* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II in Europe
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German military administration in occupied France during World War II wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Swedish iron-ore mining during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
Historiography of the Battle of France wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Budapest wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
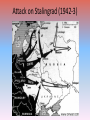
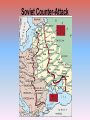
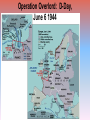
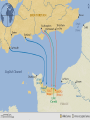
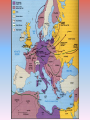
World War II in Europe Chapter 32 World War II September 1, 1939: World War II begins in Europe with the German invasion of Poland. BLITZKRIEG • “Lightning War” – coordinated and rapid attacks of planes, tanks, artillery • Soviets simultaneously took eastern half of Poland • Stalin then took the Baltic countries (Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia) The Winter War (Nov. 1939-March 1940) • When Finland would not give the Soviets military bases on their territory, USSR invaded • USSR failed to occupy Finland, but gained territory Finnish ski troops in Northern Finland Jan. 12, 1940. Fighting in Early 1940 • After invasion of Poland, Germany was idle for 7 months – “Phony War” or “Sitzkrieg” • April 9, 1940: Germany invades Denmark and Norway • May 10: German Army invades France, Belgium, Luxembourg and the Netherlands; Winston Churchill appointed British Prime Minister – French troops mass along Maginot Line Nazi Invasion of France, Netherlands, & Belgium Evacuation of Dunkirk (May-June 1940) • Britain rushed every ship (military or otherwise) to Dunkirk • Saved approx. 338,000 troops, including “Free French” June 22, 1940: France Surrenders • Germany occupied Northern France • Set up puppet government known as Vichy France • Britain now left to fight in Europe alone Winston Churchill and the Battle of Britain Winston Churchill and the Battle of Britain • Hitler’s 1st Fatal Mistake • British RAF (Royal Air Force) pilots defeated the Germans – British had radar • Battle fought over Great Britain from July 10, 1940 to October 31, 1940 • “The Blitz” begins on Sept. 7, 1940 • Germany never able to invade Great Britain Battle of Britain Cartoon • Sept. 27: Tripartite alliance formed between Germany, Italy and Japan – become Axis Powers • By 1940, Axis powers control all of W. Europe except neutral Portugal, Sweden, Switzerland • Spain technically neutral, but really pro-Axis • • • Hungary and Romania join Axis 1941: Bulgaria joins Axis Resistance movements set up in all occupied countries Axis Power Expansion through Sept. 1942 German Attack on USSR • “Operation Barbarossa” • Wanted oil and farmland • Hitler’s 2nd fatal mistake – Generals advised against it – Opened up two-front war • Soviet (“Red”) army not effective or prepared – Stalin had purged (removed) many officers in 1937 • Soviet’s “scorched earth” policy – Supply lines back to Germany too long – Winter came and decimated both sides Siege of Leningrad • The siege lasted for a total of 900 days, from September 8 1941 until January 27 1944. • The city's almost 3 million civilians (including about 400,000 children) refused to surrender and endured rapidly increasing hardships in the encircled city. Food and fuel stocks were limited to a mere 1-2 month supply, and by the winter of 1941-42 there was no heating, no water supply, almost no electricity and very little food. • In January 1942 in the depths of an unusually cold winter, the city's food rations reached an all time low of only ¼ lb.of bread per person per day. • In just two months, January and February of 1942, 200,000 people died in Leningrad of cold and starvation. 2,000,000 people total died in the siege. Allies Turn the Tide • U.S. joins the war after Pearl Harbor attacked (Dec. 7, 1941) – 1st place they attack was in North Africa • In Spring of 1942, Allies gained victory in North Africa over Erwin Rommel, the “Desert Fox”, at the Battle of El Alamein – turning point – Winston Churchill: "Before Alamein we never had a victory, after Alamein we never had a defeat.” Allies Turn the Tide (cont.) • Fall of 1942, Germans defeated by Soviets at Stalingrad • May of 1943, Germans in North Africa Surrender – Key British figure was Bernard Montgomery – First fighting by Americans on the European Front (Dwight D. Eisenhower) • The Invasion of Italy – U.S. General George S. Patton takes Sicily – Mussolini overthrown – “Bloody Anzio” • Italy officailly joins the Allies – Mussolini sets-up a quasi-government in Northern Italy – German soldiers continue to fight in Italy (hold up in the Alps) Attack on Stalingrad (1942-3) More about Stalingrad •Hitler ordered the taking of Stalingrad, and the Battle was waged from July 17, 1942 to Feb. 2, 1943. •Stalingrad was a major industrial city and was on the Volga River, a vital transportation route in Russia that could be cut off if captured. •Also important for propaganda purposes •One of the bloodiest battles/campaigns in history with about 2 million casualties •Urban warfare – fighting took place in streets, from buildings, etc.; snipers used •Battle ended with German 6th Army either killed or captured •Turning point in the War in the East Vassili Zaitsev Soviet Counter-Attack Operation Overlord: D-Day, June 6 1944 D-Day • Preparation for Invasion – Buildup troops in England – Germany prepares the coast of France for invasion • D-Day (June 6, 1944) – – – – Largest landing force in history invade Normandy 24,000 para-troopers sent the night of June 5th 175,000 troops land on the beaches 5,000 ships involved • Invasion successful, though costly • Within weeks all of France was under Allied control Normandy Beaches Assaulted http://www.geocities.com/Hollywood/Studio/1327/images.html http://www.worldwar2database.com/html/normandy.htm Cost of the Battle • Paris liberated on August 25, 1944 • Hitler made one, last desperate counterattack in what became the Battle of the Bulge from Dec. 16, 1944 – Jan. 28, 1945 Battle of the Bulge End of the War in Europe • April 28th, 1945: Mussolini and his mistress executed by members of the Italian resistance Hitler was terrified by Mussolini’s fate and wanted to avoid a similar fate at all costs. End of the War in Europe • By April of 1945, American units were approaching Berlin from the West, while Soviet troops were approaching from the East • Hitler realized it was the end, and committed suicide on April 30th after marrying his long-time mistress, Eva Braun • Germany surrendered on May 7, 1945 (V-E Day) Hitler’s Bunker