* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Endocrine and Reproductive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
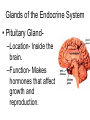
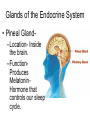
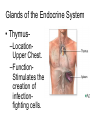
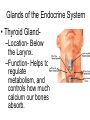
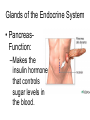
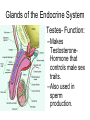
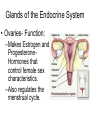
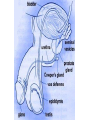
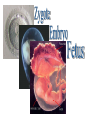
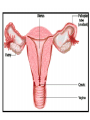
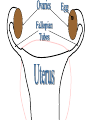
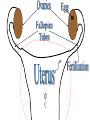
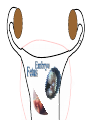
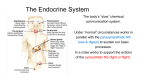
The Endocrine and Reproductive System What is the Endocrine System? • A system of glands that uses hormones to control many parts of your body. Chemical Messengers • Hormones are chemical messengers that send messages to different parts of your body. • Hormones are made by glands, and then released into the bloodstream. • Once the Hormone finds its ‘Target’, the target tissue will respond. Glands of the Endocrine System • Pituitary Gland–Location- Inside the brain. –Function- Makes hormones that affect growth and reproduction. Glands of the Endocrine System • Pineal Gland–Location- Inside the brain. –FunctionProduces MelatoninHormone that controls our sleep cycle. Glands of the Endocrine System • Thymus–LocationUpper Chest. –FunctionStimulates the creation of infectionfighting cells. Glands of the Endocrine System • Thyroid Gland–Location- Below the Larynx. –Function- Helps to regulate metabolism, and controls how much calcium our bones absorb. Glands of the Endocrine System • Adrenal Glands–Location- On top of Kidneys. –Function- Adrenalin controls how you react to stressful situations. –Controls the Fight or Flight response. Glands of the Endocrine System • PancreasFunction: –Makes the insulin hormone that controls sugar levels in the blood. Glands of the Endocrine System • Testes- Function: –Makes TestosteroneHormone that controls male sex traits. –Also used in sperm production. Glands of the Endocrine System • Ovaries- Function: –Makes Estrogen and ProgesteroneHormones that control female sex characteristics. –Also regulates the menstrual cycle. What is Reproduction? • The process that continues life on earth. • Hormones from the endocrine system help control male and female reproduction. The Male Reproductive System • Penis and Scrotum- The Scrotum contains the two Testes. –Testes- Male sex organs that produces Testosterone and Sperm. The Male Reproductive System • Sperm- Male reproductive cell. • Has a tail and a head- Within the head is hereditary information (DNA). The Male Reproductive System • Fluid is added to the sperm by the Seminal Vesicle and the Prostate. • Once fluid is added to the sperm, it is called Semen. • Semen leaves the body through the Urethra. Female Reproductive System • Ovaries- Female sex organs that produce eggs. • Ovulation- The release of an egg from the ovaries. • Once the egg leaves the ovary, it enters a Fallopian TubeTube that connects the Ovary to the Uterus. – Fertilization of the egg occurs in the Fallopian Tube. Female Reproductive System • Once fertilized, the egg travels to the Uterus- A muscular organ where the egg develops into a baby. • The Cervix- The opening into the Uterus. • The Cervix leads into the Vagina- The birthing tube that leads to outside the body. Development before Birth • After the sperm enters an egg, the two nuclei fuse into one- This creates a Zygote. • After the Zygote attaches to the wall of the Uterus, it is called an Embryo. • After the first two months of pregnancy, the developing embryo is called a Fetus. The Menstrual Cycle • Before an egg is released, the body prepares to have a baby. • The uterus’s wall thickens with blood in case an egg is fertilized. – If the egg is fertilized, the blood gives nutrients to the egg. – If the egg is not fertilized, the blood and egg are flushed out of the body.