* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - White station history
American mutilation of Japanese war dead wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
World War II casualties wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Naval history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aleutian Islands Campaign wikipedia , lookup
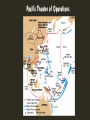
UNITED STATES HISTORY CHAPTER 12 – WORLD WAR 2 BELL WORK – 4/3 Answer these brief fill in the blank questions to test your knowledge of lesson1…This will help prepare for quiz tomorrow! (lessons 1 & 2) 1.Second generation Japanese Americans served in the 100th Infantry and the __________________, becoming the most decorated units in the history of the United States military. 2.The great symbol of the campaign to hire women was “_____________________________”, a character that appeared on posters, in newspapers, and in magazines. 3. Due to the high demand for raw materials and supplies, shortages were created. This led to ______________, or limiting the purchase of many products to make sure enough were available for military use. 4. Leading African American newspaper, the Pittsburgh Courier, launched the ____________________ Campaign to urge readers to support the war to win a double victory over Hitler’s racism abroad and racism at home. 5. In 1942 President Roosevelt created the ______________________________ to improve the public’s understanding of the war and to act as a liaison office with the various media. 6. After the bombing of Pearl Harbor, most of the West Coast was declared a military zone, and people of Japanese ancestry were evacuated to 10 ____________camps farther inland. 7. In early1941, the air force created its first African American unit, the 99th Pursuit Squadron, whose pilots became known as the ______________________. 8. To increase and hurry up production, the government offered ____________ contracts, agreeing to pay a company the cost to make a product plus a guaranteed percentage as profit. WHERE WAS WWII FOUGHT? First truly global war Two main theatres of operation: 1) European/Atlantic 2) Asian/Pacific *North Africa = 3rd campaign area Combat took place on land, sea, and air TWO THEATRES OF WAR AMERICAN EXPERIENCE: WWII European Theatre: (major battles) Stalingrad – true turning point of the war in Europe D-Day Battle of the Bulge Pacific Theatre: Strategy = Island Hopping & “Leap frogging” Guadalcanal; Midway; Okinawa; Iwo Jima JAPANESE INTERNMENT Executive Order 9066 As wartime hysteria mounted, the U.S. government rounded up 120,000 people of Japanese ancestry—77,000 of whom were U.S. citizens—and forced them into interment camps in early 1942. Given just days to sell their homes, businesses, and personal property, whole families were marched under military guards to rail depots, then sent to remote, inhospitable sites where they lived in cramped barracks surrounded by barbed wire and watchtowers. THE HOME FRONT Women Work For Victory Opportunities to work while men fought Challenged long held traditions even further Women worked in heavy industry (50% of working women in defense jobs) Married women worked (75% were married; 60% over 35 years old.) Rosie the Riveter THE HOME FRONT African Americans Demand Fair Employment Discrimination Defense industry jobs disproportionately went to whites 240 out of 100,000 workers were African American *Military was segregated “Double V” Campaign Fighting against the tyranny and oppression of fascism overseas…what about the discrimination & oppression in the states? Pittsburgh Courier – Called African Americans to support the war to win victory against racism abroad and at home THE HOME FRONT African Americans Demand Fair Employment A. Philip Randolph Head of the Brotherhood of Sleeping Car Porters (Pullman Car Company) Organized threat of a march on DC FDR = Executive Order 8802 Ensured fair hiring practices in gov’t funded jobs C.O.R.E. Congress of Racial Equality Helped establish the agenda for the Civil Rights movement of the 1950s & 60s THE HOME FRONT Mexican Americans deal with