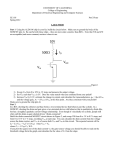
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download V to
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
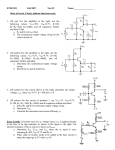
12.5 Common Source Amplifiers vin? vo ? Voltage gain Av=vo/ vin? Common-Source Amplifiers •C1 and C2 are coupling capacitors and Cs is the bypass capacitor. The capacitors are intended to have large impedances for the dc signal and very small impedances for the ac signal. 1 Zc j 2fC Zc , f 0 Zc 0, f 0, or C is large Common-Source Amplifiers •For DC analysis, the capacitors are replaced by open circuits to determine the quiescent operation point (Q point). The transconductance gm for the small-signal equivalent circuit is also determined. •For AC analysis, the capacitor are replaced by short circuits to determine the ac voltage gain Av=vo/vin. DC Analysis Coupling capacitors DC voltage sources Bypass capacitors The Small-Signal Equivalent Circuit •In small-signal midband analysis of FET amplifiers, the coupling capacitors, bypass capacitors, and dc voltage sources are replaced by short circuits. •The FET is replaced with its small-signal equivalent circuit. Then, we write circuit equations and derive useful expressions for gains, input impedance, and output impedance. AC Analysis DC voltage sources Coupling capacitors Bypass capacitors DC voltage sources Coupling capacitors Bypass capacitors SMALL-SIGNAL EQUIVALENT CIRCUITS (12.4) id (t ) g m v gs (t ) A more complex equivalent circuit consider drain resistance rd 1 rd id (t ) g m vgs (t ) vds / rd iD v DS Q point Common Source Amplifiers: FET source 端接ground Common Source Amplifiers: Equivalent load resistance 1 RL 1 rd 1 RD 1 RL Input voltage & output voltage vo g m v gs RL vin v gs Voltage Gain vo Av g m RL vin Common Source Amplifiers: Input Resistance vin Rin RG R1 R2 iin Output resistance •disconnect the load, •replace the signal source by the internal resistance, • find the resistance by looking into the output terminals. 1 Ro 1 RD 1 rd Example 12.4 Analyze the following circuit. KP=50uA/V2, Vto=2 V, L=10um, W=400um (identical to example 12.2). Assume v(t ) 100 sin( 2000t )mV rd Find •midband voltage gain •input resistance •output resistance •output voltage Example 12.4 Analyze the following circuit. KP=50uA/V2, Vto=2 V, L=10um, W=400um (identical to example 12.2). DC Analysis Fine Q point (see example 12.2) I DQ K (VGSQ Vto )2 0.784mA Example 12.4 Analyze the following circuit. KP=50uA/V2, Vto=2 V, L=10um, W=400um (identical to example 12.2). AC Analysis Fine gm(see Ch 12.4) g m 2 K (VGSQ Vto ) 2 KP W / L I DQ 1.77mS Equivalent load resistance 1 RL 3197 1 rd 1 RD 1 RL Voltage Gain ( rd ) vo Av g m RL 5.66 vin Example 12.4 Analyze the following circuit. KP=50uA/V2, Vto=2 V, L=10um, W=400um (identical to example 12.2). Input Resistance vin Rin RG R1 R2 750k iin 1 RD 4.7 k 1 RD 1 rd Rin vin (t ) vgs (t ) v(t ) 88.23 sin( 2000t )mV Rin R Output Resistance R o Input voltage Output voltage vo (t ) Av vin (t ) 500 sin( 2000t )mV 12.7 CMOS Logic Gate CMOS: Complementary Metal-Oxide- Semiconductor (互補 式金氧半導體是一種積體電路製程,可在矽晶圓上製作出 PMOS(P-channel MOSFET)和NMOS(N-channel MOSFET)元件,由於PMOS與NMOS在特性上為互補性 ,因此稱為CMOS。 MOSFET Summary VGS=VDD (high) VGS= −VDD NMOS ON PMOS ON VGS=0 (low) NMOS OFF VGS=0 PMOS OFF CMOS Inverter NMOS VGS=Vin Vin=VDD (high) PMOS VGS= Vin -VDD NMOS VGS= VDD ON, PMOS VGS= 0 OFF, Vout=0 (low) Vin=0 (low) NMOS VGS= 0 OFF PMOS VGS= -VDD ON, Vout= VDD (high) CMOS NAND Gate 1. A= high & B= high M1 and M2 OFF M3 and M4 ON Vout low 2. A= low & B= low M1 and M2 ON M3 and M4 OFF Vout high CMOS NAND Gate 3. A= high & B= low M1 OFF and M2 ON M3 ON and M4 OFF Vout high 4. A= low & B= high M1 ON and M2 OFF M3 OFF and M4 ON Vout high CMOS NOR Gate 1. A= low & B= low 3. A= high & B= high M1 and M2 ON M1 and M2 OFF M3 and M4 OFF M3 and M4 ON Vout high Vout low 2. A= high & B= low M1 and M4 OFF M2 and M3 ON Vout low