* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Lambeth academy sport
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
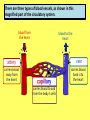
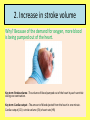
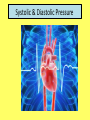
Please copy down the date, title and learning outcome and complete the starter The Cardiovascular System During Exercise Learning Objectives: Taking a look at the immediate and short-term effects of exercise on the cardiovascular system Learning Outcome: A*/A Students will be able to explain in detail the immediate and short-term effects of exercise upon the cardiovascular system. Reference will be made to blood pressure, blood vessels and the respiratory system. Tricky Complete the placemat worksheet Trickier Complete the placemat worksheet and then support other students A healthy, active lifestyle and your cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system consists of: 1. The heart (cardio), 2. Blood and the 3. Blood vessels (vascular) The heart is a muscular pump (cardiac muscle!), which pushes blood throughout the many blood vessels in the body Blood being pushed around has 3 main functions: 1. To supply the body with oxygen & nutrients 2. To remove waste products e.G. Carbon dioxide 3. Return blood to the lungs for oxygenation Blood vessels run throughout the body, allowing blood to travel everywhere Blood Vessels 1. Arteries 2. Capillaries 3. Veins There are three types of blood vessels, as shown in this magnified part of the circulatory system. blood from the heart blood to the heart vein artery carries blood away from the heart carries blood back into the heart carries blood to and from the body’s cells What happens to the cardiovascular system during exercise? Immediate and short-term effects of exercise on the cardiovascular system • What immediate effects do you think exercise has upon the cardiovascular system?! Higher Order Thinking… • What happens and why do they happen? • How can these immediate effects be measured? 1. Increased Heart Rate Why? Increased oxygen delivery and increased removal of carbon dioxide. Key term: Heart rate – the number of times the heart beats per minute. 2. Increase in stroke volume Why? Because of the demand for oxygen, more blood is being pumped out of the heart. Key term: Stroke volume - The volume of blood pumped out of the heart by each ventricle during one contraction. Key term: Cardiac output - The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one minute. Cardiac output (CO) = stroke volume (SV) x heart rate (HR) 3. Increase in (systolic) blood pressure Why? Blood pressure increases during exercise because more blood is needed to be pumped around the body, increasing pressure on the blood vessels. Key term: Blood pressure - the force exerted by blood on the walls of the blood vessels Systolic & Diastolic Pressure Systolic & Diastolic Pressure Systolic pressure – the pressure on blood vessels when blood is pumped out of the heart (‘squeeze stage’). Diastolic pressure - the pressure of the blood on the blood vessels during the relaxation phase, between heart beats (when heart is at rest). Youtube support: http://www.mayoclinic.org/condition/high-bloodpressure/multimedia/what-is-blood-pressure/vid-20084747 Lifestyle choices and your cardiovascular system 4 Factors that may have negative effect on the CV system and increase the risk of coronary heart disease 1. High cholesterol, perhaps due to a diet high in animal fats 2. Recreational drugs 3. Sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise 4. Stress High cholesterol, perhaps due to a diet high in animal fats • Cholesterol is a fatty substance carried in the blood by lipoproteins. • High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) - GOOD And • Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) - BAD High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) • Foods rich in HDL include fruit, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes (e.g. peas and beans). • This why it is recommended we have our ‘5 a day’! Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) • …consist mainly of fat and is known as ‘bad cholesterol’. • It is the major cause of cholesterol in the blood, and can lead to a build up of plaque which can restrict blood flow in the arteries. Useful clip! http://www.explania.com/en/channels/health/detail/what-ischolesterol Recreational drugs • Recall from previous unit! • Cigarettes (nicotine), which raise blood pressure because they release adrenaline. Adrenaline constricts the arteries and causes the heart to beat faster • Tobacco smoke is a major risk factor of heart disease. Smoking lowers HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol!) levels and increases the tendency for blood to clot, which can lead to serious problems such as heart attacks or strokes! • Alcohol in moderation is believed to increase HDL and so in the long term can help lower blood pressure. However, too much alcohol and binge drinking can have serious adverse effects. Sedentary lifestyle and lack of exercise (hypokinetic disease) • Inactivity means that the cardiovascular system does not receive the benefits of exercise. • Sedentary living is also believed to be one of the main reasons for increasing rates of obesity Stress • The stress that may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease is different to the stress felt before a competition or while taking an exam. • Negative stress builds up over time and can affect the cardiovascular system by leading to an increase in blood pressure and elevated heart rate. It may also lead to depression and mood swings. Key terms review… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Heart Rate (HR) Resting / Working HR Recovery rate Blood pressure HDL and LDL (which one is good? #high5) Cardiac output Stroke Volume Rest