Thesis - UvA-DARE - University of Amsterdam
... sediment particles by bioturbating fauna that functions as a “conveyer belt” (Jørgensen & Nelson 2004; Fig. 2). Iron sulfide and pyrite are transported up to the sediment surface where they are reoxidized to iron (hydro)oxide: FeS2 + 5/2 H 2O + 15/4 O2 à FeOOH + 4H + + 2SO42- (19) Iron (hydro)oxid ...
... sediment particles by bioturbating fauna that functions as a “conveyer belt” (Jørgensen & Nelson 2004; Fig. 2). Iron sulfide and pyrite are transported up to the sediment surface where they are reoxidized to iron (hydro)oxide: FeS2 + 5/2 H 2O + 15/4 O2 à FeOOH + 4H + + 2SO42- (19) Iron (hydro)oxid ...
The geological cycle of plastics and their use as a stratigraphic
... decades to centuries at least. They are easily transported by wind (Gasperi et al., 2015) and water through the environment, where they may accumulate. Plastics are proving to be much more mobile than other human-made materials such as ceramics or glass. It took ceramics thousands of years to achiev ...
... decades to centuries at least. They are easily transported by wind (Gasperi et al., 2015) and water through the environment, where they may accumulate. Plastics are proving to be much more mobile than other human-made materials such as ceramics or glass. It took ceramics thousands of years to achiev ...
Effects of Chemical and Mechanical Weathering Processes on the
... sea floor deposition and burial, black arrows point to ingestion and entanglement by marine organisms, and red arrows indicate water borne debris (modified from Ryan et al. 2009). ...
... sea floor deposition and burial, black arrows point to ingestion and entanglement by marine organisms, and red arrows indicate water borne debris (modified from Ryan et al. 2009). ...
1_Activity_2_Sediments_blank
... nature of the sea floor. This was the first time that such a large and organized attempt was made to study marine sediments and the sea floor. The data it generated has greatly expanded the field of oceanography as well as our understanding of climate change, Earth history, marine resources, natural ...
... nature of the sea floor. This was the first time that such a large and organized attempt was made to study marine sediments and the sea floor. The data it generated has greatly expanded the field of oceanography as well as our understanding of climate change, Earth history, marine resources, natural ...
Benthic Exchange and Biogeochemical Cycling in Permeable
... exchange processes in the sediment surface layers. This fluid exchange tightly couples shelf water column and sedimentary biogeochemical processes. In contrast to the deep ocean, where environmental conditions are relatively constant, on the continental shelves the proximity to land and decreasing wa ...
... exchange processes in the sediment surface layers. This fluid exchange tightly couples shelf water column and sedimentary biogeochemical processes. In contrast to the deep ocean, where environmental conditions are relatively constant, on the continental shelves the proximity to land and decreasing wa ...
Student_Worksheet_sediments
... microscope to determine sediment composition. The sediment observed under the microscope is matched with categories of known grain types such as those shown below, including minerals and mineral groups, volcanic glass, and microfossils. There are whole classes in the GES department at Stanford devot ...
... microscope to determine sediment composition. The sediment observed under the microscope is matched with categories of known grain types such as those shown below, including minerals and mineral groups, volcanic glass, and microfossils. There are whole classes in the GES department at Stanford devot ...
Indicator 3 Quantification and classification of beach litter items
... Please provide scientific background for the indicator including reference materials Surveys of litter stranded or being left on beaches are a primary tool for monitoring the load of litter in the marine environment and have been used world-wide to quantify and describe marine litter pollution. It a ...
... Please provide scientific background for the indicator including reference materials Surveys of litter stranded or being left on beaches are a primary tool for monitoring the load of litter in the marine environment and have been used world-wide to quantify and describe marine litter pollution. It a ...
Stories in IPRC Climate
... out what is buried below the rocks. It is a brutally hot, sunny day. Thank goodness for the canopy that shades at least the 3 m x 3 m hole, which they are digging in order to get a rough estimate of the amount of plastic that has piled up on the beach. Their technique: with the top layer, about 30 c ...
... out what is buried below the rocks. It is a brutally hot, sunny day. Thank goodness for the canopy that shades at least the 3 m x 3 m hole, which they are digging in order to get a rough estimate of the amount of plastic that has piled up on the beach. Their technique: with the top layer, about 30 c ...
