* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Definition - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Sobolev space wikipedia , lookup
Multiple integral wikipedia , lookup
Distribution (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental theorem of calculus wikipedia , lookup
Series (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Generalizations of the derivative wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
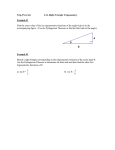
Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ Adapted from Howard Anton, Calculus 8th edition _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 20 Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ 2.1 Derivatives and Integrals involving Inverse Trigonometric Functions Inverse Trigonometric Functions The six basic trigonometric functions do not have inverse because their graphs repeat periodically and hence do not satisfy the horizontal line test. Can we still find the inverses? Definition The inverse sine function, denoted by sin1 , is defined to be the inverse of the restricted sine function sin x , x 2 2 Definition The inverse cosine function, denoted by cos 1 , is defined to be the inverse of the restricted cosine function cos x , 0 x Definition The inverse tangent function, denoted by tan 1 , is defined to be the inverse of the restricted tangent function tan x , x 2 2 Definition The inverse secant function, denoted by sec 1 , is defined to be the inverse of the restricted secant function ,0 x , x 2 _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 21 Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ Identities for Inverse Trigonometric functions If we interpret sin1 x as an angle in radian measure whose sine is x, and if that angle is nonnegative, then we can represent sin1 x geometrically as an angle in a right triangle in which the hypotenuse has length 1 and the side opposite to the angle sin1 x has length x. Listed below are some useful identities involving inverse Trigonometric functions which are valid for 1 x 1 sin1 x cos1 x 2 cos sin1 x 1 x2 sin cos1 x 1 x2 tan sin1 x x 1 x2 Simplifying Expression involving Inverse Trigonometric Functions Triangle Method In order to evaluate expression involving inverse trigonometric function, we can represent the inverse trigonometric function as an angle in a right triangle. _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 22 Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ Example 1 Determine the exact value without using a calculator: sin1 1 Example 2 Determine the exact value without using a calculator: 1 sin1 2 Example 3 Determine the exact value without using a calculator: 1 cos1 2 Example 4 Without using the calculator, find the value of cos tan 1 3 Example 5 Use the triangle method to simplify tan cos ec 12y _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 23 Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ Example 6 Use the triangle method to evaluate sin tan 1 3 cos1( 1 ) . 2 Apr 2009 Derivative of inverse Trigonometric Functions Motivation Example 7 Find the derivative of y sin1 x _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 24 Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ Generalized Derivative Formula for Inverse Trigonometric Functions If u is a differentiable function of x, the chain rule produces the following generalized derivative formula: 1 d 1 du sin u dx 1 u2 dx 1 d 1 du cos u dx 1 u2 dx 1 d 1 du tan u dx 1 u2 dx 1 d 1 du cot u dx 1 u2 dx 1 d 1 du sec u 2 dx u u 1 dx 1 d 1 du csc u 2 dx u u 1 dx _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 25 Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ Example 8 Find dy if y sin1 x 4 dx Example 9 Find dy if y cos14x dx Example 10 Find dy if y tan1 x2 dx Example 11 Find dy if y e2 x sin13x dx _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 26 Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ Integrals involving Inverse Trigonometric Functions du 1 u 1 u du u 2 2 sin1 u c (1) tan 1 u c du u 1 2 (2) sec 1 u c (3) Example 12 Evaluate 1 3x dx 2 Hint: let u = _________ Example 13 Evaluate ex 1 e 2x dx Hint: let u = _________ _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 27 Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ Example 14 Evaluate a 2 dx where a 0 is a constant. x2 Hint: let u = _________ Generalization Formula for (1), (2) and (3) du 1 u tan 1 c 2 a a a u u 2 du a 2 u2 du u2 a 2 sin1 u c a 1 u sec 1 c a a _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 28 Handout 2 MAT199 July – Nov. 2010 ________________________________________________________________ Example 15 Evaluate dx 2 x2 . Let us try another example. Example 16 Evaluate x dx 9 x4 . APR 2008 _______________________________________________________________________ rajasulaiman.wordpress.com 29