* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Second Half Study Guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
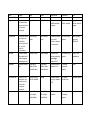
Family Magnoliid Clade Magnoliaceae Foliage Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium Fruit Trees/shrubs blade with pellucid dots containing ethereal oils (aromatic terpenoids) Tepals distinct Tepals distinct Many undifferentiated stamens Numerous distinct, superior aggregate of follicles, seed red, dangles Myristicaceae bark exudes reddish sap; blades with pellucid dots containing ethereal oils; contains myristicin (=hallucinogen Three connate tepals Three connate tepals filaments connate into a solid column; stamens 2 to numerous one ovule, ovary superior leathery follicle, large seed, colorful aril Lauraceae contain ethereal oils (made from 5 carbon fragment called terpenoid) contains ethereal oils Usually 6 tepals Usually 6 tepals one carpel, ovary superior Drupe or one seeded berry No perianth! Spikes of thick, minute flowers No perianth! Spikes of thick, minute flowers filaments with nectar producing appendages; stamens 3-12 filaments distinct; stamens 1-10 1 ovule per gynoecium, superior drupe Aristolochiaceae ethereal oils with pellucid dots and aristolochic acids, bitter yellow nitrogenous compounds connate, showy, dull red, mottled missing filaments adnate to style; stamens 6-12 4-6 carpels, inferior ovary Septicidal capsule Saururaceae with ethereal oils Absent-- Flowers with a single petaloid bract Absent-- Flowers with a single petaloid bract 3-8 distinct stamens 3-4 carpels united at the base; superior capsule Piperaceae Family Monocots (nonCommelinoid Clade) Liliaceae Foliage Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium Fruit bulbs or rhizomes, parallel venation Six distinct tepals Six distinct tepals Stamens 6, filaments distinct 3 connate carpels, ovary superior Loculicidal capsule Melanthiaceae poisonous alkaloids often present (hence the “Death Camas Family”!) leaves smooth with marginal fibers in Yucca; leaves toothed in Agave Equitant (& conduplicate) 6 mostly distinct tepals 6 mostly distinct tepals usually 6 distinct stamens capsule 6 distinct tepals 6 distinct tepals 6 distinct stamens 3-10 connate carpels, usually 3 distinct styles; superior to slightly inferior 3 connate carpels; ovary superior in Yucca, inferior in Agave 6 tepals, inner somewhat differentiated from outer 6 tepals, inner somewhat differentiated from outer Three connate carpels, inferior ovary Loculicidal capsule Roots strongly mycorrhizal, parallel venation and sheathing at the base 6 Tepals, inner 3 and outer 3 somewhat differentiated, one of the inner ones forming the labellum 6 Tepals, inner 3 and outer 3 somewhat differentiated, one of the inner ones forming the labellum Three distinct filaments, specialized pollination anatomy stamens fused to stigma forming a column; pollen forming masses called pollinia ovary inferior, 3 carpels, stigma highly modified capsule/minute seeds; seeds lacking endosperm Agavaceae Iridaceae Orchidaceae loculicidal capsule, seeds with black phytomelan crust Family Basal Eudicots (NOT a clade) Ranunculaceae Foliage Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium Fruit variable (simple or Usually 4 or 5 compound, but distinct sepals usually pinnate or palmate venation) Usually 4 or 5 distinct petals stamens numerous with distinct filaments carpels distinct, 5 to numerous achene (berry or follicle in other genera than Ranunculus) Papaveraceae lobed/dissected 2 quickly deciduous sepals (caducous) 6 petals many stamens, can be distinct or connate superior ovary, 2 connate carpels (syncarpous gynoecium) capsule Berberidaceae Leaves spinoseserrate 6 distinct sepals 6; anthers opening by flaps that open from the base Superior ovary, one carpel, capitate stigma Berry Platanaceae Trees, lobed leaves, toothed stamens 3-7, filaments very short superior ovary with 5-9 distinct carpels multiple of achenes (follicles, drupes or others in other genera that Platanus) 6 outer petals and 6 inner petals that are probably really petal-like staminodes (staminode= sterile stamen) Flowerheads Flowerheads unisexual, flowers unisexual, flowers very reduced, in very reduced, in globose heads, 3- globose heads, 37 minute petals 7 minute petals and sepals and sepals Family Caryophyllales Cactaceae Nyctaginaceae Foliage Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium Fruit succulent, spiny stems, leaves reduced and falling quickly; Tepals numerous, distinct and petallike Tepals numerous, distinct and petallike numerous distinct touch sensitive stamens ovary becoming inferior with 3 to numerous connate carpels Berry; seeds arillate Tepals (usually 5) connate into distinct tube with proximal green and distal petal like portions. Tepals (usually 5) connate into distinct tube with proximal green and distal petal like portions. Usually five distinct stamens Ovary superior, but looks inferior; one carpel achene, enclosed in persistant perianth tube– a situation called an “anthocarp” Flowers often densely clustered and small. 