* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The forest floor - South america unit of work
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
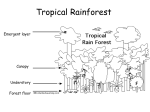
The Amazon Rainforest The world's ancient forests are in trouble. Only one fifth of original forest cover globally remains in large tracts, and almost half of that is under threat from activities such as mining, agriculture and, most importantly, commercial logging. The Amazon Rainforest, also known as the Amazon Jungle, is located in South America in an area known as the Amazon River basin. The Amazon Rainforest is the largest rainforest in the world and makes up about half of the planet’s rainforest space. According to scientists, the Amazon Jungle was created millions of years ago when the Amazon River changed direction. The Amazon Rainforest is also one of the world’s largest eco-systems, containing one of the most diverse array of species on Earth. The forest floor The rainforest floor is not crowded. It is often dark and humid due to constant shade from the canopy’s leaves. Despite its constant shade, the rainforest floor is an important part of the forest ecosystem. The forest floor is where decomposition takes place. Decomposition is the process by which fungi and microorganisms break down dead plants and animals and recycle essential materials and nutrients. There are many different animals and plants that live on the forest floor. Plants of the forest floor. Plants of the forest floor Saprophytes are the organisms that act as the rainforests decomposers. Many saprotrophs are so small, called microbes, that they cannot be seen with the naked eye. Buttressed roots, grow out from the base of the trunk sometimes as high as 15 ft above the ground. Epiphytes, or air plants, grow everywhere but can be found mainly on the branches, trunks, and even the leaves of trees. Bromeliads have thick waxy leaves which form a bowl shape in the centre for catching rainwater. Strangler trees use another tree to grow around. The seed is dropped from animals. It grows quickly and suffocates the host tree leaving a tall upright strangler which is hollow in the middle. Most stranglers are members of the fig family. Plants of the forest floor Lianas are a type of climbing vine found throughout tropical rainforests. Orchids comprise one of the most abundant and varied of flowering plant families. There are over 20,000 known species Carnivorous plants are adapted to obtain nutrients from animal matter. The best known of these is probably the Venus fly trap, but more impressive is the pitcher plant Nepenthes rafflesiana, found in southeast Asia. This plant grows to 30 feet tall and may have pitchers 12 inches in length, usually crammed full of digested insects. Mangroves grow in wet, muddy soil at the water's edge which can be subject to tides and flooding. Animals of the forest floor. Scorpions prey on insects and some other small animals. The have two venom glans used for hinting and self defence. Their “sting” is on the tip of their tail. Anteaters a mostly solemn animals . They use their long curved claws to rip open ant and termite nets. Their tongue extends to a length greater than their head. Tapirs look something like pigs with trunks, but they are actually related to horses and rhinoceroses they are a large herbivorous mammal. Army ants are aggressive and are predators for many living things. They use their mandibles to slice their prey. While doing this they spread a dissolving acid which melts the muscles and tendons. The ants eat everything that does not run or fly away in time. The Arapaima is native to the Amazon Basin. They are the largest freshwater fish of South America, and among the largest freshwater fish in the world. The diet of the arapaima consists of fish, crustaceans, and even small land animals that walk near the shore. The Matamata is a large, sedentary turtle with a large, triangular, flattened head. It lives in fresh water and is a carnivorous being. It eats small fish. Caiman’s have a narrower body than alligators and crocodiles. They live only in the Central and South America in swampy mangrove areas. The caiman is carnivorous it eats mainly fish but sometimes hunts small mammals, birds and insects. Piranha’s are known for their sharp teeth, powerful jaws, and uncontrollable appetite for meat. Piranhas are indigenous to the Amazon basin. Piranhas are vicious and have been known to attack humans. There have been deaths related to this. Their teeth are used by natives to make tools and are also a food source. The Jaguar is the third-largest feline This spotted cat most closely resembles the leopard physically, although it is usually larger and of sturdier build and its behavioural and habitat characteristics are closer to those of the tiger. The jaguar enjoys swimming and usually lives near water. It is at the top of the food