* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Indezine Template
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Typhoid fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Infectious mononucleosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
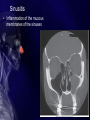
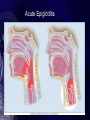
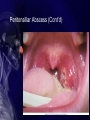
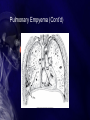
Chapter 33 Care of Patients with Infectious Respiratory Problems Mrs. Marion Kreisel MSN, RN NU230 Adult Health 2 Fall 2011 Rhinitis • Inflammation of the nasal mucosa • Often called “hay fever” or “allergies” • Interventions include: • Drug therapy—antihistamines and decongestants, (be careful with decongestants, pts will keep using them until all congestion is gone: can OD on this med) antipyretics, antibiotics • Complementary and alternative therapy • Supportive therapy Sinusitis • Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the sinuses Sinusitis (Cont’d) • Nonsurgical management: • Broad-spectrum antibiotics • Analgesics for pain and fever • Decongestants • Steam humidification • Hot and wet packs over the sinus area • Nasal saline irrigations Surgical Management • Antral irrigation • Caldwell-Luc procedure • Nasal antral window procedure • Endoscopic sinus surgery Pharyngitis • Sore throat is common inflammation of the mucous membranes of the pharynx. • Assess for odynophagia, dysphagia, fever, and hyperemia. • Strep throat can lead to serious medical complications. • Epiglottitis is a rare complication of pharyngitis. Acute Epiglottitis Tonsillitis • Inflammation and infection of the tonsils and lymphatic tissues located on each side of the throat • Contagious airborne infection, usually bacterial • Antibiotics • Surgical intervention Peritonsillar Abscess • Complication of acute tonsillitis • Pus behind the tonsil, causing onesided swelling with deviation of the uvula • Trismus and difficulty breathing • Percutaneous needle aspiration of the abscess • Completion of antibiotic regimen Peritonsillar Abscess (Cont’d) Laryngitis • Inflammation of the mucous membranes lining the larynx, possibly including edema of the vocal cords • Acute hoarseness, dry cough, difficulty swallowing, temporary voice loss (aphonia) • Voice rest, steam inhalation, increased fluid intake, throat lozenges • Therapy—relief and prevention Influenza • “Flu” is a highly contagious acute viral respiratory infection. • Manifestations include severe headache, muscle ache, fever, chills, fatigue, weakness, and anorexia. • Vaccination is advisable. • Antiviral agents may be effective. Pneumonia • Excess of fluid in the lungs resulting from an inflammatory process • Inflammation triggered by infectious organisms and inhalation of irritants • Community-acquired infectious pneumonia • Nosocomial or hospital-acquired • Atelectasis • Hypoxemia Pneumonia • History • Physical assessment: weak, nonproductive cough effort • Clinical manifestations • Psychosocial assessment Laboratory Assessment • Gram stain, culture, and sensitivity testing of sputum • Complete blood count • Arterial blood gas level • Serum blood urea nitrogen level • Electrolytes • Creatinine • Imaging assessment and others Treatment • • • • Priority to get antibiotic in pt asap. Treat Pain Treat Fever Treat Cough Pneumonia: Community-Based Care • Home care management • Health teaching • Health care resources Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) • A virus from a family of virus types known as “coronaviruses” • Virus infection of cells of the respiratory tract, triggering inflammatory response • No known effective treatment for this infection • Prevention of spread of infection Avian Influenza “Bird Flu” • Concern of possible mutation of strain to allow first bird-to-human infection • Virus spreads in birds by oral-fecal transmission • Prevention • If pt admitted to hospital immediate Respiratory Isolation Pulmonary Tuberculosis • Highly communicable disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis • Transmitted via aerosolization • Secondary TB • Increase related to the onset of HIV Pulmonary Tuberculosis (Cont’d.) Copyright © 2010, 2006, 2002 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. Clinical Manifestations of TB • • • • • • • • Progressive fatigue Lethargy Nausea Anorexia Weight loss Irregular menses Low-grade fever, night sweats Cough, mucopurulent sputum, blood streaks TB: Assessment • History • Physical assessment • Clinical manifestations: • Private Room • Negative Air flow • Acid Fasting Test • Respiratory Isolation N-95 mask Diagnostic Assessment • Manifestation of signs and symptoms • Positive smear for acid-fast bacillus • Confirmation of diagnosis by sputum culture of M. tuberculosis • Tuberculin test (Mantoux test)—purified protein derivative given intradermally in the forearm • Induration of 10 mm or greater diameter indicative of exposure Diagnostic Assessment (Cont’d) • Positive reaction does not mean that active disease is present but does indicate exposure to TB or dormant disease Interventions • Combination drug therapy with strict adherence to prevent organism resistance: • Isoniazid: Side effect is vision problems (pg651 pharm book) • Rifampin • Pyrazinamide • Ethambutol • Teach patient to look for Yellow tinged skin or yellow eyes (jaundice) Dark brown urine, & bruise easilly. • Negative sputum culture indicative of patient no longer being infectious TB: Community-Based Care • Home care management • Health teaching: • Health care resources Lung Abscess • Localized area of lung destruction caused by liquefaction necrosis, usually related to pyogenic bacteria • Pleuritic chest pain • Interventions: • Antibiotics • Drainage of abscess • Frequent mouth care for Candida albicans Inhalation Anthrax • Bacterial infection is caused by the gram-positive, rod-shaped organism Bacillus anthracis from contaminated soil. • Fatality rate is 100% if untreated. • Two stages are the prodromal stage and the fulminant stage. • Drug therapy includes ciprofloxacin, doxycycline, and amoxicillin. Pulmonary Empyema • A collection of pus in the pleural space • Most common cause—pulmonary infection, lung abscess, and infected pleural effusion • Interventions include: • Emptying the empyema cavity • Re-expanding the lung • Controlling the infection Pulmonary Empyema (Cont’d) NCLEX TIME Question 1 How many cases of pneumonia occur in the United States annually? A. B. C. D. 400,000 to 700,000 750,000 to 1 million 2 to 5 million 6 to 8 million Question 2 Which is the most common manifestation of pneumonia in the older adult patient? A. B. C. D. Fever Cough Weakness Confusion Question 3 A patient is being examined because of symptoms of pharyngitis. Which features would indicate that the pharyngitis is of viral origin? A. High fever (over 101 F [38 C]) B. White blood cell count lower than 10,000/mm3 C. White blood cell count over 12,000/mm3 D. Abrupt onset Question 4 A health care worker’s purified protein derivative (PPD) test results are positive. Previously the results had been negative. This positive PPD indicates: A. Exposure to TB B. The presence of active tuberculosis (TB) disease C. Previous vaccination with bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) D. An allergic reaction to the PPD serum Question 5 A patient is experiencing fever, chills, night sweats, and weight loss. In addition, the patient’s point of maximal impulse (PMI) is noted to be displaced when cardiac palpation is performed, and the patient is hypotensive. These symptoms are indicative of: A. B. C. D. Pneumonia Tuberculosis Influenza Pulmonary empyema