* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is isostasy? The balancing downward force of the crust and the
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
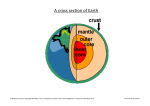
What is isostasy? The balancing downward force of the crust and the upward force of the mantle. How does a dome form? Magma works its way up to the earth’s surface without actually breaking through or erupting, causing the earth’s crust to fold upward. What is shear stress and provide one example. Two plates are sliding past each other in opposite directions building up stress and tension as they go. Ex. San Andreas Fault What is compression stress and give one example. Compression squeezes rocks together often forming mountains. Ex. Himalaya’s, Appalachian What is tension stress and give one example. Tension pulls rocks of the crust apart. Ex. Mid-Atlantic Ridge, or East African Rift Valley How do rift valley’s form? 2 plates pull away from each other (tension stress) causing a block of land to fall between 2 normal fault lines. When are rocks more likely to fold then fault? Whey the rocks are hot, under pressure, ductile, and stressed gradually Why are some countries sinking and other countries rising? Compare faulting and folding. Faulting occurs when rocks on one side of a fault slide past the other side. Folding occurs when rocks bend rather than break, and not fault is produced. In what ways can plateaus be formed? 1. An gentle uplifting of an area brought on by horizontal forces. 2. Lava flows 3. The build-up of sediment between mountain peaks