* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Renaissance
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
Spanish Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Brancacci Chapel wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Italian Renaissance wikipedia , lookup
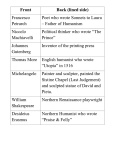
Renaissance A Rebirth of Learning Distinctive Features Rediscovery of Greco-Roman culture Emphasized reason, a questioning attitude, experimentation and free inquiry Glorified the individual and approved worldly pleasure Focused on worldly matters Featured great achievement in literature, art and science. Renaissance begins in Italy Was center of Greco-Roman culture Located on the Mediterranean Sea Wealthy people who became patrons Popes in Rome Wealthy merchants in Venice Sforza family in Milan d’Este family in Genoa Medici family in Florence Florence – Perfect Renaissance City Outstanding city of Italian Renaissance Many Florentine painters, writers sculptors, architects and sculptors People of talent from other parts of Italy came to work in Florence Ruled by Medicis in 15th cen. Merchants/Bankers – wool trade Lorenzo the Magnificent – leading member Renaissance Florence Renaissance Spreads 15th century – ideas spread from Italy to France, the German states, Holland, and England Resulted from religious, military and commercial contacts Northern scholars traveled to Italy to absorb Italian art and learning Humanism Definition – literary movement that began in the 14th century which emphasized worldly things such as everyday human problems rather than religious matters. Drew inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman manuscripts Early Humanists Petrarch – Italian; studies classics and wrote in both Italian and Latin; wrote sonnets that expressed romantic love and appreciation of nature Erasmus – Dutch; wrote In Praise of Folly – ridiculed superstition, prejudice, upper class privileges and Church abuses; encouraged people to think about reform Early Humanists Sir Thomas More – English; wrote Utopia – portrayed an ideal country, free from war, injustice, poverty, ignorance; word utopia now refers to an ideal state By Hans Holbein Vernacular replaces Latin Definition – language of everyday speech such as French, Italian, Spanish, German or English Early great writers Dante – Italian Father of modern Italian Divine Comedy – long poem about imaginary trip through hell, purgatory and heaven guided by Vergil Vernacular replaces Latin Early Great Writers Chaucer – English Canterbury Tales – related by journeying religious shrine Canterbury stories pilgrims to the at Invention of Printing Moveable Type Johann Gutenberg About 1450 1st book - Bible Advantages Increase output and accuracy Decreased cost More people could own books Encouraged people to write Renaissance Literary Achievements Machiavelli Italian (Florence) Served in government Dismissed by Medicis Retired to country The Prince Ethics and Government “end justifies the means” Renaissance Literary Achievements Cervantes Spanish Ridiculed feudal society, especially knighthood and chivalry Don Quixote Mad knight of La Mancha Renaissance Literary Achievements Shakespeare English Greatest poet and playwright of all time Masterful command of English language and deep understanding of human beings Renaissance Literary Achievements Shakespeare Famous Works Macbeth, Hamlet, Romeo and Juliet, King Lear, A Midsummer Night’s Dream, Taming of the Shrew. Famous Quotations “at one fell swoop,” “foul play,” “good riddance,” “high time,” “lie low,” “mum’s the word,” “vanish into thin air,” “neither here nor there,” and “the game is up.” Art and Patronage Italians were willing to spend a lot of money on art. Art communicated social, political, and spiritual values. Italian banking & international trade interests had the money. Public art in Florence was organized and supported by guilds. Therefore, the consumption of art was used as a form of competition for social & political status! 1. Realism & Expression Expulsion from the Garden Masaccio 1427 First nudes since classical times. 2. Perspective The Trinity Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Masaccio 1427 Perspective! First use of linear perspective! What you are, I once was; what I am, you will become. 3. Classicism Greco-Roman influence. Secularism. Humanism. Individualism free standing figures. Symmetry/Balance The “Classical Pose” Medici “Venus” (1c) 4. Emphasis on Individualism Batista Sforza & Federico de Montefeltre: The Duke & Dutchess of Urbino Piero della Francesca, 1465-1466. 5. Geometrical Arrangement of Figures The Dreyfus Madonna with the Pomegranate Leonardo da Vinci 1469 The figure as architecture! Two predominant art forms Madonna – Mary with the Baby Jesus Pieta – Mary with the Crucified Christ Renaissance Artistic Achievements Giotto 1266-1337 Florence Painter/Architect First Renaissance artist Ghiberti – Gates of Paradise Baptistry Door, Florence – 1425 - 1452 The Winner! Donatello 1386-1466 Florence Sculptor Friezes David 1430 First free-form bronze since Roman times! Self-Portrait -- da Vinci, 1512 Artist Sculptor Architect Scientist Engineer Inventor 1452 - 1519 Leonardo da Vinci Paintings Michelangelo Buonorrati 1475 – 1564 He represented the body in three dimensions of sculpture. David Michelangelo Buonarotti 1504 Marble The Popes as Patrons of the Arts The Pieta Michelangelo Buonarroti Only 23 yrs old when completed 1499 marble The Sistine Chapel Michelangelo Buonarroti 1508 - 1512 The Sistine Chapel’s Ceiling Michelangelo Buonarroti 1508 - 1512 The Sistine Chapel Details The Creation of the Heavens The Sistine Chapel Details Creation of Man The Sistine Chapel Details The Fall from Grace The Sistine Chapel Details The Last Judgment 15c What a difference a century makes! 16c Renaissance Artistic Achievements Rembrandt Dutch Greatest painter of Northern Renaissance Contrasts of light and shadow Renaissance Artistic Achievements Durer German Painter Metal and Wood Engraver Renaissance Artistic Achievements Hans Holbein German Portrait Painter Renaissance Musical Achievements Written in vernacular Sung by troubadours Madrigal – “fa la la” Characteristics of Renaissance Science Built on work of Greeks and Romans Developed scientific method for observation and experimentation Challenged medieval superstition and Aristotle’s theories Knowledge of the physical world Geocentric v. heliocentric Improved health and controlled environment Foundation for modern scientific progress Renaissance Science Copernicus Polish astronomer Sun is center of the universe Galileo Invented scientific method Telescope Law of falling bodies Supported the Copernican theory Renaissance Science Kepler German Astronomer Mathematician Planets follow an elliptical not a circular orbit around the sun Vesalius Flemish Physician Founded science of Anatomy Renaissance Science Harvey English Demonstrated that blood circulates through the body Descartes French Scientist Mathematician Philosopher Founder of Analytical Geometry “I think, therefore I am.” Renaissance Science Leeuwenhoek Dutch Microscope Newton English Mathematician Astronomer Physicist Gravity Calculus Laws of light and color Laws of motion Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy