* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Survey of AI for games - Ohio State Computer Science and
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
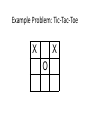
Survey of AI for games AI vs. AI for games • Traditional AI: – Made to handle unseen inputs, large state space – Too many options possible to compute an exact optimal solution – Engineering criteria: best possible performance • Game AI: – The game world is known, though it can still be large – In a known world, optimal solutions can be precomputed – Entertainment criteria: smart enough to pose a challenge, but not smart enough to be undefeatable Game AI related courses • CSE 3902 Project: Design, Development, and Documentation of Interactive Systems – State machines • CSE 3541 Computer Game and Animation Techniques – Agents and 3D spatial movement • CSE 3521 Survey of Artificial Intelligence I: Basic Techniques – Search, logic, knowledge representation • CSE 5522 Survey of Artificial Intelligence II – Probabilities and research topics • CSE 5524 Computer Vision for Human-Computer Interaction – Computing with images as input Adding AI into a Game • Friend – Autonomous, intelligent NPC helpmates – Configurable (scripted) behaviors: different characters solve a problem in different ways – Player may trade places with NPC: automation • Foe – Opponents get better with time – Opponents are less predictable because the individuals’ behavior is not uniform • Scene Clutter – Provides a richness to your environment. – Animals grazing, birds flying, people milling about, automobiles driving, etc. Goal-driven behavior • Multiple steps required to achieve a desired effect • Useful in – Action-adventure type games - puzzles to solve – RPG - task underlings with a multi-step job • Good discussion in Programming Game AI by Example Ch. 9 – Each ‘goal’ is an instance of a composite class – Many different goals can be created with minimal coding Goal-driven agents • Different classes of agents solve problem in different ways, based on their abilities – “Block door”: • Strong trolls move boulders in the way • Small hobbits shovel sand into the opening – Each agent’s response to the goal depends on his abilities, available tools, etc. – Goal object contains alternative recipes – One goal at a time is active for each agent • In more complex games, might have goal queue Other AI principles: observability • Don’t let the agents have perfect knowledge: they have to operate in the environment like the players do – Sense and remember events in their sensory horizon, memories can have a timestamp – Perhaps in more advanced levels, they can communicate with each other about what they know • See article on “adding stupidity to AI” Example Problem: Tic-Tac-Toe X X O Example Problem: Natural language processing • “Time flies like an arrow” • Grammatically valid interpretations: – 1. time passes quickly like an arrow – 2. command: time the flies the way an arrow times the flies – 3. command: only time those flies which are like an arrow – 4. “time-flies” are fond of an arrow