* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 3 Learning and Memory
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
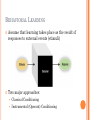
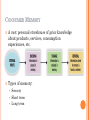
LEARNING & MEMORY Chapter 3 Sessions 5-6 THE LEARNING PROCESS Learning Learning is an Ongoing Process A relatively permanent change in behavior caused by personal experience or observation Constantly being revised Can be either simple association (logo recognition) or complex cognitive activity (learning for exams) Two popular learning theories Behavioral Cognitive BEHAVIORAL LEARNING Assume that learning takes place as the result of responses to external events (stimuli) Two major approaches: Classical Conditioning Instrumental (Operant) Conditioning CLASSICAL CONDITIONING APPLICATIONS OF CLASSICAL CONDITIONING PRINCIPLES Conditioned Product Associations pairing products with positive stimulus to create desirable associations Advertising Choosing novel tunes (as opposed to popular ones) for jingles CS precedes UCS for effective conditioning Stimulus Generalization Tendency of a stimulus similar to a CS to evoke similar, conditioned responses (Halo effect) Strategies based on SG principle: Emergence of me-too brands & look-alikes Family branding & line extensions Licensing Masked branding (hiding true product origin) INSTRUMENTAL CONDITIONING Occurs as the individual learns to perform behaviors that produce positive outcomes and avoid behaviors that yield negative outcomes Can be Positive Reinforcement Punishment Behaviors that lead to “favorable” consequences Behaviors that lead to “unfavorable” consequences Negative Reinforcement Behaviors that help avoid “unfavorable” consequences AD DEPICTING NEGATIVE REINFORCEMENT APPLICATIONS OF INSTRUMENTAL CONDITIONING PRINCIPLES Reinforcement of Consumption Thank you Rebates Follow-up phone calls Frequency Marketing Reinforces regular purchases by giving them rewards with values that increase along with the amount purchased Frequent flyer miles K&Ns loyalty card COGNITIVE LEARNING Stresses the importance of active internal mental processes in learning We learn because we develop conscious hypotheses & then act on them Observational Learning Occurs when people watch the actions of others and note reinforcements received for their behaviors and use this knowledge to guide their own behavior Effect of violence & sex on TV on kids Marketing applications include depicting benefits of using products in ads, celebrity endorsements, etc. OBSERVATIONAL LEARNING (KIDS) CONSUMER MEMORY A vast personal storehouse of prior knowledge about products, services, consumption experiences, etc. Types of memory: Sensory Short term Long term HOW MEMORIES ARE CREATED SENSORY MEMORY Very temporary storage of information we receive from our senses Operates automatically & is very fleeting Sensory input is stored as it is If information is relevant it passes the ‘attentional gate’ into our short-term memory SHORT-TERM MEMORY Holds the information we are currently processing usually in light of existing knowledge (working memory) ST LT can be enhanced by: Chunking Rehearsal Involves repetition or actively thinking about the information Ex: Jingles that we love to hum or repeat (Diamond Supreme Foam) Recirculation Grouping items to process as a unit Ex: phone numbers (McDonald’s 11-12-44-622) Repeatedly encountering the info (externally) Ex: Repeating brand name within ad (Omore), repeating ads (Mezan), using multiple media for the same message (Tarang) Elaboration Relating info to prior knowledge & past experiences Ex: Ads that make you think, relate info to past concepts, relevant messages in communication CHUNKING ELABORATION? LONG-TERM MEMORY Where info is permanently stored for later use Two types Autobiographical (Episodic) Knowledge we have about ourselves & our past experiences (emotions, sensations etc.) Ex: Memories of eating at Aylanto, sweating in the summer heat without AC, eating a paratha on Sunday morning Useful in advertising (empathizing with customers) Semantic General knowledge or beliefs about the world from what we heard, read, etc. Ex: France is a place for romantic vacations, CaCl2 means Calcium Chloride, good GPA gets you a good job STORING INFORMATION IN MEMORY Semantic (Associative) Networks Set of links or associations that represent autobiographic & semantic memories connected to a particular concept/s in our mind Each ‘node’ in the network can be an attribute, a brand, a person, a belief, etc. Different links have different strengths of association Marketers try to strengthen these links through recirculation & encouraging customers to rehearse & elaborate on incoming information The process of ‘spreading of activation’ helps us to recall many different nodes when one is activated depending on the strength of those links PERFUMES – SEMANTIC NETWORK RETRIEVAL The process of recovering information from LTM Factors affecting the likelihood of retrieval: Situational Factors Pioneering (prototypical) brands are generally easier to retrieve from memory Descriptive brand names easier to recall than names that do no provide cues to what the product is State-Dependent Retrieval A process by which consumers are better able to access info if their mood or setting is the same at the time of their recall as when the info was learned Pictorial vs. Verbal Cues Visual memory > verbal memory Pictorial ads may enhance recall (of ad and brand), but do not necessarily improve comprehension. RETRIEVAL Products and ads can serve as powerful retrieval cues Products & ads can remind us of past experiences (activate episodic memories) and create positive feelings in us Popularity of Nostalgia Marketing State Life Insurance Habib Cooking Oil latest TVC CREATING NOSTALGIA THROUGH AD CREATING NOSTALGIA THROUGH AD