* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 20150210090647
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Silverthrone Caldera wikipedia , lookup
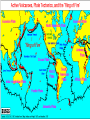
Volcanoes Get Ready for an ERUPTION!!! What is a volcano? • A weak spot in the crust where molten material, or magma, comes to the surface • Magma- melted rocks and minerals from the mantle • Lava- Magma that reaches the surface Where are volcanoes located? • Volcanoes can be found: – Diverging Plate boundaries (mid-ocean ridge) – Converging plates with subduction zones • Oceanic plate vs. oceanic plate • Oceanic plate vs. continental plate – Hot spots • Area where magma from deep within the mantle melts through the crust like a blow torch – Example: Hawaiian Islands What is the Ring of Fire? • The majority of Volcanoes on earth are located around the edge of the Pacific Plate, which is the tectonic plate that holds the Pacific ocean. • The outer boundary of this plate is nicknamed the Ring of Fire because of the number of Earthquakes and Volcanoes that occur there. Results of Volcanoes • Are constructive: – add new rock to existing land – form new islands • Can be destructive – explosive eruptions changes the landscape of and around the volcano Eruptions • Why do volcanoes erupt? – Less dense magma seeps upward through cracks and creates volcanoes – Gas in the magma is trapped and builds pressure – Closer it gets to surface the less pressure it has and the gases separate (bubbles) – Gases dissolve on the surface and magma is carried out Types of Eruptions • determined by amount of silica (material made from the elements oxygen and silicon) • 2 types: – Quiet • Lava moves steadily and easily – Explosive • Thick, sticky lava plugs vent like a cork and builds up pressure • Explodes and releases pyroclastic flow – Volcanic ash: fine, rock particles – Cinders: pebble sized particles – Bombs: baseball to car sized particles Types of Rocks Produced • Type of lava produces different types of rocks – High silica lava: thicker, sticky, lighter colored • Rhyolite • Pumice • obsidian – Low silica lava: flows readily, dark colored • basalt Stages of a Volcano • Active: (live) erupting or has shown signs that it may erupt In the near future • Dormant: (Sleeping) is not currently erupting but may/can erupt in the future • Extinct: (dead) unlikely to erupt again Other Volcanic Activity • Hot springs – Groundwater is heated by near by magma rising to the surface and collects in natural pools Other Volcanic Activity • Geyser – Rising hot water and steam that gets trapped underground and builds pressure until it sprays to the surface Land Formations from Lava & Ash • Shield Volcano – Created by hot spots – Gently sloping • Cinder Volcano – Steep – Cone-shaped hill/mountain • Composite Volcano – Tall, cone-shaped mountain – Alternating layers of ash and lava Land Formations from Lava & Ash • Lava Plateaus – Lava moves far from the volcano before cooling which forms high plateaus • Calderas – Huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain • All magma has been emptied leaving a hollow shell that collapses