* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NPTs in Context
Body odour and sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive health wikipedia , lookup
History of human sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Sex in advertising wikipedia , lookup
Sex and sexuality in speculative fiction wikipedia , lookup
Consent (criminal law) wikipedia , lookup
Sexual attraction wikipedia , lookup
Female promiscuity wikipedia , lookup
Human male sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Human female sexuality wikipedia , lookup
Reproductive health care for incarcerated women in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Lesbian sexual practices wikipedia , lookup
Slut-shaming wikipedia , lookup
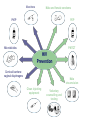
WWW.ICAD-CISD.COM New Prevention Technologies Workshop Module 2: NPTs in context National Policy HIV prevention (including NPTs) is a core component of the following national policy frameworks: Leading Together: Canada Takes Action on HIV/AIDS Federal Initiative to Address HIV/AIDS in Canada Canadian HIV Vaccines Initiative Canadian HIV Vaccines Plan Canadian Microbicides Action Plan Percentage of at-risk people with access to HIV prevention <20% Sex workers with access to behaviour change programmes 11% HIV+ pregnant women with access to PMTCT Rose to 45% recently 10–12% Adults in Africa accessing HIV testing 9% Men who have sex with men with access to appropriate behaviour change programmes 9% Sexually active people with access to male condoms 8% Injection drug users with access to harm reduction programmes 0 20 40 60 80 100 Imagine a full spectrum of interventions Point of transmission Prior to exposure Rights-focused behaviour change Male & Female condoms and lubricant Voluntary counselling & testing Treatment to prevent vertical transmission (PMTCT) Sexually transmitted infection screening and treatment Male medical circumcision Preventative vaccines Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) After infection Antiretroviral treatment Treatment for opportunistic infections Basic care/nutrition Prevention for positives Clean injecting equipment Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) Vaginal & rectal microbicides Cervical barriers Education and rightsfocused behaviour change Therapeutic vaccines Functional cure Vaccines Male and female condoms PrEP PEP Microbicides PMTCT HIV Prevention Cervical barriers: vaginal diaphragms Male circumcision Clean injecting equipment Voluntary counselling and testing Protection in Primary Partnerships: Difficult to Achieve People generally are willing to use condoms with new partners, or during casual or commercial sex But once “trust” enters the equation the condom comes off Sex with a primary partner is the biggest source of HIV infection among women globally Why condoms are not enough ABCs…not so simple ABC—abstinence, be faithful, use a condom Abstinence – not relevant in the context of primary sexual partnerships, and unrealistic for most people Be Faithful – partner’s fidelity is outside of an individual’s control Use Condoms - not relevant in the context of primary sexual partnerships, doesn’t allow conception, under control of male partner Partial efficacy Condoms and NPTs DISCUSSION QUESTION What is higher priority: Advocating for improved access to existing prevention interventions? Advocating for more prevention options? Both? WHY?