* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.4.2 Inverting Amplifier Word Document | GCE AS/A
Oscilloscope wikipedia , lookup
Audio crossover wikipedia , lookup
Loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Superheterodyne receiver wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Home cinema wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Cellular repeater wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Instrument amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Standing wave ratio wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Wilson current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Distortion (music) wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Scattering parameters wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Public address system wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
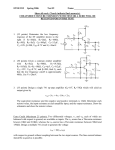
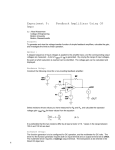
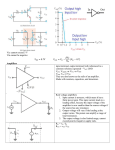
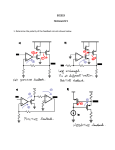
Topic 1.4.2 – Inverting amplifier Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; draw and recognise the inverting amplifier circuit; design an inverting amplifier using resistive negative feedback to achieve specified voltage gain; select and use the formulae G Vout R f . Vin R in use the approximation that the input impedance is equal to the resistance of the input resistor. 1 Module ET1 Introduction to Analogue and Digital Systems. Inverting Amplifier. The first amplifier that we will look at is the inverting amplifier. The circuit diagram for this type of amplifier is shown below: Rf +V Rin Note : The power supply connections are often left off the diagram of the amplifier to make the circuit easier to follow. Vin + -V Vout 0V The voltage gain of this amplifier is given by the following formulae. Voltage Gain Vout R f Vin R in Important things to remember for this amplifier are as follows: i. Voltage gain can be determined either if Vout and Vin are known or if Rf and Rin are known. ii. The ‘-‘ sign in the formula indicates the inverting action of this amplifier, so for a positive input voltage, the output will be negative, and vice versa. iii. The input impedance of this amplifier is equal to the value of Rin. iv. If you are designing an amplifier of this type then all resistors chosen must be greater than 1kΩ. We will now look at an example: 2 Topic 1.4.2 – Inverting amplifier Example 1: An inverting amplifier is required to act as a preamplifier for a public address system. The amplifier requires a gain of -20 and should have an input impedance of 10kΩ. (a) Draw the circuit diagram for an inverting amplifier. Rf Rin + Vin Vout 0V (b) Determine suitable resistors for Rin and Rf. In the question we are told that the input impedance must be 10kΩ. This means that Rin must be equal to 10kΩ. We are also told that the gain needs to be -20, so we now apply the gain formula as shown below; Gain Rf R in Rf 10 R f 20 10 20 R f 200k 3 Module ET1 Introduction to Analogue and Digital Systems. Example 2. The following circuit shows an inverting amplifier connected to a ±10V power supply. 120kΩ 2kΩ + Vin Vout 0V (a) (b) What is the voltage gain of this amplifier ? Gain Rf R in Gain 120 60 2 If Vin = 100mV, determine the value of Vout. Gain Vout Vin Vout 100 60 100 6000mV 6V 60 Vout (c) What is the input impedance of this amplifier ? Input impedance = Rin = 2kΩ 4 Topic 1.4.2 – Inverting amplifier (d) The graph below shows an alternating signal applied to Vin. On the axes below sketch the graph of Vout. Vin/mV 100 75 50 25 0 -25 -50 -75 -100 Vout/V Peak output voltage = peak input voltage x gain 8 6 4 2 0 -2 -4 -6 -8 Output graph inverted - i.e. negative becomes positive etc. Frequency remains the same Here are a couple of examples for you to do ! 5 Module ET1 Introduction to Analogue and Digital Systems. Exercise 1: 1. The following circuit shows an inverting amplifier connected to a ±12V power supply. 390kΩ 13kΩ Vin + Vout 0V (a) What is the voltage gain of this amplifier ? ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... (b) If Vin = 300mV, determine the value of Vout. ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... (c) What is the input impedance of this amplifier ? Input impedance = ........................................... 6 Topic 1.4.2 – Inverting amplifier (d) The graph below shows an alternating signal applied to Vin. On the axes below sketch the graph of Vout. Label the graph of Vout with suitable values. Vin/mV 300 225 150 75 0 -75 -150 -225 -300 Vout/V 0 7 Module ET1 Introduction to Analogue and Digital Systems. 2. An inverting amplifier is required to act as a preamplifier for an electric guitar pickup. The amplifier requires a gain of -400 and should have an input impedance of 2kΩ. (a) Draw the circuit diagram for an inverting amplifier. (b) Determine suitable resistors for Rin and Rf. ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... ....................................................................................................................................... 8 Topic 1.4.2 – Inverting amplifier Solutions to Student Exercises. Exercise 1: 1. (a) Gain Rf R in Gain 390 30 13 (b) Gain Vout Vin Vout 300 30 300 9000mV 9V 30 Vout (c) Input impedance = Rin = 13kΩ (d) Vout/V 12 9 6 3 0 -3 -6 -9 -12 9 Module ET1 Introduction to Analogue and Digital Systems. 2. (a) Rf Rin + Vin Vout 0V (b) Rin = 2kΩ, (since input impedance should be 2kΩ.) Gain Rf R in Rf 2 R f 400 2 400 R f 800k No examination questions have been included with this section, as these will be included in Topic 1.4.5 – Practical voltage amplifiers. 10 Topic 1.4.2 – Inverting amplifier Self Evaluation Review Learning Objectives My personal review of these objectives: draw and recognise the inverting amplifier circuit; design an inverting amplifier using resistive negative feedback to achieve specified voltage gain; select and use the formulae G Vout R f Vin R in use the approximation that the input impedance is equal to the resistance of the input resistor. Targets: 1. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2. ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 11