chain and preys on animals such as adult caimans, deer, tapirs, dog and sometimes even anacondas. They also eat small creatures such as frogs, mice, birds, sloths, monkeys as well as some other animals. An Anaconda is the largest snake in the world and is found in tropical South America. Anacondas can reach 30 feet long. They can stay under water for 10 minutes. They eat a range of things such as turtles, fish, pigs jaguar and deer, along with a range of other things. The Understory The Understory The understory is hot, damp, and the air is still. This part of the rainforest is under the leaves but above the ground. The understory is a tangle of shrubs, young trees, palms and woody plants that can grown in the shade of the taller trees. There is a small amount of light within the understory. The leaves of many of the plants are very large, so that they can absorb or soak in as much sunlight as possible. The plants in this layer of the forest hardly ever grow higher than twelve feet. Many houseplants are found in this part of the rainforest, these plants can live in your living room as well as the understory because both places get little sunlight. Plants of the understory Philodendrons are a common house plant but are also found widely in the rainforest. They are a flowering plant with large leaves and can come in a variety of shapes, sizes and colours. Prayer Plants have small flowers clustered leaves which are flat during the day and they are folded and stand up right at night. There are a number of different species and the leaf patterns vary. Zebra Plants are native to Brazil. They grow into up right shrubs. They need medium light to grow well which is why the understory is a perfect environment for them. They rarely flower but with prolonged light they can. Peace Lilies are an evergreen plant with large leaves. They do not need a lot of water or sunlight to survive. While it is pretty, the peace lily can be toxic to humans and animals if ingested. It can also cause skin irritation. Animals of the understory Poison dart frogs can be blue, yellow, red or green. Their colours warn predators away. One touch of their skin can kill. The Green Tree Boa is a non venomous snake and feeds mainly on small mammals. They have slow metabolisms which means they can go several months without eating. The Boa Constrictor is not venomous but it is just as deadly, as it will wait for its prey and ambush it. It will first strike at the prey, grabbing it with its teeth; it then proceeds to constrict the animal until it is dead. The Boa Constrictor comes in many colour variations’ but it is highly distinctive. Fruit Bats can also be referred to as Flying Foxes. These bats have large eyes and they also have excellent vision. They do not eat fruit as such, they will crush the fruit with their sharp teeth and consume the nectar. The Kinkajou also know as the honey bear are omnivorous which means they can eat meat and plant products, however they mainly eat fruit and plants. The Margay is a small cat native to Central and South America and is listed as near threatened. This cat eats small mammals (sometimes including monkeys), birds, eggs, lizards and tree frogs. They prefer to spend most of their life in the trees, but also travel across the ground, especially when moving between hunting areas Blue tailed Iguanas can grow between 4 and 7 feet in length and are one of the rarest lizards in the world. They eat mainly leaves, fruit, and flowers, but occasionally insects, eggs or small vertebrates. Spider monkeys live in the tropical rain forests of Central and South America. They find food in the treetops and feast on nuts, fruits, leaves, bird eggs, and spiders. They can be noisy animals and often communicate with many calls, screeches, barks, and other sounds. Coatimundi’s are omnivores and can live off meat and plant products, They are found in North and South America and are related to the raccoon. They are great climbers which is why they are often found in the under story. The Canopy The Canopy The trees in this layer can grow as high as 100 feet. They form a green roof over the forest below. This roof is like an umbrella or canopy. The canopy is the busiest part of the rainforest. The leaves, flowers and fruit that grow there provide food for monkeys, birds, insects and other animals. The canopy protects the ground from the sun and light rain. Very heavy rains will get to the ground. Some animals up there never go to the forest floor. Many butterflies, and birds live in the canopy. Many of the leaves on the plants in the canopy are pointed, so that the rain can run off the tips of the leaves. These drip tips keep the leaves dry and free of mould. It is very hard to study the rainforest canopy, because it's so hard to reach. So scientists have built walkways up in the trees so that they can just walk around up there. Animals of the Canopy The