* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics Study Guide
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
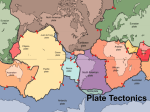
Plate Tectonics Study Guide 1. What is the layer of Earth called that’s made up of the rocks basalt and granite? 2. As you go deeper beneath Earth’s surface, what happens to the temperature and pressure beneath the surface? 3. How do geologists study Earth’s interior? 4. List the layers of the Earth starting at the surface and going towards the center. 5. What is ridge push? crust It increases Seismic waves Crust, mantle, outer core, inner core oceanic crust slides downhill under the continental crust due to gravity 6. What is slab pull? oceanic crust is denser than continental crust, so it pulls the rest of the plate with it as it sinks into the mantle 7. Where are the convection currents located that move Earth’s plates? The Athenosphere 8. What is a convection current? the movement of heat energy throughout a fluid caused by differences in temp/density 9. What happens to convection currents when the heat source is removed? they stop 10. What does Wegener’s theory of continental drift state? All continents have once been joined together and have since drifted apart 11. What is the name of the super continent that existed millions of years ago called? Pangaea 12. What do we call any trace of an ancient organism preserved in rock? fossil 13. What are the three categories of evidence Landforms, fossils, ancient climates Wegener used to support his theory of continental drift? 14. Why was Wegener’s theory rejected by No explanation of the force that moved the geologists of his time? continents 15. What do we call the longest chain of mountains in the world? Mid-ocean ridge 16. In the mid-1990’s what technology did scientists use to map the ocean floor? Sonar 17. In sea-floor spreading where on the ocean floor At the mid-ocean ridge does molten material erupt onto the ocean floor? 18. What were scientists able to determine by taking drilling samples of the ocean floor? The age of the rocks at the center of the ridge were youngest 19. What did deep diving submersibles observe at the mid-ocean ridge? Pillow lava 20. What is the term used to describe ocean floor sinking into a deep-ocean trench? subduction 21. As new oceanic crust cools, what happens to its density? It increases 22. What is the force that causes Earth’s plates to move? Convection currents in the asthenosphere 23. What is the name of the theory that states that Plate Tectonics Earth’s plates are in constant slow motion? 24. What do we call a boundary where two plates collide? 25. If two continental plates collide, what is produced? 26. What do we call a boundary where two plates slip past one another? 27. What type of rock primarily makes up oceanic crust? 28 What type of rock primarily makes up continental crust? 29. What is the name of the boundary where two plates are moving away from each other? 30. What happens to a plate, as it is subducted into the mantle? Convergent Boundaries mountain ranges transform boundaries Basalt Granite divergent boundaries It melts and returns into magma. 31. What type of boundary occurs at a subduction zone? Convergent boundaries 32. What geologic feature is formed at a divergent boundary? Mid-ocean ridge/rift valley 33. What is being created at a mid-ocean ridge? Mountain chains/ new crust 34. Describe the crust: very thin, solid layer, least dense, coolest, upper 35. Describe the mantle: 67% of Earth’s mass, rock is soft (plastic/putty like), pressure, density, temperature increase as you go deeper. Convection currents here drive plate tectonics 36. Describe the core: 33% of mass, deepest, densest, hottest layer. Has two parts, inner and outer. 37. What is the lithosphere? Crust and rigid part of the mantle. Divided into tectonic plates. 38. What is the asthenosphere? “Plastic” layer of the upper mantle. Tectonic plates float on this layer. 39. What is the mesosphere? Strong, lower portion of the mantle 40. What is the outer core? Liquid iron and nickel, spins rapidly to create the Earth’s magnetic field 41. What is the inner core? Solid iron and nickel 42. What was Rodinia? Super-continent before Pangaea 43. Where is old crust destroyed? subduction zone 44. Where is new crust created? mid-ocean ridge/rift valley 45. Describe the three ways mountains are formed: Folded mountains: squeezed together (converging boundary) and forced upwards (Alps, Himalayas) Fault block mountains: Caused by tension (diverging boundary) causes areas to drop down relative to other rocks. Makes these other rocks higher. Volcanic mountains: usually at convergent zones where old crust is subducted. Create ranges of volcanic mountains or island arcs of volcanic islands. Draw a Convergent Boundary Draw a Transform Boundary Draw a Divergent Boundary