discrimination Bracero Program US – Mexico = hire migrant workers to help farm during the war Over 50,000 Mexican laborers were brought to the United States to help work during WW2 in war related industries Zoot Suit Riots Mexican Americans attacked by off duty sailors in LA (1943) Latino youths known as “Pachucos” caused a sensation by donning zoot suits, pork pie hats and dangling watch chains, and it wasn’t long before their eye-catching garb earned them an overblown reputation as street thugs and juvenile delinquents. Tensions grew especially high between zoot-suiters and the large contingent of white sailors and Marines stationed in Los Angeles. Mexican Americans were serving in the military in high numbers, but many servicemen viewed the zoot-suit wearers as World War II draft dodgers. Since wool and other textiles were subject to wartime rationing, they also considered the oversized suits an unpatriotic waste of resources. A mob of U.S. servicemen took to the streets in taxicabs and began attacking Latinos and stripping them of their suits Victims arrested & Zoot Suits were banned Gov. Earl Warren “ARSENAL OF DEMOCRACY” US War Production “The Americans can’t build planes…only iceboxes and radios” – Nazi official 1942, War Production Board was established(WPB) Office of War Mobilization (OWM) = Oversaw Allocate scarce materials into proper industries Regulate production of civilian goods Establish production contracts Negotiate with organized labor Control inflation National War Labor Board “ARSENAL OF DEMOCRACY” Government War-time production Authority to set wages and hours Mediate disputes b/w labor & man. War Manpower Commission Supervise mobilization for the military & industry Office of Price Administration Ration scarce products Control inflation by setting prices on consumer goods OPA was responsible for two types of rationing programs. The first limited the purchase of certain commodities (tires, cars, metal typewriters, bicycles, stoves and rubber shoes) to people who had demonstrated an especial need for them. The second limited the quantity of things–like butter, coffee, sugar, cooking fat, gasoline and non-rubber shoes–which every citizen was allowed to buy. As a result, of course, the black market flourished–studies estimated that 25 percent of all purchases during the war were illegal. “ARSENAL OF DEMOCRACY” US Wartime production accomplishments *$320 Billion spent by USA *17 million new jobs •*Increased wages by 50% •*Increased Corporate profits by 70% “To American production, without which the war would have been lost.” – J. Stalin 300,000 Military aircraft 2.6 million machine guns 6 million tons of bombs 5,000 cargo ships 86,000 warships By late 1942, 1/3 of economy was committed to war production More industrial plants built in first 3 years of war than in previous 15 years of peace Examples of war production: *Crude Rubber supply (from SE Asia) cutoff by Japan = US Government invested $700 million in 50 new synthetic rubber factories Merry-go-round factory = produced gun mounts Pin-ball machine maker = produced armorpiercing shells “ARSENAL OF DEMOCRACY” MILITARY INDUSTRIAL COMPLEX Defense spending 1940 = 9% of GNP 1945 = 46% of GNP Government support of Business “If you are going to try to go to war in a capitalist country, you have to let business make money out of the process or business won’t work” – Sec. of War, Henry Stimson Guaranteed profits Provided generous tax write-offs & subsidies Suspended anti-trust legislation *2/3 of all war spending went to 100 largest companies Federal Civilian Employees 1.1 million (at beginning of war) – 3.8 million by end of war Two American Commanders PACIFIC THEATRE *After the battles of Coral Sea & Midway, the Japanese were no longer on the offensive and were forced to fight to hold onto territories they had previously won General Douglas MacArthur Southwestern Pacific Left Philippines – Based out of Australia Admiral Chester Nimitz Central Pacific Strategies Leap Frogging Island Hopping Major Battles Coral Sea Guadalcanal Midway Iwo Jima Okinawa Pacific Theater of Operations