* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Microbiology
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial morphological plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
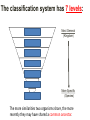
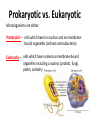
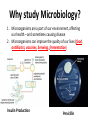
REVIEW Classification and the 6 Kingdoms • Classification: Scientists way of grouping organisms together based on how closely they are related – consider appearance, behaviour, and DNA when grouping The classification system has 7 levels: Kingdom Most General (Kingdom) Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species More Specific (Species) The more similarities two organisms share, the more recently they may have shared a common ancestor. What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the field of biology that studies microorganisms such as: • Viruses • Bacteria • Protozoa • Fungi Organisms that cause disease are called pathogens Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Microorganisms are either: Prokaryotic – cells which have no nucleus and no membranebound organelles (archaea and eubacteria) Eukaryotic – cells which have numerous membrane-bound organelles including a nucleus (protists, fungi, plants, animals) They can be so small! Microorganisms usually require magnification to be observed. Many are unicellular (made of a single cell) and others form multicellular groups of associated cells. Why study Microbiology? 1. Microorganisms are a part of our environment, affecting our health – and sometimes causing disease 2. Microorganisms can improve the quality of our lives (food, antibiotics, vaccines, brewing, fermentation) Insulin Production Penicillin Why study microbiology? 3. Microorganisms are good tools to study life processes and molecular biology a. Simple life forms b. Can grow quickly c. Biotechnology and genetics research tool • • • • • • • • The Bad Side: Diseases caused by microorganisms Common Cold AIDS/ HIV Leprosy Salmonella Cholera Meningitis Tetanus Tuberculosis Who is W.H.O.? • World Health Organization • a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) that is concerned with international public health • It’s primary goal: "is the attainment by all people of the highest possible level of health” • One of its greatest achievements was the eradication of smallpox through vaccinations