* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Circuits – Resistors in Parallel
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
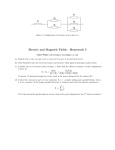
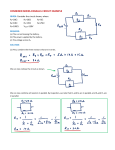
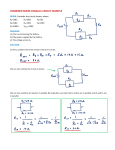
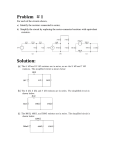
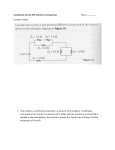
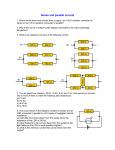
Name _______________________________ Date ____________ Period _____ Electric Circuits – Resistors in Parallel 1. You are given 2 different resistors: R1 = 30 Ω, R2 = 15 Ω. You also have access to a 6 V battery. Please determine the following: a. the equivalent resistance when all resistors are connected in Parallel; b. the total current IT for the circuit; c. the voltage across each of the resistors; d. the current through each of the resistors. e. the power dissipated by each resistor, and by the entire circuit. a) 10 Ω; b) 0.6 A; c) 6 V; d) 0.2 A, 0.4 A; e) 1.2 W, 2.4 W, 3.6 W 2. You are given 3 different resistors: R1 = 300 Ω, R2 = 200 Ω, R3 = 120 Ω. You also have access to a 12 V battery. Please determine the following: a. the equivalent resistance when all resistors are connected in Parallel; b. the total current IT for the circuit; c. the voltage across each of the three resistors; d. the current through each of the three resistors. e. the power dissipated by each resistor, and by the entire circuit. Physics Simple Parallel Circuits Bradshaw Name _______________________________ Date ____________ Period _____ a) 60 Ω; b) 0.2 A; c) 12 V; d) 0.04 A, 0.06 A, 0.1 A; e) 0.48 W, 0.72 W, 1.2 W, 2.4 W 3. You are given 4 different resistors: R1 = 100 Ω, R2 = 200 Ω, R3 = 300 Ω, and R4 = 400 Ω. You also have access to a 24 V battery. Please determine: a. the equivalent resistance when all resistors are connected in Parallel; b. the total current IT for the circuit; c. the voltage across each of the resistors; d. the current through each of the resistors. e. the power dissipated by each resistor, and by the entire circuit. a) 48 Ω; b) 0.5 A; c) 24 V; d) 0.24 A, 0.12 A, 0.08 A, 0.06 A; e) 5.76 W, 2.88 W, 1.92 W, 1.44 W, 12 W Physics Simple Parallel Circuits Bradshaw