PACIFIC THEATRE Douglas MacArthur “Leap Frogging” PACIFIC THEATRE Chester Nimitz Island Hopping U.S. Surrenders at Corregidor, the Philippines [March, 1942] Bataan Death March: April, 1942 76,000 prisoners [12,000 Americans] Marched 60 miles in the blazing heat to POW camps in the Philippines. BATAAN DEATH MARCH The surrendered Filipinos and Americans soon were rounded up by the Japanese and forced to march some 65 miles from Mariveles, on the southern end of the Bataan Peninsula, to San Fernando. The men were divided into groups of approximately 100, and what became known as the Bataan Death March typically took each group around five days to complete. The exact figures are unknown, but it is believed that thousands of troops died because of the brutality of their captors, who starved and beat the marchers, and bayoneted those too weak to walk. Survivors were taken by rail from San Fernando to prisoner-of-war camps, where thousands more died from disease, mistreatment and starvation. Bataan Death March: Aftermath America avenged its defeat in the Philippines with the invasion of the island of Leyte in October 1944. General Douglas MacArthur, who in 1942 had famously promised to return to the Philippines, made good on his word. In February 1945, U.S.-Filipino forces recaptured the Bataan Peninsula, and Manila was liberated in early March. After the war, an American military tribunal tried Lieutenant General Homma Masaharu, commander of the Japanese invasion forces in the Philippines. He was held responsible for the death march, a war crime, and was executed by firing squad on April 3, 1946. PACIFIC THEATRE Progress made in the Pacific after Pearl Harbor Important Early Battles Coral Sea *Day after Philippines fell in May 1942 Clash off the NE Australia 1st naval battle fought entirely by planes from aircraft carriers Each side lost a carrier; Japanese advance on Australia is stopped Midway June 1942 US Signal Corps broke Japanese code American dive-bombers sank 4 Japanese carriers Guadalcanal August 1942; Solomon Islands 6 months of fighting 25,000 Japanese troops killed ISLAND HOPPING The war in the Pacific involved a major geographic obstacle: the Pacific Ocean. In order to attack Japan, U.S. forces would have to advance across thousands of miles of ocean and attack heavily fortified Japanese positions on small, strategically important islands. The U.S. strategy involved a twopronged advance: The U.S. navy would island hop through the central Pacific while the Army advanced through the Solomon Islands, New Guinea, and the Philippines ISLAND HOPPING Problems with Island Hopping: By the fall of 1943, the U.S. navy was ready to launch its island-hopping campaign, but the geography of the central Pacific posed a problem. Many of the islands were coral reef atolls. The water over the coral reef was not always deep enough to allow landing craft to get to the shore. If the landing craft ran aground on the reef, the troops would have to wade to the beach. Wading ashore under enemy fire led to very high casualty rates among U.S. troops. The vehicle was a boat with tank tracks, nicknamed the “the alligator.” This amphibious tractor, or amphtrac was used successfully by the navy throughout the war. “Island-Hopping”: US Troops on Kwajalien Island PACIFIC THEATRE – KAMIKAZE *America takes back the Philippines: To take back the Philippines, America put together a huge invasion force of 700 ships carrying 160,000 men. On October 20, American ships landed on the island of Leyte, and the USA had taken back the Philippines. The Battle of Leyte Gulf was the largest naval battle in history. It was also the first time the Japanese used KAMIKAZE pilots in battle. “Kamikaze” means DIVINE WIND, and refers to the great storm that defeated the Mongol fleet in its invasion of Japan in the 13th century. Japanese Kamikaze Planes became known as The Scourge of the South Pacific. Effective: Sank more than 300 Allied warships and caused more than 15,000 casualties *The campaign to take back the Philippines was long and difficult. More than 80,000 Japanese were killed, while