* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 3 class
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
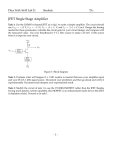
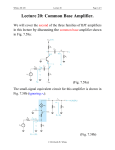
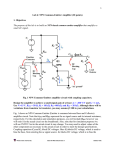
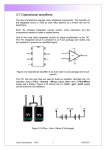
UNIT III JFET and MOSFET Amplifiers OUTLINE • Small signal Analysis of JFET amplifiers • Small signal Analysis of MOSFET and JFET • BICMOS cascode Amplifier FET ( Field Effect Transistor) • • Unipolar device i. e. operation depends on only one type of charge carriers. Voltage controlled Device (gate voltage controls drain current). • Very high input impedance (109-1012 ). • Source and drain are interchangeable in most Low-frequency applications. • Low-power consumption. • • Less Noisy as Compared to BJT. Very small in size, occupies very small space in Ics. Types of Field Effect Transistors (The Classification) » FET JFET MOSFET (IGFET) Enhancement MOSFET n-Channel EMOSFET p-Channel EMOSFET n-Channel JFET p-Channel JFET Depletion MOSFET n-Channel DMOSFET p-Channel DMOSFET The Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) Figure: n-Channel JFET. JFET • There are two basic configurations of junction field effect transistor, the N-channel JFET and the P-channel JFET. • The N-channel JFET’s channel is doped with donor impurities meaning that the flow of current through the channel is negative (hence the term Nchannel) in the form of electrons. SYMBOLS Gate Gate Gate Source n-channel JFET Drain Drain Drain Source n-channel JFET Offset-gate symbol Source p-channel JFET Small signal Analysis • The coupling capacitors bypass capacitor are short circuitED • Short the DC supply voltage • Replace the FET with the hybrid-p model Common source JFET Small signal -Common source JFETcontd… Small signal -Common source JFETcontd… Source Follower JFET Small signal equivalent-Source Follower JFET Av= gmRs/(1+gmRs) Common Gate JFET Small signal model-Common Gate JFET AV= -gmRd Rin=1/gm Self bias of JFET Small signal equivalent -Self bias of JFET-contd… Enhancement MOSFET showing channel length L and channel width W. MOSFET- SYMBOL Small-signal equivalent circuit for FETs. FET small-signal equivalent circuit that accounts for the dependence of iD on vDS. MOSFET Characteristics Common source Amplifier -MOSFET Small signal -Common source Amplifier -MOSFET For drawing an a c equivalent circuit of Amp. •Assume all Capacitors C1, C2, Cs as short circuit elements for ac signal •Short circuit the d c supply •Replace the FET by its small signal model Analysis of CS Amplifier A C Equivalent Circuit Simplified A C Equivalent Circuit Analysis of CS Amplifier-contd… v Voltage gain, A o v v gs Input imp., Z v i R g v R o A v o L v o v 1 G 2 m gs L g R , R R r m L gs in R R R L D d Out put imp., Z r R o d D r R d D r R d D Small Signal ‘T’ Model : NMOSFET Small Signal Models ‘T’ Model Analysis of CS Amplifier with Potential Divider Bias Av gm(rd || RD) This is a CS amplifier configuration therefore the input is on the gate and the output is on the drain. Zo rd || RD Av gm(rd || RD) Av gmRD, r 10 R d Zi R1 || R2 Zo RD D rd 10RD An Amplifier Circuit using MOSFET(CS Amp.) A small signal equivalent circuit of CS Amp. Common Source Amplifier (CS) • Signal ground or an ac earth is at the source through a bypass capacitor • Not to disturb dc bias current & voltages coupling capacitors are used to pass the signal voltages to the input terminal of the amplifier or to the Load Resistance • CS circuit is unilateral – Rin does not depend on RL and vice versa Small Signal Hybrid “π” Model : (CS) vo vo vgs Gv vsig vgs vsig RG vgs vsig RG Rsig Small Signal Hybrid “π” Model : (CS) Rin RG R o ro || RD vo g m v gs ro || RD || RL RG vo Gv g m ro || RD || RL vgs R R G sig Small-signal analysis performed directly on the amplifier circuit with the MOSFET model implicitly utilized Rin RG R o ro || RD RG vo g m ro || RD || RL v gs RG Rsig Common-source amplifier with a resistance RS in the source lead The Common Source Amplifier with a Source Resistance • The ‘T’ Model is preferred, whenever a resistance is connected to the source terminal. • ro (output resistance due to Early Effect) is not included, as it would make the amplifier non unilateral Small-signal equivalent circuit with ro neglected. i vg 1 RS gm Small-signal Analysis. Rin RG Ro RD Voltage Gain : CS with