* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MS Word
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
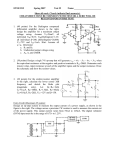
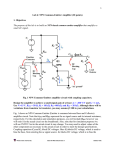
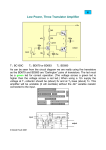
Name ______________________________ ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 3 (Fall 2016 – Due Monday, September 26, 2016) Problem 1 (25 points) A common-emitter amplifier uses a BJT with current gain = 100 when biased at IC = 0.5 mA. It has a collector resistance of RC = 10 k. (a) Calculate Rin, Ro and AVO. (b) The amplifier is driven with a signal source vsig has resistance Rsig = 10 k and has a load resistance RL = 10 k connected to the output terminal. Calculate both AV and GV . Page (d) Continuing on with part (c) above, what peak-to-peak output voltage appears across the load resistor RL? 1 (c) If the peak-to-peak voltage of a sinusoidal signal across the base-emitter junction is limited to 5 mV, what signal source voltage vsig is allowed? Problem 2 (15 points) A MOSFET connected in a common-source configuration has transconductance gm = 5 mA/V (mS). When a source resistor RS is connected to the source terminal, the effective transconductance g’m is reduced to 2 mA/V (mS). Estimate the value of this resistor RS. [Note: Source resistor RS is not bypassed with a capacitor.] Problem 3 (20 points) A bipolar common-gate (CG) amplifier is operated with a load resistance of RL = 10 k, a collector resistance of RC = 10 k and a signal source resistance of Rsig = 50 . (a) What collector current IC will give an input resistance of Rin = 50 ? Page 2 (b) What is the resulting overall voltage gain assuming 1 (i.e., unity)? (c) For the common-base amplifier shown schematically below, Find the output voltage vo if Rsig >> re and 1. [Remember that re is the emitter resistance (See page 404 of Sedra & Smith).] Problem 4 (20 points) An emitter follower (i.e., common-collector) stage is operating at a collector current bias of 0.5 mA and is used to connect a 10 k source resistance to a 1k load resistance. Assume the nominal current gain of the transistor to be 100. Page 3 (a) What output resistance Rout is obtained at the emitter follower’s output and what is its overall voltage gain Gv? (b) If is reduced to 50 (from 100), find the corresponding Rout and Gv values. Problem 5 (20 points) Two identical common-emitter gain stages are cascaded together. The collector terminal resistance is identical for both stages, namely, RC1 = RC2 = 10 k. The first stage is driven from voltage source vsig having source resistance Rsig = 10 k. A load resistance of RL = 10 k is connected to the collector of the second stage. Both BJT transistors (i.e., both stages) are biased at IC = 0.25 mA and both have a current gain = 100. (a) Sketch the small-signal equilvalent circuit for the overall amplifier. Label the important voltages. Page 4 (b) Calculate the overall voltage gain, v02/vsig.