fewer than 1,000 Japanese surrendered. *MacArthur’s troops did not capture MANILA until March 1945. Japanese Kamikaze Planes: The Scourge of the South Pacific Kamikaze Pilots Suicide Bombers http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/world-war-ii-history/videos/kamikaze-pilots Gen. MacArthur “Returns” to the Philippines! [1944] PACIFIC THEATRE IWO JIMA Feb. – March, 1945 Nearly 700 miles from Japan Marines faced a “dug-in” enemy in tunnels & concrete pillboxes 25,000 marine casualties LESSON 3 THE INVASION OF EUROPE World War 2 INVASION OF EUROPE Allies plan Strategy for Victory “Europe First” Strategy *GOAL = Fight & win a 2-front war Only Germany had the capacity to a) bomb Britain, b) wage naval campaign against US & GB, c) invade USSR on 1200 mile front Where to attack though? Stalin wanted a 2nd front of fighting in Western Europe, in order to take pressure off the SOVIETS Churchill disagreed – wanted USA to help invade N. Africa & defend GB control of SUEZ Canal FDR goes with Churchill’s plan 1) Invasion would give the United States Army some experience without requiring a lot of troops 2) It would help the British troops fight Germany in Egypt’s Suez Canal EUROPE FIRST N. Africa & Italian Campaigns North Africa – fighting here allowed the Allies to occupy Axis troops, while preparing for an invasion of ITALY May 1943 – 250,000 Germans surrendered in Tunisia Italy – Summer of 1943; Churchill suggests invasion of Sicily & Italy Sicily seized in 1 month of fighting September 8, 1943 = Mussolini deposed & Italian military officials surrender to Allies *Nazis invade & halt Allied progress…the intense fighting would continue until the end in May 1945 **300,000 Allied Casualties in Italy – Very deadly EUROPE FIRST Major Turning Points in the war Casualties: German = 841,000 Soviet = 1,130,000 Battle of Stalingrad August 1942 – January 1943 Key city for USSR: Stalin’s namesake – will require troops to protect at all costs Access to the Black & Caspian Seas– vital trade route Caucasus Oil Fields Industrial city on the Volga River 4 months of fighting the USSR & Germany each suffered more battle deaths than the US did in the entire war *TURNING POINT OF WW2 – Hitler can’t dominate Europe STALINGRAD STALINGRAD Hitler wanted access to the oil fields of the Caucasus Mountains He also understood the symbolism. This was the essential confrontation Hitler desired – fascism vs. Bolshevism Germans experienced the legendary Russian resistance at Stalingrad as well. Oddly imprecise bombing in the north 600 German planes descended on the city one evening with incendiary bombs – 40,000 civilians killed. The two dictators insisted their armies fight to the death – by radio. Hitler neglected his flanks and was surrounded – his army trapped in the city – 80,000 German prisoners. TURNING POINT The Battle of Stalingrad ended in January 1943 and marked a turning point. The Germans would revert to a defensive position. The highly mobile Blitzkrieg army would, in one year – by 1944, transform into a ponderous, highly immobile army featuring heavy, slow tanks and dug-in infantry. Hitler had been too greedy in the east and mistakenly declared war on the U.S. HITLER Nov. 3, 1943 - Fuhrer Directive No.51 “For the last two and one-half years the bitter and costly struggle against Bolshevism has made the utmost demands upon the bulk of our military resources and energies…The situation has since changed. The threat from the East remains, but an even greater danger looms in the West: the Anglo-American landing! In the East, the vastness of the space will, as a last resort, permit a loss of territory even on a major scale, without suffering a mortal blow to Germany’s chance for survival. Not so in the West! If the enemy here succeeds in penetrating our defense on a wide front, consequences of staggering proportions will follow within a short time. I have therefore decided to strengthen the defenses in the West” STALINGRAD STALINGRAD STALINGRAD INCREASING PRESSURE ON GERMANY Incendiary Bombing Strategic Bombing Daytime flights by American Air Force Destroy Germany’s