion which connect with each other by fibers to form sympathetic chain or trunk which found on each side of ventral surface of the vertebral column and extend from base of skull to the pelvic cavity . 8. The ganglion located along the major abdominal blood vessels and in plexuses serve abdominal and pelvic viscera and are found more peripherally in thoracic , abdominal and pelvic cavities. 9. the sympathetic system subdivided into: a- cephalic part b- cervical part c- thoracic part d- abdominal part e-pelvic part. 1. Cephalic part : the fibers leave the cranial cervical ganglion to form plexus around external carotid artery and branches. This plexus called external carotid plexus which distributed in head. 2. Cervical part : on each side extend between the cervicothoracic and cranial cervical ganglion. Are designated as the cranial, middle , vertebral and caudal ganglion in domestic animals. a-Caudal cervical ganglion : found under the 1st rib, usually unite with 1st and 2nd thoracic ganglion to form the cervicothoracic ganglion called ( satellite ganglion ) between the 1st and 2nd intercostal space , from it arise the cervical sympathetic cervical trunk which pass cranially enclose opposition to vagus nerve to reach the cranial cervical ganglion, than that separated from vagus nerve and form cranial cervical ganglion emerge ranches which pass with blood vessels of the brain. The cervical sympathetic trunk and vagus nerves on each side bounded together as the vagosymphathetic trunk in common sheath. b- Cranial cervical ganglion: in fusion grayish –ping ganglion located ventral to the jugular foramen at the cranial extremity of each cervical sympathetic trunk. The cranial cervical ganglion lie enclose opposition to the internal carotid arteries. The nerves which arise from each side of ganglion include : 1-internal carotid 2- external carotid 3-jugular nerve 4- branch to the thyroid gland 5- guttural pouch 6- laryngeopharyngeal branches 7-branches joining the vagus m glossopharyngeal , hypoglossal , accessory and just cervical nerve. c-Middle cervical ganglion : found in the inlet of the thoracic cavity , from it arise the middle cervical nerve , which inter the cervical vertebral canal and gives branches at each intervertebral foramen ( which thin therefore continuous with spinal nerve)and innervated the muscles of the neck , blood vessels and glands. c-Vertebral or mediovertebral ganglion : is located at the cranial junction of cranial and caudal limb of the ansa subclavian medial to the origin of the vertebral artery. Nerve from it , may contribute to form adjacent arteries to the formation of the vertebral nerve and thoracic cardiac nerve, which innervated trachea , esophagus , great vessels and lung . 3-Thoracic part : extend caudally ventral to the costo-vertebral joints from the cervicothoracic ganglion to the crura of the diaphragm , and pass between the latter and psoas minor muscle to be continued by the abdominal part. It has thoracic ganglia which located at each intercostal space and partly on the head of the rib , they are flattened ,small , fusiform and more difficult to differentiated in the adult than in the young animals. a-The 1st and 2nd thoracic ganglion are unites with the caudal cervical ganglion to form the cervicothoracic ganglion. b-The thoracic spinal nerve are connected with the thoracic ganglion by white and gray rami communication. c-Thoracic sympathetic nerves give branches to the heart , great vessels , lung , esophagus , and thymus as well as forming abdominal splanching nerves. *Numerous small aortic nerve , pass ventrally from sympathetic chain and ramify on the thoracic aorta, forming around that vessels the thoracic aortic plexus. **Thoracic cardiac nerve : arising from left trunk between the 2 nd and 5th intercostals spaces , fine twig unite to form a large thoracic cardiac nerve. This nerve passes ventrally along the costocervical trunk and continues with the left subclavian artery to the heart. Thoracic nerves concur with cervical , cervicothoracic , vagus and recurrent cardiac informing the cardiac plexus which located dorsal to the base of the heart on concavity of the aortic arch and between the aortic arch and tracheal bifurcation. ***The greater splanching : arise by a series of roots derived from the 6 th or 5th to the 14th or 15th thoracic ganglia. It extends along the bodies of the vertebral media ventral to the thoracic trunk, then crosses the latter ventrally passes caudally between the crus of the diaphragm and the lateral border of the psoas minor and joins the celiac-mesenteric plexus. ****The lesser splanching nerve : is formed by roots derived from the last two or three thoracic ganglia. It runs caudally with the greater splanching nerve , but ends in the celiac- mesenteric , renal and adrenal plexuses . 