* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
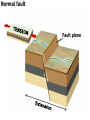
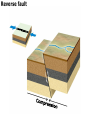
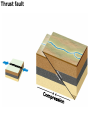
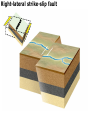
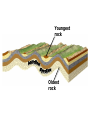
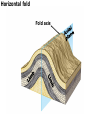
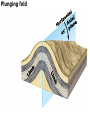
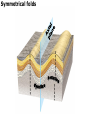
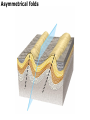
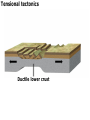
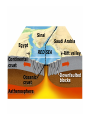
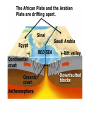
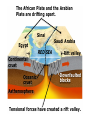
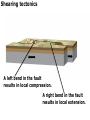
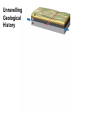
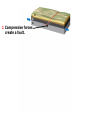
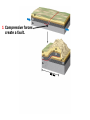
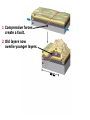
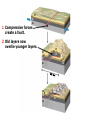
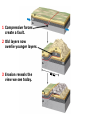
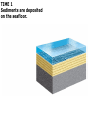
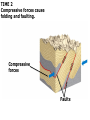
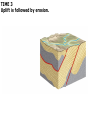
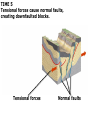
DEFORMATION Modifcation of Rocks by Folding and Fracturing Chapter 7 Folded Tilted Faulted Mangled! Strike and Dip N W S Dip 45° angle E N W S 45° Dip angle E A special compass is used by geologists for the purpose of recording the orientation and dip of planar rock structures like folds, beds, faults, and metamorphic laminations. These measurements are reported on 2-D geological maps to help geologists see how the structure is are oriented relative to the north pole, and the surface of the earth. N W S Dip 45° angle E N W S 45° Dip angle Water trickles down slope parallel to dip. The strike is oriented 90 degrees to the dip. E Rocks strain when subjected to stress. The strain is released through folding (plastic deformation) or faulting (brittle deformation). An undeformed sample Under conditions representative of the shallow crust, the marble is brittle. Under conditions representative of the deeper crust, marble is ductile. An undeformed sample Normal fault Fault plane Index Fossils and Biostratigraphy • The shorter the time-stratigraphic range of the fossil, the more precise are the correlations that can be made • Fossils representing free swimming or drifting organisms can be found world wide and deposited in a wide variety of rock type (different depositional environments). These are the most useful for global correlation of the stratigraphic records. They are called Index Fossils. Reverse fault Thrust fault Left-lateral strike-slip fault Right-lateral strike-slip fault Oblique-slip faulting is caused by a combination of forces. Tectonic Forces Determine the Style of Faulting Click here to view the Flash animation in your web browser Youngest rock Oldest rock Horizontal fold Fold axis Plunging fold Symmetrical folds Asymmetrical folds Tensional tectonics Ductile lower crust Sinai Egypt RED SEA Continental crust Oceanic crust Asthenosphere Saudi Arabia Rift valley Downfaulted blocks The African Plate and the Arabian Plate are drifting apart. Sinai Egypt RED SEA Continental crust Oceanic crust Asthenosphere Saudi Arabia Rift valley Downfaulted blocks The African Plate and the Arabian Plate are drifting apart. Sinai Egypt RED SEA Continental crust Oceanic crust Saudi Arabia Rift valley Downfaulted blocks Asthenosphere Tensional forces have created a rift valley. Compressive tectonics Shearing tectonics A left bend in the fault results in local compression. A right bend in the fault results in local extension. San Francisco Lavas offset from volcano Northwest Offset of 315 km Volcano Los Angeles Stream Offset of 130 m Southeast Stream Pacific Plate North American Plate Unravelling Geological History C D B A C D B A 1 Compressive forces create a fault. C D B A 1 Compressive forces create a fault. D B A C C D B C D B C D B A 1 Compressive forces create a fault. 2 Old layers now overlie younger layers. D B A C C D B C D B C D B A 1 Compressive forces create a fault. 2 Old layers now overlie younger layers. D B C B C C D B A D C B A D B C D B C D B A 1 Compressive forces create a fault. 2 Old layers now overlie younger layers. D B C B C C D B A 3 Erosion reveals the view we see today. D C B A D B C D B Keystone thrust fault, southern Nevada B D TIME 1 Sediments are deposited on the seafloor. TIME 2 Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. Compressive forces Faults TIME 3 Uplift is followed by erosion. TIME 4 Volcanic eruptions flood the new surface with lava sheets. Lava flows TIME 5 Tensional forces cause normal faults, creating downfaulted blocks. Tensional forces Normal faults