* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 555timer - EngineeringDuniya.com
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
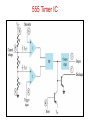
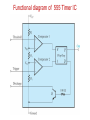
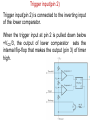
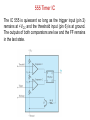
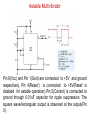
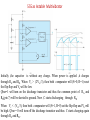
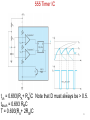
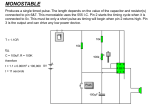
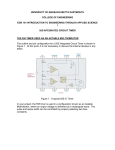
555 Timer by D.V.Kamat , Faculty Department of E&C Engg., MIT 555 Timer IC The 555 Timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of timer and multivibrator applications. The IC was brought to market in 1971 by Signetics (later acquired by Philips).The original name was the SE555 (metal can)/NE555 (plastic DIP). It has been claimed that the 555 gets its name from the three 5 kΩ resistors used in typical early implementations. 555 IC specifications The typical specifications of NE555 are as follows: Supply voltage (VCC) Output current (maximum) Compatible with Operating temperature 3 to 15 V 200 mA TTL,CMOS ICs 0 to 70 °C 555 Timer IC Functional diagram of 555 Timer IC 555 Timer IC Inside 555 timer IC ,there are two comparators : Upper noninverting comparator and Lower inverting comparator A resistive voltage divider consisting of three 5 KΩ resistors provide reference voltages of 2/3 of the Vcc to the upper comparator and 1/3 of the Vcc to the lower comparator. These two reference voltages aid in determining the timing interval. The outputs of upper and lower comparators are fed to R and S of SR FF respectively. The Qbar of SR FF is driving the discharge transistor(NPN) whose collector terminal is connected to pin 7 (Discharge terminal). According to the output of FF, the transistor switches to its cut-off region or saturation region. Control input(pin 5) • The reference voltage to the upper comparator can be varied by applying a modulation voltage to the control input terminal(pin 5). • In most of the time this pin is unused. In applications ,where no such modulation is intended ,it is recommended that a 0.01uF capacitor be connected between control pin and ground to bypass the power supply noise. Trigger input(pin 2) Trigger input(pin 2) is connected to the inverting input of the lower comparator. When the trigger input at pin 2 is pulled down below +VCC/3, the output of lower comparator sets the internal flip-flop that makes the output (pin 3) of timer high. Threshold input(pin 6) Threshold input(pin 6) is connected to the non-inverting input of the upper comparator. However, if the threshhold input(pin 6) is now raised above +2VCC/3,the output will return to ground and the discharge transistor will be turned on again. When the threshhold input returns to ground, the IC will remain in this state. The easiest way to allow the threshhold voltage (pin 6) to gradually rise to (2/3)+VCC is to connect it to a capacitor being allowed to charge through a resistor. In this way we can adjust the R and C values for almost any time interval we might want. 555 Timer IC The IC 555 is quiescent so long as the trigger input (pin 2) remains at +VCC and the threshold input (pin 6) is at ground. The outputs of both comparators are low and the FF remains in the last state. Reset Input(pin 4) • The reset input is of active-low type and can be used to reset the FF in a manner to override the effect of set input of the FF coming from lower comparator. • When reset input is at Low(less than about 0.4V) the reset transistor conducts and forces the output of timer to Low. • When the reset is not used or to be disabled, it is to be connected to VCC. Discharge pin(pin 7) • If the SR FF is in reset condition (S=0 , R=1) ,then Qbar is high which turns on the discharge transistor ,thus grounding whatever is connected to the discharge pin. 555 Timer IC Pin Name Purpose 1 GND Ground, low level (0 V) OUT rises, and interval starts, when this input 2 TRIG falls below 1/3 VCC. 3 OUT This output is driven to +VCC or GND. A timing interval may be interrupted by driving 4 RESET this input to GND. "Control" access