4-Abdominal part : is the continues of the thoracic sympathetic trunk passes between the crura of the diaphragm and psoas minor muscle. It has: *The vertebral or Paravertebral ganglion : which called lumber ganglion and connect with the ventral roots of the lumber nerve by communicating branches. There are two large ganglia located in the dorsal part of the abdominal cavity adhere to the origin of the single blood vessel which extend in the digestive system in this origin theses are: 1-The celiac mesenteric ganglia ( celiac and cranial mesenteric ganglia ) are diffused mass situated on the dorsal wall of the abdominal cavity , are two in number right and left are situated on each side of the celiac and cranial mesenteric arteries. Each ganglia receive the greater splanching nerve of same side and give branches which innervated the visceral organ which found in the abdominal cavity . 2-The caudal mesenteric ganglion : is unpaired and is irregular satellite, it is situated at the origin of the caudal mesenteric artery. It is connected with the celiac-mesenteric ganglia by means of the intermesenteric plexus. It receive preganglionic fiber from ventral roots of the lumber nerve of sympathetic system. *The branches of the cranial celiac-mesenteric ganglia formed the : ((celiac , hepatic , celiac mesenteric , gastric , splenic , abdominal aortic , and renal plexuses.)) **The branches of caudal celiac-mesenteric ganglia formed the: ((caudal mesenteric, spermatic and utero-ovarian plexuses)) 1Pelvic part :is the continuation of the abdominal part inside the pelvic cavity and pass on pelvic surface of the sacral bone to the 3rd or 4th sacral vertebral. In this region divided into medial and lateral branch. Medial branch –connect in two side and passes caudally in tail with middle coccigeal artery. In this uniting region there is ganglion called ganglion impars , also in pelvic part found sacral ganglion beside the ventral foramen of the sacral bone , the branches of it connected with sacral nerves. Therefore the pelvic part contain—(sacral ganglion , communicating branches , transverse branches)these are formed the pelvic plexus which innervated the organ in pelvic cavity. The parasympathetic system : 1-The main autonomic ganglion in the head region are locates in relation to the oculumotor nerve and the several division of the trigeminal nerve. They are anatomically and functionally connected with brain by means of preganglionic fibers which leave the brain stem as part of cranial nerve III,VII, IX, and X. 2-the parasympathetic system is the cranial –sacral part of the autonomic nervous system and contains general visceral efferent fibers which originates in cranial nuclei of certain cranial nerves and in the sacral portion of the spinal cord. 3-the cranial out flow include fibers in the Oculomotor , facial , glossopharyngeal and vagus nerve , the 1st three mentioned nerves are distributed to the head region where as the vagus nerve supply autonomic fibers to the cervical , thoracic and abdominal visceral as far caudal as the transverse colon. 4- the parasympathetic preganglionic fibers which leave the spinal cord as part of the ventral roots of the sacral nerves . 5-the major ganglia in the cephalic region are anatomically and functionally connected with the brain stem via their preganglionic fibers arising from the various cranial nerves .these ganglia are : a-Ciliary ganglion : location : it is enclose proximity to the ventral division of the Oculomotor nerve . preganglionic fibers : receive from the Oculomotor nerve postganglionic fibers : supply motor enervation the sphincter pupillae and ciliary muscles of the eye . b- The otic ganglion : location: is a small stellate body lying on or near the medial surface of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve immediately outside the oval foramen , it is lateral to the cartilaginous portion of the auditory tube. preganglionic fibers : receive from the glossopharyngeal nerve postganglionic fibers : secrtomotor enervation the parotid gland . c-Mandibular ganglion : preganglionic fibers : receive from the lingual nerve and chorda tympani postganglionic fibers : enervation the sublingual and mandibular glands. d-The pterygopalatine ganglion: location : in the pterygopalatine fossa closely attached to the branches of the maxillary nerves. preganglionic fibers : receive from the facial nerve via greater petrosal nerve postganglionic fibers : are secretmotor to the salivary glands and glands of the nasal cavity and lacrimal gland. e- Terminal ganglion : preganglionic fibers : receive from the vagus nerve postganglionic fibers : supply heart , trachea and most of the intestine and abdominal viscera