* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Browning Reactions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
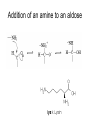
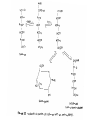
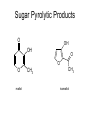
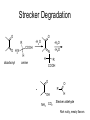
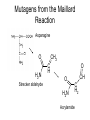
Browning Reactions FDSC400 Important Types of Browning • Enzymatic (polyphenoloxidase). Fresh cut vegetables, non-toxic, no flavor • Caramelization. Sugars at very high temperatures. • Lipid Browning. Polymerization of frying oils • Vitamin C Browning. Similar to Maillard • THE MAILLARD REACTION Maillard Browning • “the sequence of events that begins with reaction of the amino group of amino acids with a glycosidic hydroxyl group of sugars; the sequence terminates with the formation of brown nitrogenous polymers or melanoidins” – John deMan The Maillard Reaction • Occurs between reducing sugars and amines at high temperatures – Produces flavor – Produces color – Produces antioxidant products – Produces toxic products – Destroys nutrients (lysine) Addition of an amine to an aldose The Amadori Rearrangement DH – A Crucial Intermediate Amines Strecker aldehydes Polymerize Pyrolytic products Sugar Pyrolytic Products O OH OH O O O maltol CH3 CH3 isomaltol Strecker Degradation O O -H2O R O H2N -H2O COOH H N H amine dicarbonyl O -H2O ine N H H OH R COOH NH3 CO2 Stecker O R -H2O R COOH O R -H2O O -H2O COOH O OH NH3 CO2 H Stecker aldehyde Rich nutty, meaty flavors Mutagens from the Maillard Reaction Asparagine O H2N Strecker aldehyde CH2 O C H O H2N CH C H2 Acrylamide Control Steps • Rapidly accelerated by temperature • Significant acceleration at intermediate water activities • Sugar type – Pentose>hexose>disaccharide>>polysaccharide • protein concentration (free amines) • Inhibited by acid – amines are protonated – and used up, pH drops • Sulfur dioxide Inhibition by Sulfite SO3- DH DSH