Golden Lion Tamarin lives in South America and is an endangered species due to logging and deforestation on Brazil’s Atlantic coast. Golden lions live primarily in the trees. They sleep in hollows at night and forage by day while traveling from branch to branch. Long fingers help them stay high and they eat things such as insects, fruit, lizards, and birds. Howler Monkeys are found in tropical Central and South America. They can use their tail as an extra arm to grip or even hang from branches, this is often helpful as they rarely leave the canopy. They eat primarily fruit and nuts and their good senses can smell food from almost 2km away. Sloths are classified as folivores (eating from specific trees), as the bulk of their diets consist of buds, tender shoots, and leaves. Sloths are found primarily in South America and are less likely to survive outside of this area. Sloths' claws serve as their only natural defence. Despite sloths' apparent defencelessness, predators do not pose special problems: sloths blend in with the trees and their slow movement does not attract attention. Woolly Monkeys originate from the rainforests of South America. They most often live in the high tops of the canopy. Woolly monkey diets consist of fruit with an addition of leaves, seeds, flowers and insects. Toucans are native to Southern Mexico, Central America, the northern portion of South America, and the Caribbean region. They generally live in tropical. They make their nests in tree hollows and holes made by other animals such as woodpeckers—the toucan bill has very limited use as an excavation tool. Toucans are primarily frugivorous (fruit eating), but will sometimes hunt prey such as insects and small lizards. The pygmy marmoset is native to rainforests of South America. It is the smallest monkey and one of the smallest primates in the world. This monkey has a specialised diet of tree gum. It gnaws holes in the bark of appropriate trees and vines When the sap puddles up in the hole, it laps it up with its tongue. It also waits for insects, especially butterflies, which are attracted to the sap holes. It also eats fruit and nectar. The Emergent Layer The Emergent Layer Only a few very tall trees break through the canopy into the emergent layer. These trees can be as tall as skyscrapers. The tops of the trees are shaped like umbrellas and they grow on long, thin trunks. These trees get the most sunlight but also have to put up with the hot sun and strong winds. Because these trees are out in the open, they often have thick, waxy leaves that protect them from the sun and the wind. Many animals that live in the emergent layer are also found in the canopy. Animals of the Emergent Layer Macaws are native to Central America (especially Mexico), South America, and formerly the Caribbean. Most species are associated with forests, especially rainforests, but others prefer woodland or savannah-like habitats. The majority of Macaws are now endangered in the wild and a few are extinct. Macaws eat a variety of foods including seeds, nuts, fruits, palm fruits, leaves, flowers, and stems. The Harpy Eagle is rare but can be found from Mexico (almost extinct), through Central America and into South America to as far south as Argentina but is most common in Brazil. The Harpy Eagle is an actively hunting carnivore and is an apex predator, meaning that adults are at the top of a food chain and have no natural predators. Its main prey are tree-living mammals and a most of their diet has been shown to focus on sloths and monkey but can also prey on larger animals. They have a wing span of between 5’9ft up to 7’4. There are many other animals that live in the rainforest. Logging and deforestation are playing a large part in a number of species becoming endangered or extinct. Lovebirds originated in Africa but can be found in many places. Wild lovebirds are mostly green with a variety of colours on their upper body. There are nine species of lovebirds and their colours and markings vary. Love birds eat a range of leaves, seeds, nuts and grains. The Blue-headed Parrot is mainly green with a blue head and neck and red under tail feathers. Its habitat is forest and semi-open country but is more likely to be found in tropical areas. They mainly eat fruit and seeds. Butterflies are abundant in the Amazon rainforest and there are too many species to identify each individual. They come in a variety of colours and they often find ways to blend in to the environment that surrounds them. Why is the Amazon important? Lets have a look at the following conservation website to see the impact humans have had on the Amazon basin. http://www.conservation.org/where/pages/amazonia.aspx? gclid=Cj0KEQiAkJyjBRClorTki_7Zx8QBEiQAcqwGMTL2bL vXjC9eWsZga6VPYxpy0KjHeaofA2qxoLRWq6waAkGK8P8 HAQ But first, what is conservation? Conservation is the action of conserving something and preventing loss.