to the internal voltage divider 5 CTRL (by default, 2/3 VCC). The interval ends when the voltage at THR is 6 THR greater than at CTRL. Open collector output; may discharge a 7 DIS capacitor between intervals. V+, Positive supply voltage is usually between 3 8 VCC and 15 V. 555 Timer for multivibrator applications The 555 has three operating modes: Monostable mode: In this mode, the 555 functions as a "one-shot". Applications include timers, touch switches, frequency divider, capacitance measurement etc Astable or free running mode: In this mode, 555 can operate as an oscillator. Uses include LED and lamp flashers, moving displays, square wave/pulse generation, clock generation for logic circuits, tone generation, security alarms etc. Bistable mode : the 555 can operate as a flip-flop. 14 Applications of 555 Timer • The 555 can operate in either monostable or astable mode, depending on the connections to and the arrangement of the external components. • In the monostable mode , it can either produce a single pulse when triggered. • In astable mode , it can produce a continuous pulse train as long as it remains powered. No trigger input needs to be applied. Astable Multivibrator Pin 8(Vcc) and Pin 1(Gnd) are connected to +5V and ground respectively. Pin 4(Reset’) is connected to +5V(Reset’ is disabled for astable operation).Pin 5(Control) is connected to ground through 0.01uF capacitor for ripple suppression. The square wave/rectangular output is observed at the output(Pin 3). Astable Multivibrator The trigger(Pin 2) and threshold(Pin 6) are shorted and connected to a capacitor C .Here ,both the trigger and threshold inputs are controlled by the capacitor voltage and thus the 555 Timer can trigger itself repeatedly. No external trigger input is applied as in Monostable multivibrator. In this case, two resistors RA and RB are in the capacitor charging path so that one of them can also be in the capacitor discharge path. The common point of RA and RB are connected to Discharge(Pin 7) terminal. 555 as Astable Multivibrator Initially ,the capacitor is without any charge. When power is applied ,it charges through RA and RB . When Vc > (2Vcc/3), then both comparator will (S=0, R=1) reset the flip-flop and Vo will be low. Qbar=1 will turn on the discharge transistor and thus the common point of RA and RB(pin 7) will be shorted to ground. Now ,C starts discharging through RB . When Vc < (Vcc/3), then both comparator will (S=1, R=0) set the flip-flop and Vo will be high. Qbar = 0 will turn off the discharge transistor and thus C starts charging again through RA and RB . 555 Timer IC tch = 0.693(RA+ RB)C Note that D must always be > 0.5. tdisch = 0.693 RBC T = 0.693(RA+ 2RB)C 19 555 Timer Astable operation In this mode, the initial pulse when power is first applied is a bit longer than the others, having a duration of 1.1(RA+ RB)C. However, from then on, the capacitor alternately charges and discharges between the two comparator threshhold voltages. When charging, C starts at (1/3)VCC and charges towards VCC. However, it is interrupted exactly halfway there, at (2/3)VCC. Therefore, the charging time, t1 = 0.693 RA + RB)C. When the capacitor voltage reaches (2/3)VCC, the discharge transistor is enabled (pin 7), and this point in the circuit becomes grounded. Capacitor C now discharges through RB alone. Starting at (2/3)VCC, it discharges towards ground, but again is interrupted halfway there, at (1/3)VCC. The discharge time, t2= 0.693(RB)C. The total period of the pulse train is t1 + t2, or 0.693(RA + 2RB)C. The output frequency of this circuit is the inverse of the period, or 1.44/(RA + 2RB)C. Note that the duty cycle of the 555 timer circuit in astable mode cannot reach 50%. On time must always be longer than off time, because RA must have a resistance value greater than zero to prevent the discharge transistor from directly shorting VCC to ground. Such an action would immediately destroy the 555 IC. 20 Applications of 555 Timer • • • • • • • Precision timing Pulse generation Sequential timing Time delay generation Pulse width modulation Pulse position modulation Linear ramp generator … END 21