* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Union Dissolves
Blockade runners of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Conclusion of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fort Fisher wikipedia , lookup
East Tennessee bridge burnings wikipedia , lookup
Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Capture of New Orleans wikipedia , lookup
Anaconda Plan wikipedia , lookup
Economy of the Confederate States of America wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Kentucky in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Lost Cause of the Confederacy wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Secession in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Confederate privateer wikipedia , lookup
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Alabama in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Virginia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
South Carolina in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
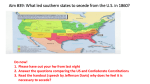
• John Brown’s raid on Harpers Ferry was a turning point for the South. Southerners feared an African American uprising and were angered that Northerners would arm them and encourage them to rebel. • Republicans renounced John Brown’s raid, but many Southerners blamed the Republicans since they opposed slavery. • In 1859 the Democratic Party was torn apart by the debate over slavery in the western territories. Southern Democrats upheld the Dred Scott decision and supported slaveholders’ rights in the territories. • They wanted a federal slave code for the territories. • Northern Democrats supported popular sovereignty. • The Democratic Party could not agree on a candidate for the 1860 election. Northern Democrats chose Stephen A. Douglas, who supported popular sovereignty. • Southern Democrats chose John C. Breckenridge of Kentucky. -vice president at the time. -supported the Dred Scott decision and a federal slave code for the western territories. • • • • The Constitutional Union Party was formed by people who wanted to uphold the Constitution and the Union. Their candidate was former Tennessee senator John Bell. The Republican candidate was Abraham Lincoln. The Republicans campaigned against slavery in the western territories, against John Brown’s raid, and for the right of the Southern states to preserve slavery within their borders. Lincoln tried to appeal to as many people as he could by avoiding any radical stances • Lincoln won the election. • The South saw his election as a victory for the abolitionists. • South Carolina was the first state to secede. • By February 1861, six more states in the Lower South voted to secede. • • Seceding Southern states seized federal property in their states. Only a few places remained in the Union’s hands, including Fort Sumter in Charleston Harbor. Crittenden’s Compromise, by Senator John J. Crittenden of Kentucky, suggested several amendments to the Constitution to try to compromise with seceding states and save the Union. The amendments would guarantee slavery where it already existed. It would reinstate the Missouri Compromise line, extending it to California. Slavery would be banned north of the line and protected south of the line. (The compromise did not pass) A peace conference was held in Washington, D.C., but members failed to agree on a plan to save the Union. No secessionist states attended the conference. Seceding states met, and on February 8, 1861, declared themselves to be the Confederate States of America, or the Confederacy. The Confederate Constitution was similar to the U.S. Constitution except it stated that each state was independent and it guaranteed the existence of slavery in the Confederacy. It also banned protective tariffs and limited the term of the presidency. Jefferson Davis of Mississippi was chosen president of the Confederacy. How was John Brown’s raid on Harpers Ferry a turning point for the south? How were the Democrats divided in this election? Describe the Republican campaign/goals. Who won the election? What was the southern reaction? What was the purpose of the Crittenden’s Compromise What did the states that seceded call themselves? Who was their president? 1. Southerners started to believe that the North was not only against slavery but taking actions to abolish it with the use of violence 2. Southern Democrats upheld Dred Scott decision and wanted specific slave codes and for slavery to be allowed wherever slave owners want them. Northerners believed in popular sovereignty 3. The Republicans campaigned against slavery in the western territories, against John Brown’s raid, and for the right of the Southern states to preserve slavery within their borders. The Republicans also wanted higher tariffs, a new homestead law for western settlers, and a transcontinental railroad. 4. Abraham Lincoln won – southerners saw this a win for the abolitionists and thus began to secede from the Union 5. Crittenden’s Compromise was to try to save the Union by negotiating with southern states 6. Seceding states declared a new nation called The Confederacy with Jefferson Davis as their president In his inaugural speech, Lincoln told seceding states that he would not interfere with slavery where it existed, but he said, “the Union of these States is perpetual.” He also said that the Union would hold on to the federal property in the seceding states. Lincoln announced plans to resupply Fort Sumter in Charleston Harbor. • President Jefferson Davis of the Confederacy ordered an attack on the fort. • After hours of fighting, the Union commander surrendered. • This was the beginning of the Civil War. • President Lincoln asked for 75,000 volunteers to serve in the Union army. • The Upper South seceded, beginning with Virginia. • • • • The capital of the Confederacy immediately was changed to Richmond, Virginia. North Carolina, Tennessee, and Arkansas also seceded. Lincoln did not want the border states to secede, especially Maryland. Since Virginia had seceded, he did not want Washington, D.C., to be surrounded by Confederate territory. Martial law (military control) was imposed in Baltimore to prevent Maryland’s secession. • • • • Under martial law, the military takes control of an area and suspends certain civil rights. Kentucky was important to the Union because it controlled the Ohio River’s south bank. Kentucky remained neutral until Confederate forces invaded it. Then Kentucky’s legislature voted to stay in the Union. Missouri voted to stay with the Union, but it needed the support of federal forces. 1. Why did Southerners blame the Republicans for John Brown’s Raid? 2. How was the Democratic Party torn apart by the debate over slavery? 3. Describe the Republican campaign. 6. Describe the new Constitution of the Confederacy. 4. Why did South Carolina secede after Lincoln’s victor? 5. Explain what it was and the elements of the Crittenden’s Compromise. 7. Why did Jefferson Davis order an attack on Fort Sumter in South Carolina? 8. How did Lincoln prevent Maryland from seceding? 9. What might have caused Kentucky to choose the Union over the Confederacy? 10. List 5 Union States, and 5 Confederate states. Next to each slide in your Powerpoint print out packet, summarize each slide in your own words. Use the textbook to clarify any notes you don’t understand. You may work with a partner to do so or on your own.