* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Do Now
Conic section wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Cardinal direction wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
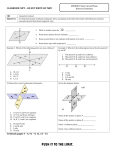
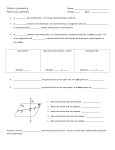
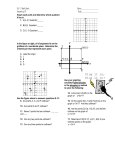
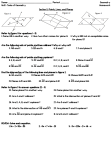
DO NOW • Take a ruler from the bookshelf. • Have your syllabus contract out and ready to turn in. • Take out your notebook for this class. • In your notebook, describe the two types of symmetry and draw an example of each. BUILDING BLOCKS OF GEOMETRY TODAY’S OBJECTIVES • Learn the terminology and notation of points, segments, lines, rays, planes, angles, and collinear and coplanar points. • Learn the idea of congruence of line segments • Learn how to mark congruence of segments on diagrams • Begin keeping a notebook of definitions • Develop Problem Solving Skills UNDEFINED TERMS • • • • Point Line Plane The three most basic building blocks of geometry. POINT • • • • Has no size. Only has location Represented with a dot Named by a capital letter LINE • Straight continuous arrangement of infinitely many points. • Has infinite length but no thickness • Extends forever in two directions • Named by the letter names of any two points on the line and the line symbol. PLANE • Has length and width, but no thickness. • Flat surface that extends infinitely along its length and width. • Represented with a 4-sided figure, like paper. • Named with a script capital letter. • P ANCIENT “DEFINITIONS” • “A point is that which has no part. A line is breadthless length.” –Greeks • “The line is divided into parts, and that part which has no remaining part is a point.” –Chinese IMPOSSIBLE TO DEFINE • We would have to use the terms point, line, and plane to define them. • So we accept them as undefined and use them to define everything else in Geometry. COLLINEAR • On the same line. COPLANAR • On the same plane RAY • Part of a line • Has an endpoint but extends forever in one direction. ANGLE • Made up of two rays who share an endpoint. LINE SEGMENT • Consists of two endpoints of the segment and all the points between them that are collinear with the two points. CONGRUENT • Two segments are congruent if they have equal measures or lengths. PRACTICE PRACTICE PRACTICE TODAY’S OBJECTIVES • Learn the terminology and notation of points, segments, lines, rays, planes, angles, and collinear and coplanar points. • Learn the idea of congruence of line segments • Learn how to mark congruence of segments on diagrams • Begin keeping a notebook of definitions • Develop Problem Solving Skills EXIT SLIP 1. Draw and mark a figure in which M is the midpoint of ST, SP=PT and T is the midpoint of PQ. 2. Explain your reasoning. 3. Draw an example of collinear points. 4. Define coplanar.