* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical System
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
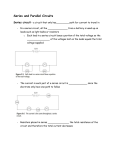
Electrical System An electrical system uses electricity to perform some sort of work. An obvious element of an electrical system is electricity which can be defined as the flow of electrons. Electrons flow from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. When electrons are carefully controlled using various components usually located on a circuit board this is known as electronics. Conductor: A conductor is a substance that easily allows electrons to flow through it. Examples of conductors would be: iron, copper, aluminum, & water. Metals tend to be good conductors of electricity because they usually have "free electrons" that can move easily between atoms. Insulator: An insulator is a type of material which does NOT allow electrons to flow through it. Examples of good insulators would be: plastic & rubber. Semiconductor: A semiconductor uses a material such as silicon to control how much electricity flows through it. A diode is a simple form of a semiconductor; it allows electricity to flow in one direction only. This idea is the heart of computer chips or IC. IC (Integrated Circuit): An integrated circuit contains thousands of components compressed into a microscopic area. With the development of the IC, came the development of small electronic devices. IC’s are found in cars, toys, homes, computers, refrigerators, electronic devices & many other devices. Binary System: A computer logic system that is base 2. The binary language is so simple, it only consists of two words: 1 or 0 (also known as On or Off, and Yes or No). Schematic: A schematic is an electronic blueprint. It shows where all the parts are located and how they are connected. Below is an example of a schematic. Switch: A switch is a gate for electricity, a switch that is “on” allows electrons to flow, a switch that is “off” does not allow electrons to flow. A switch is one way that we help to control electron flow in a circuit. A circuit breaker is a common household item that protects a circuit from an overload. A circuit breaker trips preventing current from flowing too quickly in a circuit. A fuse is similar to a switch, but rather than tripping, it is burned out and must be replaced. A fuse protects the wiring & the circuit from fire & from burning up. GFCI- A Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter AKA a GFCI monitors the amount of current flowing from hot to neutral. If there is any imbalance, it trips the circuit. So let's say you are outside with your power drill and it is raining. You are standing on the ground, and since the drill is wet there is a path from the hot wire inside the drill through you to ground. If electricity flows from hot to ground through you, it could be fatal. The GFCI can sense the current flowing through you because not all of the current is flowing from hot to neutral as it expects -- some of it is flowing through you to ground. As soon as the GFCI senses that, it trips the circuit and cuts off the electricity. Grounding- is to protect the people who use metal-encased appliances from electric shock. The casing is connected directly to the ground prong. If the metal-encased appliance comes in contact with the “hot” wire, the breaker will trip creating an “open” or “off” circuit. This protects the user from electric shock. People who cut off the “ground” or “third” prong from an electrical cord cut off their safety factor. Series Circuit: In a series circuit there is a single path for electrons to flow. If there is an “open” part of the circuit the electricity is stopped. (IE older style X-mass tree lights) Parallel Circuit: In a parallel circuit there are multiple paths for electrons to flow. Current may still flow even if there is a break in the circuit. (IE modern X-mass tree lights.) Ohms Law: explains the relationship between voltage, current and resistance. V = volts A = current (in amps) Ω = resistance (in ohms) Put your finger over the value that you want to find. Multiply the remaining values if side-by-side; divide if one is over the other. Be able to draw the following circuits: Open Circuit: Electrons do not flow. Closed Circuit: Electrons flow. Short Circuit: Electrons flow uncontrolled (no work done).











![Electricity Review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004366833_1-3acacfb89ebe2cacb343dbc81ffd5d6c-150x150.png)