* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chromosomal Anomalies
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Frontonasal dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Spina bifida wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
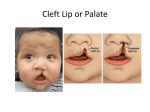
Categories of Factors Responsible for Birth Defects Abnormalities of Individual Genes (Single Gene Defects) Chromosomal Abnormalities Intrauterine Injury Multifactorial Circumstances Chromosomal Abnormalities Trisomy 21 Turner Syndrome Klinefelter’s Syndrome Chromosomal Anomalies Result from abnormal karyotypes (physical arrangement of chromosomes) resulting from: Non-disjunction - occurred during meiotic division resulting in aneuploidy or too many chromosomes Deletion - loss of genetic material Translocation - relocation of a chromosome strand on some non-homologous chromosome Trisomy 21- Downs Syndrome Epidemiology 1/800-1, 000 live births. In the United States over 350,000 people have Down syndrome At least 20 percent will be stillborn. 6-10% of all mental retardation in the U.S. Trisomy 21- Downs Syndrome Syndrome Structural- facial abnormalities, floppy joints, small stature, CV defects Functional- Immune defects, varying degrees of mental retardation Trisomy 21- Downs Syndrome RELATIONSHIP OF DOWN SYNDROME INCIDENCE TO MOTHERS' AGE Mothers Age Incidence of Down Syndrome Under 30 Less than 1 in 1,000 30 1 in 900 35 1 in 400 36 1 in 300 37 1 in 230 38 1 in 180 39 1 in 135 40 1 in 105 42 1 in 60 44 1 in 35 46 1 in 20 48 1 in 16 49 1 in 12 Trisomy 21- Downs Syndrome Anomalies of the Sex Chromosomes Failure of the X chromosome to separate during meiosis Very Common May be asymptomatic Wrong number of sex chromosomes Anomalies of the Sex Chromosomes Most Common Possibilities: Mom XX Dad O X XXX XO Y XXY YO Turner’s Syndrome XO Syndrome: * Morphologically female, but no functional ovaries. Structural- Short stature, shield chest, growth delay, prominent ears, increase risk for CVD, diabetes, infections Functional- carrying degrees of mental retardation, may be very mild and imperceptible Epidemiology: 1/2,000 live births Treatment: Estrogen therapy, psychosocial counseling Klinefelter’s Syndrome XXY Epidemiology: 1/500-1/2000 live births Syndrome: morphologically male relatively normal secondary sex characteristicsoften sterile due to lack of development of germ cells in the testes Structural- tall for age, narrow shoulders, broad hips Functional- intelligence is usually normal but some developmental delays Categories of Factors Responsible for Birth Defects Abnormalities of Individual Genes (Single Gene Defects) Chromosomal Abnormalities Intrauterine Injury Multifactorial Circumstances Intrauterine Injury Congenital abnormalities result from exposure to teratogenic substances. Teratogens take many forms- drugs, infectious agents, trauma. Generally the degree of damage is a function of two things: 1. The amount exposure 2. The time of exposure related to gestational age Fetal Alcohol Syndrome * Leading cause of preventable birth defects in this country Epidemiology: 3.5 per 10,000 live births Syndrome: Structural- Facial dismorphology, low ear set, broad mid-facial region, narrow eye slits, microcephaly, CV defects, postnatal growth deficiency Functional- Attention deficits, varying degrees of mental retardation and language deficits Tobacco Currently, about 13 percent of pregnant women in the U.S. smoke during pregnancy. In 1998, 12 percent of babies born to smokers in the U.S. were of low birth weight, compared to 7.2 percent of babies of nonsmokers. Studies by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) also suggest that smoking increases the risk of preterm delivery by about 30 percent. Cocaine •Prematurity •Lower birth weight, shorter •Smaller head circumference •A piercing cry, which is apparently indicative of neurological dysfunction •Lower Apgar score •Irritability and hypersensitivity. The newborn shoots from sleep to screaming and is inconsolable. •Poor feeding •High respiratory and heart rates •Tremulousness •Startling responses •Poor sleep patterns Isotretinoin (Accutane) Accutane: a type of retinoic acid that is orally administered and used in the treatment of acne and several other skin diseases. Causes: Increased risk of Spontaneous abortion CV defects Parathyroid hormone deficiency CNS abnormalities including cerebral abnormalities, cerebellar malformation, hydrocephalus, microcephaly, cranial nerve deficit Rubella Syndrome Syndrome: Caused by the Rubella Virus Occurs as a result of fetal viremia creating inflammation in the arteries Limits O2 supply to developing tissues. Results: Problematic if contracted during pregnancy 1st month - 50%, 1st trimester - 25%, 3rd trimester - 8% There is a 20% chance of mortality within the first 18 months of life Causes: Hearing loss, learning disabilities, growth retardation, heart defects Categories of Factors Responsible for Birth Defects Abnormalities of Individual Genes (Single Gene Defects) Chromosomal Abnormalities Intrauterine Injury Multifactorial Circumstances Multifactorial Disorders Abnormalities that reflect the combined effects of multiple genes interacting with environmental agents. Spina Bifida- Failure of the spinal column to close around the spinal cord The amount left unclosed and the location (high or low) determines the risk or problems. Other examples- cleft palate and club feet Multifactorial Disorders In general, the three types of spina bifida (from mild to severe) are: 1. Spina Bifida Occulta: There is an opening in one or more of the vertebrae (bones) of the spinal column without apparent damage to the spinal cord. 2. Meningocele: The meninges, or protective covering around the spinal cord, has pushed out through the opening in the vertebrae in a sac called the "meningocele." However, the spinal cord remains intact. This form can be repaired with little or no damage to the nerve pathways. 3. Myelomeningocele: This is the most severe form of spina bifida, in which a portion of the spinal cord itself protrudes through the back. In some cases, sacs are covered with skin; in others, tissue and nerves are exposed. Generally, people use the terms "spina bifida" and "myelomeningocele" interchangeably. Multifactorial Disorders cleft palate A cleft palate is an opening in the roof of the mouth in which the two sides of the palate did not fuse, or join together, as the unborn baby was developing. One of every 600 newborns is affected by cleft palate. A child born with a cleft frequently requires several different types of services, e.g., surgery, dental/orthodontic care, and speech therapy, all of which need to be provided in a coordinated manner over a period of years.