RS vo vo vgs vi Gv vsig vgs vi vsig vo g m v gs RD || RL 1 gm vi v gs vi 1 1 g m RS RS gm RG vi vsig RG Rsig RG g m RD || RL vo Gv vsig RG Rsig 1 g m RS Common Source Configuration with Rs • Rs causes a negative feedback thus improving the stability of drain current of the circuit but at the cost of voltage gain • Rs reduces id by the factor – (1+gmRs) = Amount of feedback • Rs is called Source degeneration resistance as it reduces the gain Small-signal equivalent circuit directly on Circuit BJT / MOSFET Rin RB || r , 1 Rin RG Rout ro || RC Rout ro || RD vo RB || r ro || RC || RL gm vsig RB || r Rsig vo RG ro || RD || RL gm vsig RG Rsig Common Source Amplifier (CS) Summary • Input Resistance is infinite (Ri=∞) • Output Resistance = RD • Voltage Gain is substantial Rin RG R o ro || RD RG vo g m ro || RD || RL R R v gs sig G MOSFET -Source follower . Small-signal ac equivalent circuit for the source follower . Equivalent circuit used to find the output resistance of the source follower. Common-gate amplifier. Small signal-Common Gate Small-signal ‘π’ models for the MOSFET Voltage swing limitation • Up swing limited by transistor going in to cut off • Vout (max)= VDD • Lower swing limited by MOSFET entering in to linear region • Vou(min)-VGG-VT A common-gate amplifier based on the circuit Common Gate (CG) Amplifier • The input signal is applied to the source • Output is taken from the drain • The gate is formed as a common input & output port. • ‘T’ Model is more Convenient • ro is neglected A small-signal equivalent circuit A small-signal Analusis : CG vi vi 1 Rin ii g m vi g m Rout RD A small-signal Analusis : CG vo vo vi Gv vsig vi vsig vo g m vi RD || RL 1 gm vsig Rin vi vsig vsig 1 Rin Rsig 1 g R m sig Rsig gm vo g m RD || RL Gv vsig 1 g m Rsig Small signal analysis directly on circuit The common-gate amplifier fed with a currentsignal input. Summary-CG • CG has much higher output Resistance • CG is unity current Gain amplifier or a Current Buffer • CG has superior High Frequency Response. . A common-drain or source-follower amplifier Small-signal equivalent-circuit model Small-signal Analysis : CD A common-drain or source-follower amplifier :output resistance Rout of the source follower. Rout 1 1 ro || gm gm A common-drain or source-follower amplifier. : Smallsignal analysis performed directly on the circuit. Common Source Circuit (CS) Common Source Circuit (CS) With RS Common Gate Circuit (CG) Current Follower Small Signal Model MOSFET : CD Small Signal Analysis CD 1/gm gmvsg D Solution Small Signal Analysis : Input Resistance 1/gm Ig=0 gmvsg Rin Rin D Solution Small Signal Analysis : Output Resistance Itest 1/gm ID IG= 0 I R gmvsgD 0V D Vtest Rout Rout Vtest I test I test I RC I D I RD Vtest RD Vtest ID 1 gm Rout Vtest 1 RD || Vtest Vtest gm RD 1 / g m Solution Small Signal Analysis : Voltage Gain + vsg - 1/gm - + vi - vo vo vsg vi vsig vsg vi vsig D gmvsg vo + vo g m RD || RL vsg Solution Small Signal Analysis : Voltage gain + vsg 1/gm + vi gmvsg D - vsg vi 1 1 gm gm RD || RL Solution Small Signal Analysis : Voltage Gain 1/gm + vi gmvsg D - vi vsig Rin Solution Small Signal Analysis : Voltage Gain vo vo vsg vi vsig vsg vi vsig vsg vi 1 1 gm gm RD || RL vo g m RD || RL vsg vo g m(RD||R L ) 1 vsig vi vsig Then 1 gm gm (RD || RL ) vo (RD||R L ) 1 (RD || RL ) vsig gm Solution Small Signal Analysis : Voltage Gain 1/gm + vi gmvsg + - vo vo vi vsig vi vsig D vo RD || RL 1 RD || RL vi gm vi vsig vo RD || RL 1 RD || RL vsig gm BICMOS BICMOS -contd… • Combining the high gain of BJT and infinite impedance of MOSFET will lead to BiCMOS differential amplifier design. • Rs = typical 100 KW • BICMOS cascode amplifier has overall voltage gain of C-S, but with frequency response comparable to CB Amplifier. BICMOS -contd… • The basic idea is to combine the high Rin and large transconductance (g m) of a commonsource (common-emitter) amplifier with the currentbuffering property and superior high-frequency response of the common-gate (common-base) circuit BICMOS -contd… • In response to input signal voltage vi, the CS transistor Q1 conducts a current signal gm1 vi in its drain terminal and feeds it to the source of the CG transistor Q 2 (cascode transistor). • Q 2 passes signal to its drain and to the load RL. Q 2 acts as a buffer, presenting low Rin to the drain of Q1 and providing high Rout at output.