* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
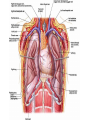
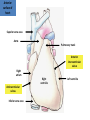
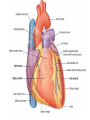
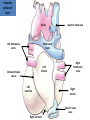
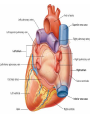
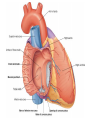
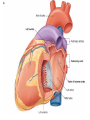
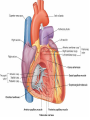
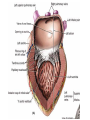
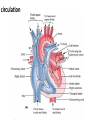
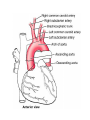
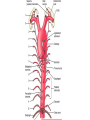
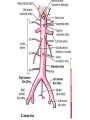
Cardiovascular system HEART • The heart has four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. Borders and surfaces Anterior surface of heart Superior vena cava Aorta Pulmonary trunk Anterior interventricular sulcus Right atrium Right ventricle Atrioventricular sulcus Inferior vena cava Left ventricle The apex of the heart • Is formed by the inferolateral part of the left ventricle. • Lies posterior to the left 5th intercostal space in adults, usually approximately 9 cm (a hand's breadth) from the median plane. • Anterior (sternocostal) surface, formed mainly by the right ventricle. • Right pulmonary surface, formed mainly by the right atrium. • Left pulmonary surface, formed mainly by the left ventricle. Posterior surface of heart Aorta Left pulmonary veins Superior vena cava Pulmonary trunk Left Atrium Atrioventricular sulcus Left ventricle Right Pulmonary veins Right atrium Inferior vena cava Right ventricle Borders of the heart • Right border formed by the right atrium and extending between the SVC and the IVC. • Inferior border formed mainly by the right ventricle and slightly by the left ventricle. • Left border formed mainly by the left ventricle and slightly by the left auricle. • Superior border, formed by the right and left atria and auricles in an anterior view ; Right atrium 1- 234- It is separated from the left atrium by the interatrial septum. The right atrium is composed of two main parts, a smooth posterior portion and a rough walled anterior portion. The large smooth part presents the following orifices : The inferior vena cava: Opens into the lower posterior part. It brings blood from the lower limbs and abdomen to the right atrium. The superior vena cava: Opens into the upper posterior part. It brings blood from head, neck, upper limbs and thorax. Tricuspid valve: It connects the right atrium with the right ventricle. It is guarded by three cups. The coronary sinus: It conveys venous blood from the heart wall to the right atrium. Left atrium The left atrium forms the greater part of the base of the heart. It wall presents a smooth surface except for a small rough part (the left auricle) which lies to the left and in front of the pulmonary trunk. The left atrium shows the following orifices: 1- The four pulmonary veins two from each lung. 2- The mitral valve connects the left atrium with the left ventricle Right ventricle It is separated from the left ventricle by interventricular septum. Its wall is muscular and is thicker than the atrial wall. The pulmonary trunk arises from the right ventricle and divides into two pulmonary arteries one to each lung. There are three papillary muscles attached to the wall of the ventricle. From the apices of the papillary muscles, fibrous cords (chorda tendinae) pass to the cusps of the tricuspid valve. Left ventricle: The left ventricle is longer than the right ventricle and forms the apex of the heart. Its wall is nearly three times thicker than the right. The ascending aorta arises from it. Its cavity presents two papillary muscles which are attached to the two cusps of the mitral valve by chorda tendinae. circulation • Conducting system of the heart: • The conducting system of the heart consists of modified cardiac muscle fibers which are responsible for initiation and maintenance of cardiac rhythm. The conducting system is formed of: • 1- Sino-atrial node (SAN). • 2- Atrioventricular node (AVN). • 3- Atrioventricular bundle (AVB). • The aorta and its main branches : • The ascending aorta arises from the left ventricle. It gives two coronary arteries, right and left. The coronary arteries supply the heart. • Ascending aorta arches to give the aortic arch. The aortic arch gives 3 arteries: 1-Brachiocephalic artery which gives the right subclavian and right common carotid arteries. 2-Left common carotid artery. 3-Left subclavian artery.