Sediments Rock - Dauphin Island Sea Lab
... from a volcano. I was hooked. Sand through a microscope is a fascinating world of fossils, shell fragments, and clues to many unsolved mysteries. As Rachel Carson Said, In every grain of sand is a story of earth." Sand is the term applied to natural particles with a grain diameter between 1/16 mm an ...
... from a volcano. I was hooked. Sand through a microscope is a fascinating world of fossils, shell fragments, and clues to many unsolved mysteries. As Rachel Carson Said, In every grain of sand is a story of earth." Sand is the term applied to natural particles with a grain diameter between 1/16 mm an ...
Answers to STUDY BREAK Questions Essentials 5th Chapter 5
... about 180 million years. Why? As you learned in Chapter 3, tectonic processes form and destroy the seabed over time. Because of subduction, seabed older than about 180 million years is rare. ...
... about 180 million years. Why? As you learned in Chapter 3, tectonic processes form and destroy the seabed over time. Because of subduction, seabed older than about 180 million years is rare. ...
Sediments Are Historical Records of Ocean
... Earth’s hot interior. Marine sediment is composed of particles from land, from biological activity in the ocean, from chemical processes within water, and even from space. The blanket of seafloor sediment is thickest at the continental margins and thinnest over the active oceanic ridges. Sediments m ...
... Earth’s hot interior. Marine sediment is composed of particles from land, from biological activity in the ocean, from chemical processes within water, and even from space. The blanket of seafloor sediment is thickest at the continental margins and thinnest over the active oceanic ridges. Sediments m ...
Waves are “disturbances”
... interfere, creating a higher wave crest. Thus, wave refraction can also increase the height of waves. This typically happens near the shallow water of a “point” or “headland.” The waves bend towards the headland, causing them to come together, increase in height, and pound the headland even more fie ...
... interfere, creating a higher wave crest. Thus, wave refraction can also increase the height of waves. This typically happens near the shallow water of a “point” or “headland.” The waves bend towards the headland, causing them to come together, increase in height, and pound the headland even more fie ...
Lab 4
... pushed along the bottom by fast-flowing water, such as might be found in a fast-flowing stream or where waves break against a beach. These larger grains can thus accumulate in relatively high flow-energy environments. Sand and silt, being intermediate in size, can be moved by moderate flows. Sand, l ...
... pushed along the bottom by fast-flowing water, such as might be found in a fast-flowing stream or where waves break against a beach. These larger grains can thus accumulate in relatively high flow-energy environments. Sand and silt, being intermediate in size, can be moved by moderate flows. Sand, l ...
Shallow-Water Waves
... Pacific Ocean: wind speed of 50 mi/hr, blowing steadily for about 42 hours over a region of size 800 miles will results in 8 meters waves – can get to 17 meter waves! (see Table 10.2) ...
... Pacific Ocean: wind speed of 50 mi/hr, blowing steadily for about 42 hours over a region of size 800 miles will results in 8 meters waves – can get to 17 meter waves! (see Table 10.2) ...
Chapter I - Shodhganga
... only be pushed along the bottom by fast flowing water, such as might be found in a fast flowing stream or where waves break against a beach. These larger grains can thus accumulate in relatively high flow-energy environments. Sand, silt, being intermediate in size, can be moved by moderate flows. Sa ...
... only be pushed along the bottom by fast flowing water, such as might be found in a fast flowing stream or where waves break against a beach. These larger grains can thus accumulate in relatively high flow-energy environments. Sand, silt, being intermediate in size, can be moved by moderate flows. Sa ...
Coastal Sand Dune Systems: Location, Formation, Morphological
... The study area extending between 21°35'48" Northern Latitude and 87°27'17" Eastern Longitude. Balasore’s coastal zone is endowed with a wide range of mangroves, salt marshes, estuaries, lagoons and a unique maritime flora and fauna with a series of parallel sand dunes. The area is a coastal alluvial ...
... The study area extending between 21°35'48" Northern Latitude and 87°27'17" Eastern Longitude. Balasore’s coastal zone is endowed with a wide range of mangroves, salt marshes, estuaries, lagoons and a unique maritime flora and fauna with a series of parallel sand dunes. The area is a coastal alluvial ...
