* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download practical File
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
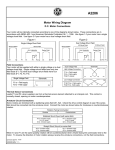
EXPERIMENT:12 AIM: Speed control of DC Shunt Motor using a) Armature control and b) Field control methods. APPARATUS REQUIRRED: Sr.no 1 2 3 4 5 Apparatus Voltmeter Ammeter Ammeter Rheostat Tachometer Range (0-300)V (0-5)A (0-2)A 250 ohm/1.5A Quantity 1 1 1 2 1 Fuse Rating: 40% of rated current 40*17/100=6.8≈10 A THEORY: (A)Flux Control method The speed of the DC motor is inversely propositional to the flux per pole, when the armature voltage is kept constant. By decreasing the flux the speed can be increased and vice – versa. Hence the main flux of field control method the flux of a DC motor can be changed by changing field current with help of a shunt field rheostat. Since shunt field current is respectively small shunt field rheostat has to carry only a small amount of current which means I2R losses is small so that rheostat is small in size .This method is very efficient. (B)Armature Control method This method is used when speed below the no load speed are required.As the supply voltage is normally constsnt the voltage across the armature is varied by inserting a variable rheostat in series with the armature circuit. As conductor resistance is increased potential difference across the armature is decreased, herby decreasing the armature speed. F or a load of constant torque speed is approximately propositional to the potential difference across the armature. PRECAUTIONS: 1. Armature rheostat must be kept at maximum resistance position. 2. Field rheostat should be kept at minimum resistance minimum position. PROCEDURE: (A)ARMATURE CONTROL METHOD: 1. Connect as per the circuit diagram 2.Close the DPST switch 3. Start the motor using three point starter 4.By keeping the field current(If) as constant value, adjust the armature rheostat and note down the corresponding armature voltage and motor speed. 5.Repeat the step four till the motor reaches the rated speed. (B)FLUX CONTROL METHOD: 1. Connect as per the circuit diagram 2.Close the DPST switch 3. Start the motor using three point starter 4.By keeping the armature voltage as constant value, adjust the field rheostat and note down the corresponding field current and motor speed. GRAPHS: 1.Field current Vs speed 2. Armature voltage Vs speed CIRCUIT DIAGRAM: OBSERVATION TABLE: (A)ARMATURE CONTROL METHOD SL.NO. Field Current If = Armature Voltage V A Speed N RPM 1. 2. 3 4 5 6 (B)FIELD CONTROL METHOD SL.NO. 1. 2. 3 4 5 6 CONCLUSION: Armature Voltage Va= V Field Current Speed N If RPM A 2 graph pages