* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science 8: Unit C: Light and Optical Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
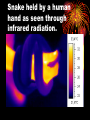
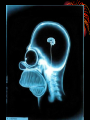
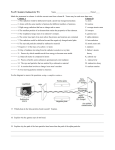
Science 8: Unit C: Light and Optical Systems Topic 8: Beyond Light The Invisible Spectrum • Stars and galaxies which produce light radiation also produce a wide spectrum of waves which are invisible to our eyes. Everything from radio waves with 1-2 km in wavelength to high energy gamma rays. Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) • Is radiation produced by a vibrating electric and magnetic fields. • The entire family of EMR is called the electromagnetic spectrum (EMS) • All EMR behaves as a wave: they travel at the speed of light, reflect, refract, diffract, absorb, etc. Radio Waves • Have the longest wavelength and lowest frequency of the EMS. They are used for AM and FM radio signals and TV signals. • Radio waves are going through us all the time, but because they are such low energy they are not considered a health hazard. Microwaves • A form of higher energy radio radiation. • Microwaves are used to vibrate water particles in food, heating them up. • They are also used in satellite and cellphone technology. Infrared Radiation • Heat radiation. Has a longer wavelength than red light. • Anything that is above absolute zero emits infrared radiation, including you. • TV remotes, heat lamps, and burglar alarms. Snake held by a human hand as seen through infrared radiation. Ozone Layer • The following EMR are too short to pass through the ozone layer because they’re wavelength is too small. Even blue and purple light rays are scattered by the ozone layer, making the sky blue. Ultraviolet Radiation • Just past the purple range of light lies UV radiation. • Most UV radiation produced by the sun is reflected by the Ozone layer in the atmosphere. • This is a good thing because UV radiation has a high enough frequency and energy to penetrate and mutate skin cells, tanning our skin, burning our skin, and if given enough exposure, causing skin cancer. X-Rays • Shorter wavelength and higher energy than UV. X-rays can penetrate and mutate skin and soft tissue, but not bone. • X-rays are used by doctors and dentists, however, they’re no longer used to try on shoes. Gamma Rays • The shortest wavelength gamma rays and therefore highest energy. • They can penetrate, mutate, or kill all tissue including bone, making them very dangerous. • Because of their ability to kill cells gamma rays are used to try and kill cancer cells. This is called radiation therapy. The downside to this therapy is that you often kill healthy surrounding cells as well as the tumor. The Gamma Ray Sky