* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Marine Processes - G. Lombardo Radice
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
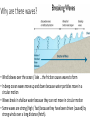
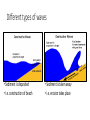
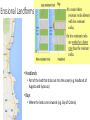
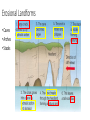
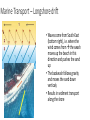
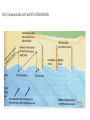
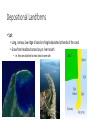
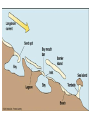
Marine Processes Wave Terminology • Crest: The top of the wave. Trough: The low area in between two waves. Wavelength: The distance between two crests or two troughs. Wave height: The distance between the crest and the trough. Wave Frequency: The number of waves per minute. Velocity: The speed that a wave is traveling. It is influenced by the wind, fetch (distance / open water) and depth of water. Swash: The movement of water and load up the beach. Backwash: The movement of water and load back down the beach. Why are there waves? • Wind blowes over the ocean / lake … the friction causes waves to form • In deep ocean waves move up and down because water particles move in a circular motion • Waves break in shallow water because they can not move in circular motion • Some waves are strong (high / fast) because they have been driven (caused) by strong winds over a long distance (fetch). Different types of waves • Sediment is deposited • I.e. construction of beach • Sediment is taken away • i.e. erosion takes place Marine Erosion • Hydraulic action • Water and rocks rub against each other causing friction • Friction breaks away particles • Corrasion / Abrasion • Rocks rub against each other causing friction • Friction breaks away particles • Corrosion / Solution • Rocks are dissolved in the water e.g. Limesone • Attrition • Rocks bang against each other causing them to break appart Erosional Landforms • Cliffs • steep section of coast line (e.g. near Taormina) • Wave-cut platform • flat area in front of a cliff, formed through erosion by high tide vs. low tide • Cliff recession • The cliff moves in land as it gets eroded Erosional Landforms • Headlands • Part of the land that sticks out into the ocean (e.g. headlands of Augusta and Syracusa) • Bays • Where the land curves inwards (e.g. Bay of Catania) Erosional Landforms • Caves • Arches • Stacks Marine Transport – Longshore drift • Waves come from South-East (bottom right), i.e. where the wind comes from the swash moves up the beach in this direction and pushes the sand up • The backwash follows gravity and moves the sand down verticaly • Results in sediment transport along the shore Effects of groynes • Groynes are build perpendicular into the sea • they stop longshore drift / beach erosion https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U9EhVa4MmEs Coastal Deposition • Sorting of beach material Depositional Landforms • Beach • Sand or shingle deposits between low and high water mark • Shingle forms a steep slope (San Giovanni Li Cuti) • Sand forms a gentle slope (Plaja) Depositional Landforms • Spit • Long, narrow, low ridge of sand or shingle deposited at bends of the coast • Grow from headland across bay or river mouth • i.e. they are attached to main land on one side Depositional Landforms • Bar • Like a spit but attached to the land on both sides • Encloses lagoon behind it Depositional Landforms • Salt Marsh • • • • Forms behind spits and bars Combination of mud flats and grass (salt tolerant) Under water at high tide, exposed at low tide Water flows along it through “tidal creeks Depositional Landforms • Tombolo • A bar that connects the mainland with an island Depositional Landforms • Barrier Island • Small islands, parallel to the coast the have a small lagoon behind it Depositional Landforms • Sand Dunes • • • • Ridges of sand formed at the back of beaches and on spits by wind deposition Ridges are moved inland because of onshore wind New “embryo” dunes are formed near the beach Marram grass stabelises the dunes and prevents the sand from being blown away • If the grass is desroyed “blow outs” can occur