* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Flowering Plants
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
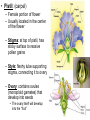
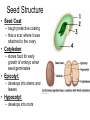
Plant Reproduction Sexual Reproduction in flowering plants (3 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1OFF2qYvLag&safe=active Crash Course: Sexual Reproduction in Plants (10 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ExaQ8shhkw8&safe=active Sexual Reproduction • Flowering Plants (Angiosperms) – Most successful and abundant modern day plants – Reproductive structures found in flowers – Seeds are enclosed with a “fruit” while developing Flower Structure • Stamens: – Male portion of flower – Filament stalk with anther tip produces pollen grains – Often more than one – Thick walled pollen grains contain 2 monoploid gametes • Pistil: (carpel) – Female portion of flower – Usually located in the center of the flower – Stigma: at top of pistil, has sticky surface to receive pollen grains – Style: fleshy tube supporting stigma, connecting it to ovary – Ovary: contains ovules (monoploid gametes) that develop into seeds • The ovary itself will develop into the “fruit” • Rings of modified leaves surround the reproductive organs of the flower – Sepals: • form a ring around the base of the flower • Enclose and protect the flower bud before it blooms – Petals: • often brightly colored to attract pollinators Pollination • Transfer of pollen from anther to stigma – Self Pollination: flower pollinates itself – Cross Pollination: pollen is taken from one plant to another (get more genetic variation) • Agents of Pollination: – Wind, birds, bats, bees, butterflies, wasps, flies, ants – Plant often adapted to attract a specific pollinator with showy petals, aromas and nectar The Biggest Flower in the World: (3 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FHaWu2rcP94&safe=active Fertilization • Pollen grains land on stigma and grow pollen tubes that grows down through the style to the ovary and enter the ovule • Double Fertilization Occurs: • One sperm fertilizes egg to make diploid zygote • One sperm fertilizes 2 polar bodies forming triploid endosperm (3n) – This becomes the tissue that stores food for the embryo 1 minute: http://videos.howstuffworks.com/discovery/30701-assignment-discovery-seed-dispersal-video.htm Fruits and Seeds • Each ovule develops into a seed • Ovary walls thicken around the seed and develop into the fruit Seed Structure • Seed Coat: – tough protective coating – Has a scar where it was attached to the ovary • Cotyledon: – stores food for early growth of embryo when seed germinates • Epicotyl: – develops into stems and leaves • Hypocotyl: – develops into roots Seed Dispersal • Dispersal: – Plants have many adaptations to help them scatter their seeds • Fruit dries and bursts open (snapdragon) • Carried by wind (dandelion) • Carried by water (coconut) • Burrs, hooks • Fruits eaten by birds or other animals and pooped out •Seed Dispersal:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rhp5k5ptSx0&safe=active Seed Germination • Germination: “seed hatching” – Seeds need water, oxygen, proper temperature Germination: (1 min) http://science.howstuffworks.com/life/30704-assignment-discovery-germination-of-a-seed-video.htm