capacity to make war Jan. 1943-May 1945 the British Royal Air Force and U.S. Air Force dropped 53,000 tons of bombs per month on German cities Severely decreased Germany’s ability to produce airplanes Saturation Bombing Night time flights by British Royal Air Force Inflict maximum damage on German cities *Hamburg (July, 1943) = incendiary bombs mixed w/ explosives killed 100,000 & destroyed city (Similar to Cologne & Dresden) SATURATION & STRATEGIC BOMBING DRESDEN STRATEGIC BOMBING INVASION OF NORMANDY TEHRAN DECLARATION (P.305) “The common understanding which we have here reached guarantees that victory will be ours. And as to peace – we are sure that our concord will win an enduring peace. We recognize fully the supreme responsibility…to make a peace which will command the goodwill of the overwhelming mass of the peoples of the world and banish the scourge and terror of war for many generations.” - December 1, 1943 Tehran Conference (Nov. 1943) Big Three meet face to face (1st time) Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin Stalin still wants 2nd front opened in W. Europe (France) Stalin promises to: 1) Divide Germany with USA after the War 2) Help defeat Japan after Germany surrenders Churchill & FDR agree Dwight Eisenhower Supreme Commander Bernard Montgomery British General = Commander of Ground Forces Omar Bradley Commander of US 1st Army George S. Patton Lead decoy army at Calais D-DAY Codenamed – “Operation Overlord” (Allied invasion of Normandy) Operation Neptune = actual assault phase **Largest air, sea, and land invasion in HISTORY June 6, 1944 Three Part Invasion 1) Night time Airborne Invasion 2) Early Morning Bombing 3) Beach Invasion D-DAY D-DAY In order to keep missions secret, the military would refer to planned attacks as taking place on “d-day” at “h-hour”….thus, D-DAY Why invade FRANCE? To drive the Germans out and free Western Europe of German command Take pressure off of the Soviets in the East PLAN After midnight, send paratroopers in behind enemy lines with the cover of darkness, to take control of major roads, bridges, farms, railroads etc… Over 13,000 men in 6 parachute regiments Early morning bombing runs at dawn. This would weaken the coastal defenses of the Germans, and allow for the invasion Storm the beaches! Large scale troop invasion of 5 different beaches 1) 1)Juno 2) Sword 3) Gold 4) Omaha* 5) Utah NORMANDY FRANCE ATLANTIC WALL GEN. EISENHOWER EISENHOWER ADDRESS TO THE TROOPS “You are about to embark on the Great Crusade, toward which we have striven these many months. The eyes of the world are upon you. The hopes and prayers of libertyloving people everywhere march with you….I have full confidence in your courage, devotion of duty and skill in battle. We will accept nothing less than full VICTORY!” AIRBORNE TROOPS TROOPS Over 156,000 troops landed at Normandy 73,000 Americans 23,250 at Utah Beach 34250 at Omaha Beach D-DAY D-DAY D-DAY ALLIED SUPPLIES ALLIED TROOPS AMERICAN SECTOR Omaha and Utah beaches Omaha = strategic Utah = important for supplies In the American sector, the landing at Utah beach began at 0630 and-despite occurring slightly south of the target area--proceeded according to plan as the U.S. 4th division advanced rapidly toward its initial objectives. At Omaha beach, where the landings began at 6:35, underwater obstacles bottled up many of the amphibious craft and the congestion provided easy targets for German gunners. The landing bogged down and it took a combination of short-range destroyer gunnery support, aerial bombardment and desperate infantry assaults to break the German defenses. It was not until noon that the U.S. 1st and 29th divisions crossed the beach line in force. CASUALTIES Overall = 9,000+ Allies American = 2,000+ Utah Beach = 197 Omaha Beach = 2,000+ *Airborne = 2,499 (238 deaths) *Perspective - Battle of the Bulge = 70,000 casualties - Iwo Jima = 23,000 casualties (36 days of fighting) - Okinawa = 50,000 casualties LESSON 4 THE WAR ENDS World war 2 The Battle of the Bulge: Hitler’s Last Offensive Dec. 16, 1944 to Jan. 28, 1945 Hitler Commits Suicide April 30, 1945 