* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1: IntroductioN and The Five Themes of Geography
Geopolitics wikipedia , lookup
Location-based service wikipedia , lookup
Environmental determinism wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Royal Geographical Society wikipedia , lookup
Department of Geography, University of Kentucky wikipedia , lookup
Children's geographies wikipedia , lookup
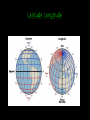
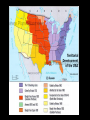
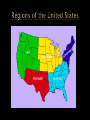
Part 1: Introduction and The Five Themes of Geography Upon completion of this unit, TSWBAT: 1. Define what geography is 2. Explain the five themes 3. List different fields and subfields of geography. 4. Explain the two types of geography-physical and human. 5. Discuss the six essential elements of geography. What does it mean to you? WASHINGTON (CNN) – After years of combat, nearly two-thirds of Americans aged 18 to 24 still cannot find Iraq on a map. Five years after Hurricane Katrina devastated New Orleans and the Gulf Coast, 33 percent could not point out Louisiana on a U.S. map. Geography is a method, not a body of knowledge. Geography is not just the location of countries or states, but also the study of the Earth’s natural systems. Geographers are people who study how the natural environment influences people, how people’s activities affect Earth, and how the world is changing. The term geography was coined by Eratosthenes, a follower of Aristotle, in the third century B.C.! The term spatial comes from the noun “space”the earthly, terrestrial space. Geography is divided into two main brancheshuman geography and physical geography. Human geography is the study of the distribution of the world’s people. Physical geography focuses on the Earth’s natural environment. Perspective –or the way a person looks at something-is a very important part of studying geography. Subfields of Physical Geography Meteorology The study of weather Cartography The study of maps and mapmaking Biogeography The study of the spatial patterns of living things Climatology The study of climate, weather conditions averaged over a period of time Oceanography The study of the oceans. It is also called oceanology and marine science. Hydrology The study of water throughout the Earth Location is divided into two parts-absolute location and relative location. Absolute location, or specific location, is often indicated by a physical address. For example, the absolute location of the Empire State Building is: 350 5th Ave New York, NY 10118 The relative, or general location, is indicated by stating where something is located in relation to something else. For example, we would say that Bel-Air Mall is located at I-65 and Airport Blvd. This is a description of what the place (location) is like. In this theme, we describe the physical as well as the human characteristics of the place. For example, when describing Denver, Colorado, one might say: Physical: Denver is located in the heart of the Rocky Mountains. The climate is extremely cold in the winter with high amounts of snowfall and bitter cold temperatures. When discussing, human characteristics of a place, one may describe Mobile is a coastal city on the Gulf of Mexico that has large seafood industry. Other crops include cotton, corn, strawberries, potatoes, and watermelon. One could even mention the Azalea Trail Run and the Azaleas, Mardi Gras, and it is generally a conservative city. This is where the people and the environment interact and work together. This theme is divided into three parts: 1. How people have been changed by the environment. 2. How the environment has been changed by people. 3. How people depend on the environment. This includes the movement of people, things, such as goods, as well as communications (the movement of ideas). We can describe the type of communications a place has and the main forms of transportation, as well as what goods are exported and imported. These all come under the heading of movement. Regions are areas that can be grouped together by a set of things special to that region. We have countries, ruled by governments, areas speaking the same language, or having the same religion, and we have areas served by a particular service, such as a school district. For example, the Southeast is considered a region. The Pacific Northwest and the Southwest are other regions in the United States 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The World in Spatial Terms Places and Regions Physical Systems Human Systems Environment and Society The Uses of Geography