* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics 1b - The Thomas Cowley High School
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Background radiation wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Health threat from cosmic rays wikipedia , lookup
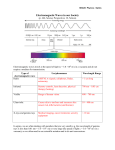
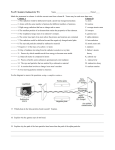
Physics 1b 1. The Electromagnetic spectrum a. b. c. d. e. Shortest Gamma rays X-rays Ultra Violet Visible light Infra red Microwaves Radio waves Longest Wave length General Electromagnetic radiation are Electric and Magnetic disturbances, travel as waves through space( vacuum) at 300million m/s Wave speed (m/s) = frequency Hertz (Hz) X wavelength metres Gamma rays and X rays Gamma rays have the shortest wavelength and highest frequency absorbed by dense materials such as bone and metal damage living tissue when they pass through X-rays used in hospitals for radiographs. Staff wear lead aprons & stand behind screens – they wear film badges to monitor exposure Gamma rays used to kill harmful bacteria in food, sterilising surgical equipment and kill cancer cells Richard Light and Ultra Violet radiation Of York UV causes tanning, over exposure can harm skin and eyes Gave UV Used in security markers Battle Visible light detected by eyes. Different wavelengths seen as different In colours. Can be transmitted down optical fibres Vain Infra-red, microwaves and Radio waves Infra red – given out by all hot objects. We sense it as heat & it can burn. Uses – Toasters, grills, radiant heaters, TV remotes -Night vision equipment detects it Microwave ovens produce frequencies that are absorbed by water molecules in food, cooking it from the inside out Microwave transmitters produce wavelengths that are able to pass through atmosphere, used to send signals to & from satellites and within mobile phone networks Radio waves used to transmit radio & TV programmes Communication Different frequencies are used for different applications – Local, national, international, emergency services and amateur radio, terrestrial TV, Satellite TV, mobile phones Optical fibres are thin glass fibres; they can be bent around curves. Light or infra red radiation is transmitted along fibre by total internal reflection (TIR) Analogue signals vary continuously in amplitude. Digital signals are either on (1) or off (0).Compared to analogue signals digital ones are free of noise and distortion. AND They are able to carry much more information 2.Radioactivity (you need to know basic structure of atoms – Chemistry 1a) a.Isotopes. Atoms of an element always have the same number of protons Isotopes have different numbers of neutrons E.g Carbon C12 C14 6 12 C 6 Protons and 6 Electons 6 Protons + 6 neutrons = 12 6 protons + 8 neutrons = 14 6 C 14 Radioactive substances contain unstable nuclei, they may become stable by emitting radiation Random – not affected by external conditions like heat/ pressure/catalysts b.Three types -Alpha particles (α), Beta particles (β) and Gamma radiation (γ) Alpha – A Helium nucleus (2 protons & 2 neutrons). Stopped by paper or few cm of air. Strongly ionising. Collisions with atoms can “knock off” electrons – producing ions. Has a positive charge and is deflected by electric & magnetic fields. Beta – high speed electrons. Stopped by thin metal or about 1m of air. Has a negative charge -deflected by electric and magnetic fields. Less ionising than α, but more penetrating. Gamma – electromagnetic waves. Have an unlimited range in air, stopped by thick lead. Weakly ionising, but strongly penetrating. Not deflected by either magnetic or electric fields c. Half life. Time taken for the number (& therefore mass) of parent atoms in a sample to halve – Also for count rate to fall to half the initial level. Count Time d.Uses Alpha – smoke alarms. Beta – control of thickness of materials like paper in manufacturing. Gamma & Beta – tracers in medicine. Gamma – sterilisation – medical equipment and perishable foods 3. Origins of Universe Our Galaxy, the milky-way contains about 100,000 million stars, there are millions of galaxies in the Universe a.Red shift – Light from distant galaxies is red-shifted to longer wavelengths, the further the galaxy the greater the red shift. b.The Big Bang Red shift shows us that distant galaxies are moving away from us. An Expanding Universe Universe started with a massive explosion from a small point “Big Bang” theory c.Looking into space Telescopes are able to detect visible light or other electromagnetic radiation (X rays, radio-waves) Telescopes on satellites do not have distortion caused by earths atmosphere & have grater detail