3-5 distinct to slightly connate tepals 5 or 6 distinct tepals, usually small flowers Flowers often densely clustered and small. 3-5 distinct to slightly connate tepals 5 or 6 distinct tepals, usually small flowers 3-5 stamens, can be distinct or connate Carpels usually 2 or 3 connate, ovary superior 5-9 stamens with distinct filaments ovary superior, 2 or 3 carpels connate Utricle in Amaranthus (but achene or capsule in other Amaranthaceae) nutlet (small seed covered by a hard layer), indehiscent and dry Tepals 4-5 appearing to be sepals. “True petals lacking, but outer whorl of 4-5 stamens very often petal-like, here called “petals”, these frequently bilobed..” 4-10 stamens, adnate to “petals” ovary superior, 25 connate carpels and glochids; betalains present leaves opposite, betalains present, hairy, involucres sepal-like with one or more flowers per involucre Amaranthaceae betalains present, very bracteate inflorescence Polygonaceae easily recognizable by distinctive ocrea; anthocyanins and not betalains betalains lost, anthocyanins present, leaves opposite, nodes swollen Caryophyllaceae loculicidal capsule Family Monocots (Commelinoid Clade) Commelinaceae Poaceae Foliage Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium Fruit Grass like, sheathing at the base; flowers enclosed in spathe sometimes Divided into blade and sheath; ligule at junction; sometimes with auricle; stem=culm Three, distinct Three distinct, usually clawed 3 or 6 stamens, sometimes with conspicuous hairs (Tradescantia) Ovary superior, 3 connate carpels Special flower anatomy c/o flower, floret, lemma, palea, glumes, lodicule, etc. Special flower anatomy c/o flower, floret, lemma, palea, glumes, lodicule, etc. 3 distinct stamens 3 superior carpels that appear as two but only produce one grain Loculicidal capsule; seeds with conspicuous conical cap, bullet shaped Grain= caryopsis Family Core Eudicots— Rosid Clade Euphorbiaceae Foliage Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium Fruit Trees, shrubs, or herbs, ours usually small and herbaceous, elsewhere can be cactus-like compound toothed leaves (but not in all Rosaceae), stipules obvious (most Rosaceae) False flower: cyathium False flower: cyathium Several distinct stamens (usually) Three connate carpels Schizocarp (but sometimes referred to as capsule) Usually 5 sepals Usually 5 petals fused onto hypanthium Many stamens fused onto hypanthium inferior with epigynous insertion in Rosa, but superior in other Rosaceae with perigynous insertion aggregate of achenes enclosed within hypanthium in Rosa…specialized fleshy fruits of other Rosaceae (e.g. apples, pears) called a “pome.” Brassicaceae basal rosette common, leaves entire to lobed or dissected 4 sepals, distinct (aposepalous) 4 petals, distinct (apopetalous) Tetradynamous to +/- same length 2 connate carpels, ovary superior, stigma capitate silicle or silique (special type of capsule) Malvaceae stellate hairs 5 distinct sepals 5 distinct petals monadelphous stamens (many) Many connate carpels, ovary superior loculicidal capsule or schizocarp Fabaceae pinnately compound in Vicia, also commonly trifoliolate 5 sepals connate papilionaceous diadelphous 9+1 frequently one carpel, ovary superior Legume (dry, elongate fruit from a single carpel that opens along two longitudinal sutures) Rosaceae Family Core Eudicots— Asterid Clade Polemoniaceae Foliage Calyx Corolla Androecium Gynoecium Fruit Very variable 5 connate sepals 5 petals connate and often forming a narrow tube 5 distinct stamens 3 connate carpels, superior ovary Loculidical capsule Solanaceae alkaloids present usually 5 sepals, connate usually 5 petals, connate and plicate usually 5 stamens adnate to corolla, anthers opening by slits or pores carpels connate, ovary superior berry or capsule Lamiaceae stems often (but not always) square in cross section; hairs gland-headed with ethereal oils; leaves usually opposite 5 connate sepals 5 connate petals usually 4 stamens, adnate to corolla schizocarp with 4 nutlets Apiaceae usually compound; pinnately compound in Ligusticum various Umbels; 5 distinct but reduced sepals 5 distinct, frequently inflexed 5 distinct stamens 2 connate carpels (each carpel with a false septum so appearing as 4 locules 2 connate carpels, ovary inferior modified into pappus of scales, awns, bristles, etc 5 connate petals forming a tube 5 distinct filaments with anthers connate (syngenesious) 2 connate carpels, inferior achene crowned by pappus Asteraceae schizocarp with 2 mericarps