* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WWII Begins September 1, 1939 – Germany invades Poland
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
The War That Came Early wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
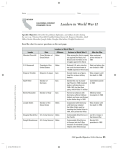
WWII Begins September 1, 1939 – Germany invades Poland • Non-Aggression Pact • Hitler & Stalin agree to invade Poland and not to attack each other December 8, 1941 America Joins WWII Which enemy should the US first concentrate their resources on? Why? Japan? Germany? Big Three: U.S. – Franklin D Roosevelt Great Britain- Winston Churchill Soviet Union – Joseph Stalin • Agree that Germany is the bigger threat • Joseph Stalin (U.S.S.R) asks for U.S. and England to invade Northern Europe • Churchill thinks they do not have the resources for such an attack. July 1942 Allies invade North Africa • Patton vs. Rommel – Tanks become important part of combat • Stalin not happy – Why? War in the Soviet Union • Hitler invades all the way to Stalingrad and Moscow(pg.431) – Kills much of the population along the way • Of the almost 50 million people killed in WWII almost half were from the Soviet Union – Half of those were civilians – Battle of Leningrad est. 1.6 – 2 Million Dead • Early 1942 Stalin begins to push Germans back Axis Military Civilian Total Germany 3,500,00 700,000 4,200,000 Japan 2,000,000 350,000 2,350,000 Romania 300,000 160,000 460,000 Hungary 140,000 290,000 430,000 Italy 330,000 80,000 410,000 Other Nations 312,000 106,000 418,000 Allied Military Civilian Total Soviet Union 10,000,000 10,000,000 20,000,000 China 2,500,000 7,500,000 10,000,000 Poland 100,000 5,700,000 5,800,000 Yugoslavia 300,000 1,400,000 1,700,000 France 250,000 350,000 600,000 Czechoslovakia 200,000 215,000 415,000 United States 400,000 0 400,000 Great Britain 326,000 62,000 388,000 Other Nations 199,000 465,000 664,000 Est. Total Deaths 20,858,000 27,372,000 48,231,000 Operation Overlord • Invasion of Northern Europe becomes priority in early 1943 • General Dwight D. Eisenhower put in charge of Allied Forces in Europe. • 2 Million U.S Soldiers based on Southern England Operation Overlord in Actions (D-Day) June 6, 1944 – July 25, 1944 • 1st Invasion – – – – – 150,000 soldiers 1500 Tanks 5300 Ships 12000 Aircraft 24000 Airborne Troops • Over 400,000 people killed in battle Germany caught between 2 fronts • Allied bombing from Western front – Berlin 25,000 killed – Dresden 60,000 killed • Soviet invasion from Eastern front – June – Sept. 1944: 1.3 Million German soldiers killed. Hitlers last chance • Battle of the Bulge (Dec. 16 1944) – Sends bulk of troops into Belgium – Attempting to: • Split Allied troops • Cut off supplies – Allied troops vastly outnumbered and trapped by speed. – Jan. 1945 Allies push back and win Allied forces invade Germany • Soviet Union takes Berlin from the east • Allied forces invade from the West • Meet at Elbe River • Results: – April 29, 1944 Hitler commits suicide – Germany soon signs peace • May 7, 1945: V-E Day (Victory in Europe) – Troops learn about the Holocaust WWII effects the World