Cyanide & Pistols The Führer’s Bunker Mr. & Mrs. Hitler V-E DAY GERMAN Surrender occurred on early morning of May 7, 1945 *Public celebrated on May 8, 1945 General Keitel DEFEAT OF JAPAN After VE day, the focus of the Allied war effort shifted to the Empire of Japan Island-Hopping was an effective strategy, which pushed the Japanese back to their home islands The USSR & US both had interests in East Asia The US didn’t want the Soviets to have any involvement in forcing the surrender of Japan Invasion of Japan held major risks Estimated that the US could lose over 1,000,000 soldiers in an invasion of Japan Harry Truman was faced with a major decision Use new atomic bombs? Potential for high casualties USSR invading & taking territory US MARINES ON MT. SURIBACHI IWO JIMA FEBRUARY 19, 1945 PACIFIC THEATRE OKINAWA April - June, 1945 350 Miles from Japan *Key staging area for the invasion of the Japanese home islands 83 days of fighting 80,000 civilian casualties 110,000 Japanese dead 50,000 American casualties JAPANESE BOMBING TOKYO March 9 – 10. 1945 B-29 Bombers dropped napalm & magnesium bombs Burned 16 square miles of the city Killed nearly 100,000 Japanese *Japanese government showed no willingness to surrender POTSDAM CONFERENCE JULY, 1945 FDR dead, Churchill out of office as Prime Minister during conference. Stalin only original of the BIG THREE The United States has the A-bomb. Allies agree Germany is to be divided into occupation zones Poland moved around to suit the Soviets. P.M. Clement President Joseph Atlee Truman Stalin THE MANHATTAN PROJECT Developing the atomic bomb The Manhattan Projects sole purpose was to develop a method for the mass production of atomic bombs. Lt. Leslie Groves Wizard Of the Manhattan Project task of overlooking the projects progress and keeping the project top secret. J. Robert Oppenheimer Scientist in charge of development THE MANHATTAN PROJECT Production of Fissile materials & fabrication of the bombs The two main sites Oak Ridge, Tennessee U235 Enrichment Harford, Washington Plutonium development Used in trinity test; Fat Man (Nagasaki Bomb) LOS ALAMOS, NM Site of bomb assembly OAK RIDGE, TN – MANHATTAN PROJECT http://www.history.com/topics/world-war-ii/world-war-ii-history/videos/secretatomic-city-is-built-in-oak-ridge-tennessee THE MANHATTAN PROJECT THE MANHATTAN PROJECT TRINITY TEST The first use of the atomic bomb (test) took place within the Jemez Mountains in New Mexico on July 16, 1945 This was known as The Trinity Test because it took place at Trinity Site The bomb was code-named Gadget THE MANHATTAN PROJECT TRINITY TEST Initially, because of uncertainty of whether the bomb would explode as planned, it was going to be placed inside Jumbo, so as to save the plutonium if the test failed THE MANHATTAN PROJECT August 6, 1945 HIROSHIMA “Little Boy” = smaller of the two developed atomic bombs The bomb was dropped by a modified American B-29 Super-fortress bomber named the Enola Gay The bomb itself was over 10 ft long, 30 in across , and weighed close to 5 tons. It had the explosive force of 20,000 tons of TNT HIROSHIMA HIROSHIMA AUGUST 6, 1945 70,000 killed immediately. 48,000 buildings. destroyed. 100,000s died of radiation poisoning & cancer later. THE MANHATTAN PROJECT NAGASAKI USSR declared war on August 8, 1945 Japanese government warned of another attack August 9, 1945 in Nagasaki, Japan Fat Man – the bigger of the two bombs Despite the increased size of the bomb, the casualties, while still high, were less than that of Hiroshima An estimate is: 40,000+ killed instantly, and 60,000 injured. NAGASAKI NAGASAKI AUGUST 9, 1945 40,000 killed Immediately. 60,000 injured. 100,000s died of radiation poisoning & cancer later. VICTORY IN JAPAN August 15,1945 – “V-J DAY” Formal Surrender took place on September 2, 1945 USS Missouri Emperor Hirohito could keep position, but would be subordinate to occupation commander Gen. MacArthur: Supervised the writing of a new constitution Allowed a defense force Women’s suffrage Democratic reforms Full economic recovery V-J DAY AUGUST 15, 1945 V-J DAY IN TIMES SQUARE, NYC