* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11 Section 3 Notes SOLVUS 7
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Baltimore riot of 1861 wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Fort Pillow wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
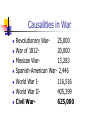
Behind the scenes of the Civil War Lincolns Position of War African Americans Women Military Prison Camps Questions to be Answered What was Lincoln’s position on the war? What was the role of women and African Americans during the war? 1 in 4 soldiers died More Americans killed in this war than any other in history of U.S. Causalities in War Revolutionary War25,000 War of 181220,000 Mexican War13,283 Spanish-American War- 2,446 World War I116,516 World War II405,399 Civil War625,000 Wartime Government Both North and South opposed war Lincoln and Davis considered to be dictators Republican party splits Extreme Democrats – Copperheads – end war at any price Lincolns Position on War One Nation Indivisible-Preserve the Union Legitimate state governments had to be established – loyal to Union South should not be punished but act “with malice towards none, with charity for all…to bind up the nations wounds” “Second American Revolution” Common Soldiers: Warfare often involved hand-tohand combat. Wartime diaries and letters home record this harsh reality. After the war, especially in the South, soldiers returned home to find destroyed homes and poverty. Soldiers on both sides lived with permanent disabilities. Raising Armies Soldiers were mostly volunteers Both sides had to draft men for military service – conscription Northerner’s could avoid service by having a substitute or by paying Union paid men to enlist African Americans The Emancipation Proclamation allowed for the enlistment of African American soldiers. Fight for the Union Commanded by White soldiers Paid less, segregated Southerners refuse to accept them 54th Massachusetts Regiment Women Served as nurses and cooks Clara Barton – founder of American Red Cross – “Angels of the Battlefield” Worked in factories in North, Ran plantations in South Women Behind the Lines: Managed homes and families with scarce resources. Often faced poverty and hunger Assumed new roles in agriculture, nursing, and war industries Supplying the Armies North Successful in financing the war (Greenbacks) South printed worthless money, defeated because of inability to produce manufactured goods Military life Away from home for long periods of time Limited food supply, shoeless, desertions Battlefield medicine – unsanitary instruments, amputations, Military Prison Camps Before Emancipation Proclamation prisoners were exchanged After E.P. South would not exchange Black soldiers, creation of prison camps South could not adequately feed the prisoners Andersonville – Southern prison camp, 100 men died a day Life in the North Economy boomed b/c of war profits Women filled labor shortages Life in the South Shortages of food for soldiers and citizens Economy suffered People were unhappy with Southern Government