* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Env. Sci. Midterm Exam Review
Survey
Document related concepts
River ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
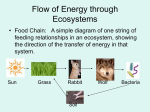
Env. Sci. Midterm Exam Review Renewable resources Hunter-gatherer, Agricultural, Industrial Revolution Biodiversity - # and variety of species in an area Loss of biodiversity concern, (food & oxygen) Law of supply and demand – availability, worth Variable – factor of interest Control – does not receive treatment Observation, hypothesis, conclusion Mean = average Env. Sci. Midterm Exam Review Ozone layer located in stratosphere Radiation, convection, conduction Gravities effects Greenhouse effect Hydrosphere, biosphere Ice caps and glaciers - most of Earth’s fresh water Earth – closed for matter, open for energy(sun) Biodegradable, breaks down naturally Ecosystem Sun provides energy in most ecosystems Env. Sci. Midterm Exam Review Organisms, species, populations, communities Survival – have or lack certain traits, reproduce Coevolution – response to long-term interactions. 6 Kingdoms for environmental, 5 for biology Bacteria convert nitrogen into a usable form Biotic and abiotic Bacteria and fungi both break down dead organisms Bacteria have only cell walls, no nuclei Protists and plants use energy from sun to make food Env. Sci. Midterm Exam Review Bacteria, fungi and plants all have cell walls Angiosperms and gymnosperms 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen Energy consumed stored in fat and sugar molecules Plants – photosynthesis – carbon back to ecosystem Carbon sink – i.e. limestone rock Biomes – usually described by their vegetation Tundra, grasslands, tropical rain forest Latitude = distance N & S of equator; longitude Env. Sci. Midterm Exam Review Temperature and precipitation = plants in a biome Estuaries – fresh nutrients from rivers & oceans Flagella – phytoplankton adaptation to prevent sinking Littoral, abundant life – benthic, bottom/deep Water absorbs light, no photosynthesis in deep water Only 10% stored energy available on food chain Cellular Respiration – (photosynthesis in reverse!) produces organism’s energy, with oxygen as the primary reactant.