Measurements of atmospheric sea salt concentrations in Hawaii
... Another potentially serious source of errors is variations in the time required to connect or remove a wire. During the first runs, up to 3 min were required to do this but as the operators became more efficient, this period was reduced to half a minute. If, e.g., the cleanest wire was exposed 50% l ...
... Another potentially serious source of errors is variations in the time required to connect or remove a wire. During the first runs, up to 3 min were required to do this but as the operators became more efficient, this period was reduced to half a minute. If, e.g., the cleanest wire was exposed 50% l ...
Waves are moving energy
... When ocean waves encounter land • The wave’s energy must now be packed into less water depth, and so the wave crests become peaked, rather than rounded • Interaction with the bottom slows the incoming wave, but waves behind it continue toward shore at their original speed • This results in a “bunch ...
... When ocean waves encounter land • The wave’s energy must now be packed into less water depth, and so the wave crests become peaked, rather than rounded • Interaction with the bottom slows the incoming wave, but waves behind it continue toward shore at their original speed • This results in a “bunch ...
Waves – Chapter 8
... When ocean waves encounter land • The wave’s energy must now be packed into less water depth, and so the wave crests become peaked, rather than rounded • Interaction with the bottom slows the incoming wave, but waves behind it continue toward shore at their original speed • This results in a “bunch ...
... When ocean waves encounter land • The wave’s energy must now be packed into less water depth, and so the wave crests become peaked, rather than rounded • Interaction with the bottom slows the incoming wave, but waves behind it continue toward shore at their original speed • This results in a “bunch ...
Oceanography Chapter 12
... most notable influences because it keeps particles from settling. Surf and waves carry small particles out to sea. Their affect diminishes further from shore traveled. ...
... most notable influences because it keeps particles from settling. Surf and waves carry small particles out to sea. Their affect diminishes further from shore traveled. ...
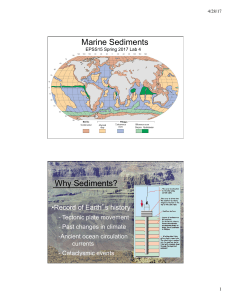
Marine Sediments Why Sediments?
... – Impact deposits • Form when large asteroids or comets collide with Earth • These impacts blast meteorite material great distances ...
... – Impact deposits • Form when large asteroids or comets collide with Earth • These impacts blast meteorite material great distances ...
mineral sands - Minerals Council of Australia
... to rivers and streams and in to the sea. These heavy minerals were then carried back onto the beach by waves, which in turn drag the lighter minerals such as quartz back into the sea. The tidal process leaves the heavy minerals on the beach. Wind further concentrates the heavy minerals as the lighte ...
... to rivers and streams and in to the sea. These heavy minerals were then carried back onto the beach by waves, which in turn drag the lighter minerals such as quartz back into the sea. The tidal process leaves the heavy minerals on the beach. Wind further concentrates the heavy minerals as the lighte ...
Ocean page samples
... Name the person who discovered the East Australian current and explain how it was discovered. ...
... Name the person who discovered the East Australian current and explain how it was discovered. ...
Sediments - cloudfront.net
... Think about Movement, transport, how did the sediment arrive, where did it come from, and how can we tell the story of the ocean basin ...
... Think about Movement, transport, how did the sediment arrive, where did it come from, and how can we tell the story of the ocean basin ...
PDF - compatibile with Acrobat 4.0
... of many areas along the Egyptian coast; most of the associated amenities are located there. The success of the tourist industry in those areas is often associated with an intact natural environment, and so water quality is an important factor for tourists in their choice of destination and should no ...
... of many areas along the Egyptian coast; most of the associated amenities are located there. The success of the tourist industry in those areas is often associated with an intact natural environment, and so water quality is an important factor for tourists in their choice of destination and should no ...
Beach

A beach is a landform along the coast of an ocean or sea, or the edge of a lake or river. It usually consists of loose particles, which are often composed of rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles, or cobblestones. The particles comprising a beach are occasionally biological in origin, such as mollusc shells or coralline algae.Some beaches have man-made infrastructure, such as lifeguard posts, changing rooms, and showers. They may also have hospitality venues (such as resorts, camps, hotels, and restaurants) nearby. Wild beaches, also known as undeveloped or undiscovered beaches, are not developed in this manner. Wild beaches can be valued for their untouched beauty and preserved nature.Beaches typically occur in areas along the coast where wave or current action deposits and reworks sediments.